Export and Import of Hazardous Waste and Hazardous Recyclable Material Regulations
SOR/2005-149
CANADIAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION ACT, 1999
Registration 2005-05-17
Export and Import of Hazardous Waste and Hazardous Recyclable Material Regulations
P.C. 2005-930 2005-05-17
Whereas, pursuant to subsection 332(1)Footnote a of the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999Footnote b, the Minister of the Environment published in the Canada Gazette, Part I, on March 20, 2004 a copy of the proposed Export and Import of Hazardous Waste and Hazardous Recyclable Material Regulations, substantially in the annexed form, and persons were given an opportunity to file comments with respect to the proposed Regulations or to file a notice of objection requesting that a board of review be established and stating the reasons for the objection;
Therefore, Her Excellency the Governor General in Council, on the recommendation of the Minister of the Environment, pursuant to section 191 of the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999Footnote b, hereby makes the annexed Export and Import of Hazardous Waste and Hazardous Recyclable Material Regulations.
Return to footnote aS.C. 2004, c. 15, s. 31
Return to footnote bS.C. 1999, c. 33
Definitions and Interpretation
Definition of hazardous waste
1 (1) In Division 8 of Part 7 and Part 10 of the Act and in these Regulations, hazardous waste means anything that is intended to be disposed of using one of the operations set out in Schedule 1 and that
(a) is set out in column 2 of Schedule 3;
(b) is included in at least one of Classes 2 to 6, 8 or 9 of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations;
(c) is set out in column 2 of Schedule 4 and is included in at least one of Classes 2 to 6, 8 or 9 of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations;
(d) is set out in column 1 of Schedule 5 in a concentration equal to or greater than the applicable concentration set out in column 2 of that Schedule;
(e) produces a leachate containing a constituent set out in column 2 of Schedule 6 in a concentration equal to or greater than the applicable concentration set out in column 3 of that Schedule, determined in accordance with Method 1311, Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure, July 1992, in Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, Volume 1C: Laboratory Manual, Physical/Chemical Methods, Third Edition, SW-846, November 1986, published by the United States Environmental Protection Agency, which, for the purposes of this definition, shall be read without reference to section 7.1.3;
(f) is set out in column 2 of Schedule 7, is pure or is the only active ingredient, and is unused; or
(g) according to information that Canada has received from the United States or in accordance with the Convention, is considered or defined as hazardous under the legislation of the country receiving it and is prohibited by that country from being imported or conveyed in transit.
Marginal note:Exclusion
(2) The definition hazardous waste in subsection (1) does not include anything that is
(a) exported, imported or conveyed in transit in a quantity of less than 5 kg or 5 L per shipment or, in the case of mercury, in a quantity of less than 50 mL per shipment, other than anything that is included in Class 6.2 of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations;
(b) collected from households in the course of regular municipal waste collection services; or
(c) part of the exporter’s or importer’s personal effects or household effects not resulting from commercial use.
Definition of hazardous recyclable material
2 (1) In Division 8 of Part 7 and Part 10 of the Act and in these Regulations, hazardous recyclable material means anything that is intended to be recycled using one of the operations set out in Schedule 2 and that
(a) is set out in column 2 of Schedule 3;
(b) is included in at least one of Classes 2 to 6, 8 or 9 of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations;
(c) is set out in column 2 of Schedule 4 and is included in at least one of Classes 2 to 6, 8 or 9 of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations;
(d) is set out in column 1 of Schedule 5 in a concentration equal to or greater than the applicable concentration set out in column 2 of that Schedule;
(e) produces a leachate containing a constituent set out in column 2 of Schedule 6 in a concentration equal to or greater than the applicable concentration set out in column 3 of that Schedule, determined in accordance with Method 1311, Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure, July 1992, in Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, Volume 1C: Laboratory Manual, Physical/Chemical Methods, Third Edition, SW-846, November 1986, published by the United States Environmental Protection Agency, which, for the purposes of this definition, shall be read without reference to section 7.1.3;
(f) is set out in column 2 of Schedule 7, is pure or is the only active ingredient, and is unused; or
(g) according to information that Canada has received from the United States or in accordance with the Convention, is considered or defined as hazardous under the legislation of the country receiving it and is prohibited by that country from being imported or conveyed in transit.
Marginal note:Exclusion
(2) The definition hazardous recyclable material in subsection (1) does not include anything that is
(a) exported, imported or conveyed in transit in a quantity of less than 5 kg or 5 L per shipment or, in the case of mercury, in a quantity of less than 50 mL per shipment, other than anything that is included in Class 6.2 of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations;
(b) collected from households in the course of regular municipal waste collection services;
(c) part of the exporter’s or importer’s personal effects or household effects not resulting from commercial use;
(d) exported to, imported from, or conveyed in transit through a country that is a party to OECD Decision C(2001)107/Final and that
(i) is in a quantity of 25 kg or 25 L or less,
(ii) is exported or imported for the purpose of conducting measurements, tests or research with respect to the recycling of that material,
(iii) is accompanied by a shipping document, as defined in section 1.4 of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations, that includes the name and address of the exporter or importer and the words “test samples” or “échantillons d’épreuve”, and
(iv) is not and does not contain an infectious substance as defined in section 1.4 of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations; or
(e) exported to, imported from, or conveyed in transit through a country that is a party to OECD Decision C(2001)107/Final and that
(i) is set out in Schedule 8,
(ii) produces a leachate containing a constituent set out in column 2 of Schedule 6 in a concentration equal to or greater than the applicable concentration set out in column 3 of that Schedule, determined in accordance with Method 1311, Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure, July 1992, in Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, Volume 1C: Laboratory Manual, Physical/Chemical Methods, Third Edition, SW-846, November 1986, published by the United States Environmental Protection Agency, which, for the purposes of this definition, shall be read without reference to section 7.1.3, and
(iii) is intended to be recycled at an authorized facility in the country of import using one of the operations set out in Schedule 2.
Marginal note:Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations
3 For the purposes of sections 1 and 2, references to the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations shall be read as follows:
(a) the reference to “public safety” in subparagraph 2.43(b)(i) shall be read as a reference to “the environment and human health”; and
(b) subparagraph 2.43(b)(i) shall be read without reference to “during transport”.
Marginal note:Definitions
4 The following definitions apply in Division 8 of Part 7 of the Act and in these Regulations.
Act
Loi
Act means the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999. (Loi)
authorities of the country
autorités du pays
authorities of the country means the competent authorities designated in the Compilation of Country Fact Sheets (CFS), Basel Convention Series No. 01/04, as amended from time to time, and the United States Environmental Protection Agency. (autorités du pays)
authorized carrier
transporteur agréé
authorized carrier means a carrier that is authorized by the authorities of the jurisdiction in which the waste or material is transported, to transport the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material that is to be exported, imported or conveyed in transit. (transporteur agréé)
authorized facility
installation agréée
authorized facility means a facility that is authorized by the authorities of the jurisdiction in which the facility is located to
(a) dispose of the hazardous waste being exported or imported using an operation set out in Schedule 1; or
(b) recycle the hazardous recyclable material being exported or imported using an operation set out in Schedule 2. (installation agréée)
Canada-USA Agreement
accord Canada-États-Unis
Canada-USA Agreement means the Agreement between the Government of Canada and the Government of the United States of America Concerning the Transboundary Movement of Hazardous Waste, which entered into force on November 8, 1986, as amended from time to time. (accord Canada-États-Unis)
Convention
Convention
Convention means the Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and their Disposal, which entered into force on May 5, 1992. (Convention)
foreign exporter
expéditeur étranger
foreign exporter means the person who exports hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material from a country other than Canada. (expéditeur étranger)
foreign receiver
destinataire étranger
foreign receiver means the person who imports hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material into a country other than Canada. (destinataire étranger)
movement document
document de mouvement
movement document means the form set out in Schedule 9. (document de mouvement)
notice
notification
notice means the notice of export, import or transit referred to in paragraph 185(1)(a) of the Act. (notification)
OECD Decision C(94)152/Final
décision C(94)152/Final de l’OCDE
OECD Decision C(94)152/Final means Decision C(88)90/Final of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, Decision of the Council on Transfrontier Movements of Hazardous Wastes, dated May 27, 1988, as amended by Decision C(94)152/Final, Decision of the Council Amending the Decision on Transfrontier Movements of Hazardous Wastes, dated July 28, 1994. (décision C(94)152/Final de l’OCDE)
OECD Decision C(2001)107/Final
décision C(2001)107/Final de l’OCDE
OECD Decision C(2001)107/Final means Decision C(2001)107/Final of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, Decision of the Council Concerning the Revision of Decision C(92)39/FINAL on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Wastes Destined for Recovery Operations, dated May 21, 2002. (décision C(2001)107/Final de l’OCDE)
permit
permis
permit means the export, import or transit permit referred to in paragraph 185(1)(b) of the Act. (permis)
registration number
numéro d’immatriculation
registration number means the number assigned by a province or country indicating the authority to undertake an activity with respect to a hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material. (numéro d’immatriculation)
PART 1Notice
Application
Marginal note:Application
5 This Part applies to the export, import and transit of hazardous waste and hazardous recyclable material other than returns of that waste or material under Part 5.
Notice Procedure
Marginal note:Notice reference number
6 The Minister shall provide a notice reference number to any person who requests one for the purpose of submitting a notice.
Marginal note:Delivery of notice
7 (1) The person that proposes to export, import or convey in transit a hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material must submit a notice to the Minister in writing within 12 months before the export, import or transit.
Marginal note:Separate notices
(2) In the case of an export or import, the notice must not include both hazardous waste and hazardous recyclable material.
Marginal note:Notice for multiple hazardous wastes or hazardous recyclable materials
(3) The notice may provide for more than one hazardous waste or more than one hazardous recyclable material, as the case may be, if they
(a) are to be shipped
(i) to the same authorized facility at the same location,
(ii) through the same port of exit or the same port of entry, and
(iii) within the same 12-month period;
(b) are to be reported to the same customs office;
(c) originate from the same person and the same facility; and
(d) in the case of an export or import, have essentially the same physical and chemical characteristics.
Marginal note:Language
(4) In the case of an export or a transit where the French or English language is not acceptable to the authorities of the country of import or transit, the person who submits the notice must submit it in the French or English language and in a language used by those authorities.
Marginal note:Application for permit
(5) The notice shall serve as an application for a permit.
Marginal note:New notice
(6) A person must submit a new notice to the Minister if there is a change to any of the information contained in the permit, except that the person who submitted the notice may advise the Minister in writing of a change to quantity of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material or the number of shipments, or may add authorized carriers, ports of exit or entry or customs offices.
Content of Notice
Marginal note:Content
8 The person who submits the notice must include the following information in the notice:
(a) the notice reference number provided by the Minister under section 6;
(b) the name, registration number, civic, mailing and electronic addresses and telephone and facsimile numbers of, and the name of the contact person for,
(i) the person submitting the notice,
(ii) the foreign receiver or the foreign exporter, as the case may be,
(iii) the facility from which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material will be shipped,
(iv) the authorized carriers that will transport the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material, and
(v) all authorized facilities that will receive the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material;
(c) all modes of transport that will be used;
(d) the proposed number of shipments;
(e) the port of exit or the port of entry through which the export or import will take place, as the case may be and, in the case of a transit, the port of exit and entry through which the transit will take place;
(f) the customs office at which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is to be reported, if applicable;
(g) the proposed date of the first and last shipments or, in the case of a transit, the proposed dates of entry of the first shipment and exit of the last shipment;
(h) the name of each insurance company and the policy number for each insurance policy required under these Regulations;
(i) the countries of transit through which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material will be conveyed and the length of time it will be in each country of transit;
(j) the following information with respect to each hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material, namely,
(i) the International Waste Identification Code under OECD Decision C(94)152/Final, substituting the disposal or recycling code with the disposal or recycling code set out in column 1 of Schedule 1 or 2 to these Regulations for the applicable operation set out in column 2 of that Schedule and, if the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is a gas, substituting the letter G for the letter L, P or S in the International Waste Identification Code,
(ii) for hazardous waste, or for hazardous recyclable material that will be exported to, imported from or transited through a country that is not a party to OECD Decision C(2001)107/Final, the applicable code set out in List A of Annex VIII of the Convention, as amended from time to time,
(iii) for hazardous recyclable material that will be exported to, imported from or transited through a country that is a party to OECD Decision C(2001)107/Final, the applicable code set out in Part II of Appendix 4 to that Decision,
(iv) the tariff item and the statistical suffix set out in the Customs Tariff Departmental Consolidation, published by the Canada Border Services Agency, as amended from time to time,
(v) the applicable identification number set out in column 1 of Schedule 3, 4 or 7 for the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material set out in column 2 of that Schedule, or the applicable hazardous constituent code number set out in column 1 of Schedule 6 for the hazardous constituent set out in column 2 of that Schedule,
(vi) the following information set out in the applicable schedules to the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations, namely,
(A) the applicable UN number set out in column 1 of Schedule 1 or column 5 of Schedule 3,
(B) the applicable class set out in column 3 of Schedule 1 or the primary class set out in column 4 of Schedule 3, and
(C) the applicable packing group and risk group set out in column 4 of Schedule 1,
(vii) the total quantity in kilograms or litres of each hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material,
(viii) the applicable disposal or recycling code set out in column 1 of Schedule 1 or 2 for every applicable operation set out in column 2 of that Schedule, and the name and description of the processes to be employed with respect to those operations, and
(ix) in the case of an export, the options considered for reducing or phasing out the export of the hazardous waste and the reason that the final disposal is taking place outside Canada;
(k) the name, quantity and concentration of any persistent organic pollutant set out in column 2 of Schedule 10 that is contained in the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material, if the concentration is equal to or greater than the concentration set out in column 3;
(l) distinct line item numbers for each hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material;
(m) in the case of an export or import, a copy of the contract or series of contracts, excluding financial information, or the statement referred to in paragraph 9(f) or 16(e); and
(n) a statement signed and dated by the person submitting the notice indicating that
(i) in the case of an export or import, the contract or series of contracts referred to in paragraph 9(f) or 16(e) is in force,
(ii) in the case of an export or import, if the hazardous waste cannot be disposed of or the hazardous recyclable material cannot be recycled in accordance with the export or import permit, the exporter or importer will implement the alternative arrangements required under Part 5 or, if alternative arrangements cannot be made, the exporter or importer will return the waste or material to the facility from which it originated in accordance with section 34 or 35,
(iii) the insurance policy referred to in section 37 will cover the period referred to in that section, and
(iv) the information in the notice is complete and correct.
PART 2Export
Conditions
Marginal note:Conditions of export
9 An exporter may export hazardous waste and hazardous recyclable material if
(a) at the time of the export
(i) the export is not prohibited under the laws of Canada,
(ii) the country of import is a party to the Convention, the Canada-USA Agreement or OECD Decision C(2001)107/Final and the import of the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is not prohibited by that country, and
(iii) the country of transit does not prohibit the transit of the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material;
(b) the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is not to be disposed of or recycled south of 60° south latitude;
(c) in the case of biomedical wastes set out in column 2 of Schedule 3 or anything that is included in Class 6.2 of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations, the export is only for the purposes of disposal;
(d) the exporter is a resident of Canada or, in the case of a corporation, has a place of business in Canada;
(e) the exporter
(i) is the owner or operator of the facility from which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is exported, or
(ii) buys and sells hazardous recyclable material for the purposes of recycling and exports it to a country that is a party to OECD Decision C(2001)107/Final;
(f) there is a signed, written contract or a series of contracts among the exporter, the foreign receiver and the authorized facilities or, if any of those persons are the same legal entity, a written statement signed by that entity, that
(i) describes the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material,
(ii) sets out the quantity of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material to be exported,
(iii) indicates that the hazardous waste will be disposed of, or the hazardous recyclable material will be recycled, in accordance with the export permit,
(iv) describes the operation set out in Schedule 1 or 2 that will be used,
(v) requires the foreign receiver to complete Part C of the movement document, or authorizes the exporter to complete Part C on the foreign receiver’s behalf if the waste or material is not considered or defined as hazardous under the legislation of the country of import, and to provide a copy of the movement document and a copy of the export permit to the exporter on delivery of the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material to the authorized facility, and
(vi) requires the foreign receiver
(A) to complete the disposal of the hazardous waste or recycling of the hazardous recyclable material within the time set out in paragraph (o),
(B) to submit written confirmation to the exporter of the disposal of the hazardous waste or recycling of the hazardous recyclable material within 30 days after the day on which the disposal or recycling is completed, and
(C) to take all practicable measures to assist the exporter in fulfilling the terms of the exporter’s obligations under these Regulations if delivery is not accepted by the authorized facility named in the export permit, or if the authorized facility cannot, or refuses to, dispose of the hazardous waste or recycle the hazardous recyclable material in accordance with the export permit;
(g) the exporter and the authorized carrier if other than Her Majesty in right of Canada or of a province are insured in accordance with section 37;
(h) the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is transported by the authorized carriers named in the export permit;
(i) he applicable safety mark is displayed on each shipment of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material in accordance with Part 4 of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations;
(j) the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is exported through the port of exit named in the export permit;
(k) the quantity of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material exported does not exceed the quantity set out in the export permit;
(l) a copy of the export permit and a copy of the movement document completed in accordance with sections 11 to 13
(i) accompanies the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material, and
(ii) is deposited by the exporter or the authorized carrier at the customs office at which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is to be reported under section 95 of the Customs Act;
(m) the hazardous waste is disposed of, or the hazardous recyclable material is recycled, at the authorized facility named in the export permit using the disposal or recycling operation set out in the export permit;
(n) after operation D13, D14 or D17 of Schedule 1 or operation R12, R13 or R16 of Schedule 2 is completed, the hazardous waste is disposed of, or the hazardous recyclable material is recycled, at an authorized facility using an operation set out in Schedule 1 or 2 other than operation D13, D14 or D17 or R12, R13 or R16;
(o) in the case of operation D13, D14 or D17 of Schedule 1 or operation R12, R13 or R16 of Schedule 2, the operation is completed within 180 days, or in all other cases, within one year, after the day on which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is accepted by the authorized facility, unless the authorities of the jurisdiction in which the authorized facility is located require shorter time periods, in which case those time periods apply; and
(p) in the event that the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is exported but is not accepted by the authorized facility named in the export permit, or if the authorized facility cannot, or refuses to, dispose of or recycle it in accordance with the export permit, the exporter
(i) immediately notifies the Minister, the foreign receiver and the authorities of the country of import of the non-acceptance or refusal and the reason for it,
(ii) if necessary, stores the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material in a facility authorized to store the waste or material by the authorities of the jurisdiction in which the facility is located, and
(iii) within 90 days after the day on which the Minister is notified, makes arrangements to return the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material to the facility in Canada from which it was shipped in accordance with section 34 or makes arrangements for the disposal of the waste or the recycling of the material in the country of import at an authorized facility other than the one named in the export permit and provides the Minister with the name and address of that facility and the name of a contact person.
Movement Document
Marginal note:Movement document reference number
10 The Minister shall provide a movement document reference number to an exporter who requests one for the purpose of completing a movement document.
Marginal note:Exporter
11 (1) Prior to shipping the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material, the exporter must complete Part A of a movement document, indicate the movement document reference number and provide a copy of the movement document and a copy of the export permit to the first authorized carrier.
Marginal note:First authorized carrier
(2) Immediately on receipt of the movement document, the first authorized carrier must complete Part B of the movement document and provide a copy to the exporter.
Marginal note:Copy of movement document
(3) Within three working days after the day on which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is shipped, the exporter must send a copy of the movement document completed in accordance with subsections (1) and (2) to
(a) the Minister; and
(b) the authorities of the province of export, if they require it.
Marginal note:Authorized carriers
(4) Every authorized carrier that transports the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material must complete Part B of the movement document and provide it and a copy of the export permit to the next authorized carrier or the foreign receiver, as the case may be, on delivery of the waste or material to that carrier or the foreign receiver.
Marginal note:Exporter
(5) The exporter must ensure that
(a) every authorized carrier that transports the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material completes Part B of the movement document; and
(b) the foreign receiver completes Part C of the movement document, unless the exporter is authorized to do so on the foreign receiver’s behalf under the contract referred to in paragraph 9(f).
Marginal note:Copy of movement document
(6) Within three working days after the day on which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is delivered to the authorized facility, the exporter must send a copy of the completed movement document to
(a) the Minister;
(b) the authorities of the province of export, if they require it; and
(c) every authorized carrier of the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material.
Marginal note:Rail consist
12 In the case of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material that is transported by rail, the movement document may be replaced by a rail consist if it contains all of the information contained in the movement document.
Marginal note:Unit of measure
13 The exporter must ensure that the quantity of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material indicated in the movement document is in the same unit of measure as is used in the export permit.
Marginal note:Retention of movement document
14 The exporter and every authorized carrier must keep a copy of the movement document at their principal place of business in Canada for a period of three years after the day on which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is exported.
PART 3Import
Department of National Defence Exemption
Marginal note:Exemption
15 This Part does not apply to the Department of National Defence if the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is
(a) generated by that Department in the course of an operation conducted by it outside Canada;
(b) transported from the site of operation to a defence establishment as defined in subsection 2(1) of the National Defence Act; and
(c) transported under the sole direction or control of the Minister of National Defence as described in section 1.20 of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations, as though the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is a dangerous good under those Regulations.
Conditions
Marginal note:Conditions of import
16 An importer may import hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material if
(a) at the time of the import
(i) the import is not prohibited under the laws of Canada,
(ii) the country of export is a party to the Convention, the Canada-USA Agreement or OECD Decision C(2001)107/Final, and
(iii) the country of transit does not prohibit the transit of the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material;
(b) in the case of biomedical wastes set out in column 2 of Schedule 3 or anything that is included in Class 6.2 of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations, the import is only for the purposes of disposal;
(c) the importer is a resident of Canada or, in the case of a corporation, has a place of business in Canada;
(d) the importer
(i) is the owner or operator of the authorized facility named in the import permit, or
(ii) buys and sells hazardous recyclable material for the purposes of recycling;
(e) there is a signed, written contract or a series of contracts among the importer, the foreign exporter and the authorized facilities or, if any of those persons are the same legal entity, a written statement signed by that entity, that
(i) describes the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material,
(ii) sets out the quantity of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material to be imported,
(iii) indicates that the hazardous waste will be disposed of, or the hazardous recyclable material will be recycled, in accordance with the import permit,
(iv) describes the operation set out in Schedule 1 or 2 that will be used,
(v) requires the foreign exporter to complete Part A of the movement document, or authorizes the importer to complete Part A on the foreign exporter’s behalf if the waste or material is not considered or defined as hazardous under the legislation of the country of export, and to provide a copy of it and a copy of the import permit to the first authorized carrier prior to the shipment of the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material,
(vi) requires the foreign exporter
(A) to send a copy of the movement document to the importer once Part A is completed by the foreign exporter, Part B is completed by the first authorized carrier and the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material has been shipped, and
(B) to take all practicable measures to assist the importer in fulfilling the terms of the importer’s obligations under these Regulations if delivery is not accepted by the authorized facility named in the import permit, or if the authorized facility cannot, or refuses to, dispose of the hazardous waste or recycle the hazardous recyclable material in accordance with the import permit;
(f) the importer and the authorized carrier if other than Her Majesty in right of Canada or of a province are insured in accordance with section 37;
(g) the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is transported by the authorized carriers named in the import permit;
(h) the applicable safety mark is displayed on each shipment of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material in accordance with Part 4 of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations;
(i) the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is imported through the port of entry named in the import permit;
(j) the quantity of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material imported does not exceed the quantity set out in the import permit;
(k) a copy of the import permit and a copy of the movement document completed in accordance with sections 18 to 20
(i) accompanies the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material, and
(ii) is deposited by the importer or the authorized carrier at the customs office at which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is to be reported under section 12 of the Customs Act;
(l) the hazardous waste is disposed of, or the hazardous recyclable material is recycled, at the authorized facility named in the import permit using the disposal or recycling operation set out in the import permit;
(m) after operation D13, D14 or D17 of Schedule 1 or operation R12, R13 or R16 of Schedule 2 is completed, the hazardous waste is disposed of, or the hazardous recyclable material is recycled, at an authorized facility using an operation set out in Schedule 1 or 2, other than operation D13, D14 or D17 or R12, R13 or R16;
(n) in the case of operations D13, D14 or D17 of Schedule 1 or operation R12, R13 or R16 of Schedule 2, the operation is completed within 180 days, or in all other cases, within one year, after the day on which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is accepted by the authorized facility, unless the laws of the jurisdiction in which the authorized facility is located requires shorter time periods, in which case those time periods apply; and
(o) in the event that the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is imported but is not accepted by the authorized facility named in the import permit, or if the authorized facility cannot, or refuses to, dispose of the waste or recycle the material in accordance with the permit, the importer
(i) immediately notifies the Minister, the foreign exporter and the authorities of the country of export of the non-acceptance or refusal and the reason for it,
(ii) if necessary, stores the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material at a facility authorized to store the waste or material by the authorities of the jurisdiction in which the facility is located,
(iii) within 90 days after the day on which the Minister is notified,
(A) makes arrangements to dispose of the hazardous waste or recycle the hazardous recyclable material in Canada at an authorized facility other than the one named in the import permit and advises the Minister of the name and address of the facility and the name of a contact person, or
(B) makes arrangements to return the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material to the facility from which it was exported in accordance with section 35, and
(iv) before shipping the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material to the authorized facility referred to in clause (iii)(A), receives confirmation from the Minister that the facility is an authorized facility.
Movement Document
Marginal note:Movement document reference number
17 The Minister shall provide a movement document reference number to an importer who requests one for the purpose of completing a movement document.
Marginal note:Importer — prior to import
18 (1) Prior to importing the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material, the importer shall provide the foreign exporter with a copy of the movement document indicating the movement document reference number and a copy of the import permit.
Marginal note:Importer — at time of import
(2) At the time of the import of the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material, the importer must ensure that
(a) the foreign exporter has completed Part A of the movement document unless the importer is authorized to do so on the foreign exporter’s behalf under the contract referred to in paragraph 16(e);
(b) the foreign exporter has provided a copy of the movement document and a copy of the import permit to the first authorized carrier; and
(c) the first authorized carrier has completed Part B of the movement document and has provided a copy to the foreign exporter.
Marginal note:Copy of movement document
(3) Within three working days after the day on which the importer receives a copy of the movement document with Parts A and B completed in accordance with subsection (2), the importer must send a copy of it to
(a) the Minister; and
(b) the authorities of the province of import, if they require it.
Marginal note:Authorized carriers
(4) Every authorized carrier that transports the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material must complete Part B of the movement document and provide it and a copy of the import permit to the next authorized carrier or the importer, as the case may be, on delivery of the waste or material to that carrier or the importer.
Marginal note:Importer
(5) The importer must ensure that every authorized carrier that transports the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material completes Part B of the movement document.
Marginal note:Copy of movement document
(6) Within three working days after the day on which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is delivered to the authorized facility, the importer must complete Part C of the movement document and must send a copy of the completed movement document to
(a) the Minister;
(b) the authorities of the province of import, if they require it;
(c) the foreign exporter; and
(d) every authorized carrier of the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material.
Marginal note:Rail consist
19 In the case of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material that is transported by rail, the movement document may be replaced by a rail consist if it contains all of the information contained in the movement document.
Marginal note:Unit of measure
20 The importer must ensure that the quantity of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material indicated in the movement document is in the same unit of measure as is used in the import permit.
Marginal note:Retention of movement document
21 The importer and every authorized carrier must keep a copy of the movement document at their principal place of business in Canada for a period of three years after the date of import.
PART 4Transit
Conditions
Marginal note:Conditions of transit
22 A person may convey hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material in transit if
(a) at the time of transit, the export or import of the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is not prohibited under the laws of Canada or the laws of the country of transit;
(b) the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is transported by the authorized carriers named in the transit permit;
(c) the applicable safety mark is displayed on each shipment of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material in accordance with Part 4 of the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations;
(d) the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is exported and imported through the port of entry and port of exit named in the transit permit;
(e) the quantity of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material conveyed in transit does not exceed the quantity set out in the transit permit;
(f) in the case of a transit through Canada, the authorized carrier if other than Her Majesty in right of Canada or of a province is insured in accordance with section 37;
(g) in the case of a transit through a country other than Canada, the exporter and importer if other than Her Majesty in right of Canada or of a province are insured in accordance with section 37;
(h) in the case of a transit through Canada, the country of export has provided the Minister with written confirmation that the country of import and any countries through which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material will be transited after it has left Canada, has consented to the proposed import into or transit through that country; and
(i) a copy of the transit permit and a copy of the movement document completed in accordance with sections 25 and 26, or 30 and 31, as the case may be,
(i) accompanies the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material, and
(ii) is deposited by the exporter, importer or authorized carrier at the customs office at which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is to be reported under sections 12 and 95 of the Customs Act.
Movement Document — Transits Through Canada
Marginal note:Application
23 Sections 24 to 27 apply to the transit of hazardous waste and hazardous recyclable material through Canada.
Marginal note:Movement document reference number
24 The Minister shall provide a movement document reference number to any person who requests one for the purpose of completing a movement document.
Marginal note:Authorized carrier
25 (1) At the time the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material enters Canada, the authorized carrier must ensure that the foreign exporter has completed Part A of a movement document and that the movement document reference number provided by the Minister is indicated on the movement document.
Marginal note:Authorized carriers
(2) Every authorized carrier that transports the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material must complete Part B of the movement document and provide it and a copy of the transit permit to the next authorized carrier on delivery of the waste or material to that carrier.
Marginal note:Copy of movement document
(3) Within three working days after the day on which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material exits Canada, the authorized carrier that transports the waste or material out of Canada must send a copy of the movement document completed in accordance with subsections (1) and (2) to the Minister.
Marginal note:Rail consist
26 In the case of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material that is transported by rail, the movement document may be replaced by a rail consist if it contains all of the information contained in the movement document.
Marginal note:Retention of movement document
27 If the authorized carrier has a place of business in Canada, the authorized carrier must keep a copy of the movement document at their principal place of business in Canada for a period of three years after the day on which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material exits Canada.
Movement Document — Transits Through a Country Other than Canada
Marginal note:Application
28 Sections 29 to 32 apply to the transit of hazardous waste and hazardous recyclable material where Canada is the country of origin and the country of destination.
Marginal note:Movement document reference number
29 The Minister shall provide a movement document reference number to any exporter who requests one for the purpose of completing a movement document.
Marginal note:Exporter
30 (1) At the time the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material exits Canada, the exporter must complete Part A of a movement document, indicate the movement document reference number provided by the Minister and provide a copy of the movement document and a copy of the transit permit to the first authorized carrier.
Marginal note:First authorized carrier
(2) Immediately on receipt of the movement document, the first authorized carrier must complete Part B of the movement document and provide a copy to the exporter.
Marginal note:Copy of movement document
(3) Within three working days after the day on which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material exits Canada, the exporter must send a copy of the movement document completed in accordance with subsections (1) and (2) to
(a) the Minister; and
(b) the authorities of the province of export, if they require it.
Marginal note:Other authorized carriers
(4) Every authorized carrier that transports the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material must complete Part B of the movement document and provide it and a copy of the transit permit on delivery of the waste or material to the next carrier or the importer, as the case may be.
Marginal note:Exporter
(5) The exporter must ensure that Part B of the movement document is completed by every authorized carrier that transports the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material.
Marginal note:Copy of movement document
(6) Within three working days after the day on which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is delivered to the authorized facility, the importer must complete Part C of the movement document and must send a copy of the completed movement document to
(a) the Minister;
(b) the authorities of the province of import, if they require it;
(c) the exporter; and
(d) every authorized carrier of the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material.
Marginal note:Rail consist
31 In the case of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material that is transported by rail, the movement document may be replaced by a rail consist if it contains all of the information contained in the movement document.
Marginal note:Retention of movement document
32 The exporter, the importer and every authorized carrier must keep a copy of the movement document at their principal place of business in Canada for a period of three years after the day on which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is imported.
PART 5Returns
Application
Marginal note:Returns
33 This Part applies to the return of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material to
(a) Canada after it has been exported from Canada; and
(b) the country of export after it has been imported into Canada.
Returns to Canada
Marginal note:Notice
34 (1) If the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is returned to Canada, the exporter that exported the waste or material from Canada must submit a notice to the Minister in writing, containing the following information:
(a) the name, civic, mailing and electronic addresses and telephone and facsimile numbers of, and the name of the contact person for, the exporter, the foreign receiver and any authorized carriers that were not named in the original export permit;
(b) the name of each insurance company and the policy number for each insurance policy required under these Regulations;
(c) the reason for the return;
(d) the quantity of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material that will be returned using the same unit of measure as in the original export permit;
(e) if the quantity of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material to be returned is less than the quantity of waste or material exported from Canada, the reason for the difference;
(f) the port of entry through which the return will take place and the customs office at which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material will be reported;
(g) the notice reference number contained in the original export permit; and
(h) the line item number contained in the original export permit for the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material that will be returned.
Marginal note:Exporter
(2) After an import permit is issued, the exporter must
(a) return the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material to the facility from which it was exported, using the authorized carriers and the port of entry named in the import permit;
(b) ensure that a copy of the import permit and a copy of the movement document with Parts A and B completed, clearly indicating that the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is being returned to Canada,
(i) accompanies the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material, and
(ii) is deposited at the customs office at which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is to be reported under section 12 of the Customs Act; and
(c) submit a copy of the movement document referred to in paragraph (b) to the Minister, every authorized carrier and if they require it, to the authorities of the province of export.
Returns to the Country of Export
Marginal note:Notice — returns to country of export
35 (1) If the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is returned to the country of export, the importer that imported the waste or material into Canada must submit a notice to the Minister in writing, containing the following information:
(a) the name, civic, mailing and electronic addresses and telephone and facsimile numbers of, and the name of the contact person for, the importer, the foreign exporter and any authorized carriers that were not named in the original import permit;
(b) the name of each insurance company and the policy number for each insurance policy required under these Regulations;
(c) the reason for the return;
(d) the quantity of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material that will be returned using the same unit of measure as in the original import permit;
(e) if the quantity of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material to be returned is less than the quantity of waste or material imported into Canada, the reason for the difference;
(f) the port of entry through which the return will take place and the customs office at which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material will be reported;
(g) the notice reference number contained in the original import permit for the import of the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material into Canada; and
(h) the line item number contained in the original import permit for the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material that will be returned.
Marginal note:Importer’s obligations
(2) After an export permit is issued, the importer must
(a) return the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material to the facility from which it was imported, using the authorized carriers and the port of exit named in the export permit;
(b) ensure that a copy of the export permit and a copy of the movement document with Parts B and C completed, clearly indicating that the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is being returned to the country of export,
(i) accompanies the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material, and
(ii) is deposited at the customs office at which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is to be reported under section 95 of the Customs Act; and
(c) submit a copy of the movement document referred to in paragraph (b) to the Minister, every authorized carrier and if they require it, the authorities of the province of import.
PART 6Miscellaneous Matters
Confirmation of Disposal or Recycling
Marginal note:Confirmation
36 (1) Within 30 days after the day on which the disposal of the hazardous waste or recycling of the hazardous recyclable material is completed, the exporter or importer must provide the Minister with a written, dated and signed confirmation indicating that the waste has been disposed of or the material has been recycled
(a) in accordance with the export or import permit;
(b) in a manner that protects the environment and human health against the adverse effects that may result from the waste or material; and
(c) within the period referred to in paragraph 9(o) or 16(n).
Marginal note:Mandatory reference
(2) The exporter or importer must include the movement document reference number and line item number for the applicable hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material referred to in subsection (1) in the confirmation.
Marginal note:Retention of confirmation
(3) The exporter or importer must keep a copy of the confirmation at their principal place of business in Canada for a period of three years after the day on which it is submitted to the Minister.
Liability Insurance
Marginal note:Coverage
37 (1) The liability insurance required by these Regulations must be in respect of
(a) any damages to third parties for which the exporter, importer or authorized carrier is responsible; and
(b) any costs imposed by law on the exporter, importer or authorized carrier to clean up the environment in respect of any hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material that is released.
Marginal note:Amount
(2) The amount of liability insurance required in respect of each export or import of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is
(a) for exporters or importers, at least $5,000,000 for hazardous waste;
(b) for exporters or importers, at least $1,000,000 for hazardous recyclable material; and
(c) for authorized carriers, the amount required by the laws of the jurisdiction in which the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material is transported.
Marginal note:Coverage period
(3) The insurance must cover liability arising
(a) in the case of an export from Canada, from the time the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material leaves the exporter’s facility to the time an authorized facility, including an authorized facility in Canada if the waste or material is returned to Canada in accordance with section 34, accepts delivery of the waste for disposal or the material for recycling;
(b) in the case of an import into Canada, from the time the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material enters Canada to the time an authorized facility in Canada accepts delivery of the waste or material, or to the time the waste or material leaves Canada for return to the country of export in accordance with section 35; or
(c) if Canada is a country of transit, at any time during the transit through Canada.
Export Reduction Plans
Marginal note:Content of plan
38 (1) The plan referred to in subsection 188(1) of the Act must contain
(a) the following information with respect to the hazardous waste to which the plan applies, namely,
(i) the International Waste Identification Code under OECD Decision C(94)152/Final, substituting the disposal code with the disposal code set out in column 1 of Schedule 1 to these Regulations for the applicable operation set out in column 2 of that Schedule and, if the hazardous waste is a gas, substituting the letter G for the letter L, P or S in the International Waste Identification Code,
(ii) the applicable code set out in List A of Annex VIII to the Convention,
(iii) the identification number set out in column 1 of Schedule 3, 4 or 7, and
(iv) the following information set out in the applicable schedules to the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations, namely,
(A) the applicable UN number set out in column 1 of Schedule 1 or column 5 of Schedule 3,
(B) the applicable class set out in column 3 of Schedule 1 or the primary class set out in column 4 of Schedule 3, and
(C) the applicable packing group and risk group set out in column 4 of Schedule 1;
(b) the name, quantity and concentration of any persistent organic pollutant set out in column 2 of Schedule 10 that is contained in the hazardous waste referred to in the plan;
(c) if the exporter generates the hazardous waste referred to in the plan, the name and a description of the process that generated the waste and the activity in which that process is used;
(d) the origin of the hazardous waste if the exporter does not generate the waste referred to in the plan;
(e) the quantity of hazardous waste exported at the start of the implementation of the plan and the quantity of export reduction to be achieved at each stage of the plan;
(f) a description of the manner in which the exporter will reduce or phase out exports of the hazardous waste referred to in the plan;
(g) the options considered for reducing or phasing out the export of the hazardous waste referred to in the plan, including options for disposing or recycling it in Canada;
(h) the stages of the plan and a schedule for implementing the plan; and
(i) for each stage of the plan, an estimate of the quantity of goods produced that generates the hazardous waste to which the plan applies and a description of the impact of any changes to the quantity produced on the reduction or phasing out of exports of that waste.
Marginal note:Retention of plan
(2) A person who submits a plan to the Minister must keep a copy of the plan at their principal place of business in Canada for a period of five years after the day on which the plan is submitted.
Environmentally Sound Management
Marginal note:Refusal to issue permit
39 If the Minister is of the opinion that the hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material will not be managed in a manner that will protect the environment and human health against the adverse effects that may result from that waste or material, the Minister may, in accordance with subsection 185(2) of the Act, refuse to issue a permit taking into account the following criteria:
(a) the implementation of an environmental management system at the authorized facility that includes
(i) procedures for ensuring the protection of the environment and human health against the adverse effects that may result from the disposal of the hazardous waste or the recycling of the hazardous recyclable material including measures for monitoring the efficiency of the procedures and modifying them in the event that they do not protect the environment and human health,
(ii) measures to monitor and ensure compliance with applicable laws with respect to the protection of the environment and human health, and
(iii) a certification that the system includes those procedures and measures;
(b) the implementation of a plan at the authorized facility to prevent, prepare for and respond to an uncontrolled, unplanned or accidental release of hazardous waste or hazardous recyclable material; and
(c) the existence of prohibitions or conditions relating to the disposal of hazardous waste or the recycling of hazardous recyclable material in Canada or abroad.
Consequential Amendment
Marginal note:Consequential amendment
40 [Amendment]
Repeal
Marginal note:Repeal
41 [Repeal]
Coming into Force
Marginal note:Coming into Force
42 These Regulations come into force on November 1, 2005.
SCHEDULE 1(Subsection 1(1), section 4, subparagraphs 8(j)(i) and (viii) and 9(f)(iv), paragraphs 9(n) and (o), subparagraph 16(e)(iv), paragraphs 16(m) and (n) and subparagraph 38(1)(a)(i))
Disposal Operations for Hazardous Waste
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Disposal Code | Operation | |
| 1 | D1 | Release into or onto land, other than by any of operations D3 to D5 or D12. |
| 2 | D2 | Land treatment, such as biodegradation of liquids or sludges in soil. |
| 3 | D3 | Deep injection, such as injection into wells, salt domes, mines or naturally occurring repositories. |
| 4 | D4 | Surface impoundment, such as placing liquids or sludges into pits, ponds or lagoons. |
| 5 | D5 | Specially engineered landfilling, such as placement into separate lined cells that are isolated from each other and the environment. |
| 6 | D6 | Release into water, other than a sea or ocean, other than by operation D4. |
| 7 | D7 | Release into a sea or ocean, including sea-bed insertion, other than by operation D4. |
| 8 | D8 | Biological treatment, not otherwise set out in this Schedule. |
| 9 | D9 | Physical or chemical treatment, not otherwise referred to in this Schedule, such as calcination, neutralization or precipitation. |
| 10 | D10 | Incineration or thermal treatment on land. |
| 11 | D11 | Incineration or thermal treatment at sea. |
| 12 | D12 | Permanent storage. |
| 13 | D13 | Blending or mixing, prior to any of operations D1 to D12. |
| 14 | D14 | Repackaging, prior to any of operations D1 to D13. |
| 15 | D15 | Release, including the venting of compressed or liquified gases, or treatment, other than by any of operations D1 to D12. |
| 16 | D16 | Testing of a new technology to dispose of a hazardous waste. |
| 17 | D17 | Interim storage, prior to any of operations D1 to D12. |
SCHEDULE 2(Subsection 2(1), subparagraph 2(2)(e)(iii), section 4, subparagraphs 8(j)(i) and (viii) and 9(f)(iv), paragraphs 9(n) and (o), subparagraph 16(e)(iv) and paragraphs 16(m) and (n))
Recycling Operations for Hazardous Recyclable Material
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Recycling Code | Operation | |
| 1 | R1 | Use as a fuel in an energy recovery system, where the net heating value of the material is at least 12 780 kJ/kg. |
| 2 | R2 | Recovery or regeneration of substances that have been used as solvents. |
| 3 | R3 | Recovery of organic substances that have not been used as solvents. |
| 4 | R4 | Recovery of metals and metal compounds. |
| 5 | R5 | Recovery of inorganic materials other than metals or metal compounds. |
| 6 | R6 | Regeneration of acids or bases. |
| 7 | R7 | Recovery of components used for pollution abatement. |
| 8 | R8 | Recovery of components from catalysts. |
| 9 | R9 | Re-refining or re-use of used oil, other than by operation R1. |
| 10 | R10 | Land treatment resulting in agricultural or ecological improvement. |
| 11 | R11 | Use of residual materials obtained by any of operations R1 to R10 or R14. |
| 12 | R12 | Exchange of a recyclable material for another recyclable material prior to recycling by any of operations R1 to R11 or R14. |
| 13 | R13 | Accumulation prior to recycling by any of operations R1 to R11 orR14. |
| 14 | R14 | Recovery or regeneration of a substance or use or re-use of a recyclable material, other than by any of operations R1 to R10. |
| 15 | R15 | Testing of a new technology to recycle a hazardous recyclable material. |
| 16 | R16 | Interim storage prior to any of operations R1 to R11 or R14. |
SCHEDULE 3(Paragraphs 1(1)(a) and 2(1)(a), subparagraph 8(j)(v), paragraphs 9(c) and 16(b) and subparagraph 38(1)(a)(iii))
Hazardous Wastes and Hazardous Recyclable Materials
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Identification No. | Description of Hazardous Waste and Hazardous Recyclable Material | ||
| 1 | HAZ1 | Biomedical waste – the following wastes, other than those generated from building maintenance, office administration or food preparation and consumption, that are generated by human or animal health care establishments, medical, health care or veterinary teaching or research establishments, clinical laboratories or facilities that test or produce vaccines and needle and syringe exchange programs:
Biomedical waste does not include
| |
| 2 | HAZ2 | Used lubricating oils in quantities of 500 L or more, from internal combustion engines or gear boxes, transmissions, transformers, hydraulic systems or other equipment associated with such engines. | |
| 3 | HAZ3 | Used oil filters containing more than 6% of oil by mass. | |
| 4 | HAZ4 | Cyanide, or substances containing cyanide, in a concentration equal to or greater than 100 mg/kg. | |
| 5 | HAZ5 | Wastes that contain more than 2 mg/kg of polychlorinated terphenyls or polybrominated biphenyls described in Schedule 1 to the Act. | |
| 6 | HAZ6 | Wastes that contain, in a concentration of more than 100 ng/kg of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin equivalent,
| |
| The concentration is calculated in accordance with “International Toxicity Equivalency Factor (I-TEF) Method of Risk Assessment for Complex Mixtures of Dioxins and Related Compounds”, Pilot Study on International Information Exchange on Dioxins and Related Compounds, Committee on the Challenges of Modern Society, North Atlantic Treaty Organization, Report Number 176, August 1988, as amended from time to time, using the following factors: | |||
| 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxin | 1.001 | ||
| 1,2,3,7,8-pentachlorodibenzodioxin | 0.5 | ||
| 1,2,3,4,7,8-hexachlorodibenzodioxin | 0.1 | ||
| 1,2,3,7,8,9-hexachlorodibenzodioxin | 0.1 | ||
| 1,2,3,6,7,8-hexachlorodibenzodioxin | 0.1 | ||
| 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-heptachlorodibenzodioxin | 0.01 | ||
| octachlorodibenzodioxin | 0.001 | ||
| 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzofuran | 0.1 | ||
| 2,3,4,7,8-pentachlorodibenzofuran | 0.5 | ||
| 1,2,3,7,8-pentachlorodibenzofuran | 0.05 | ||
| 1,2,3,4,7,8-hexachlorodibenzofuran | 0.1 | ||
| 1,2,3,7,8,9-hexachlorodibenzofuran | 0.1 | ||
| 1,2,3,6,7,8-hexachlorodibenzofuran | 0.1 | ||
| 2,3,4,6,7,8-hexachlorodibenzofuran | 0.1 | ||
| 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-heptachlorodibenzofuran | 0.01 | ||
| 1,2,3,4,7,8,9-heptachlorodibenzofuran | 0.01 | ||
| octachlorodibenzofuran | 0.001 | ||
SCHEDULE 4(Paragraphs 1(1)(c) and 2(1)(c) and subparagraphs 8(j)(v) and 38(1)(a)(iii))
PART 1
Hazardous Wastes and Hazardous Recyclable Materials from Non-specific Sources
| Column 1 | Column 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Item | Identification No. | Description of Hazardous Waste and Hazardous Recyclable Material |
| 1 | F001 | The following spent halogenated solvents used in degreasing: tetrachloroethylene, trichloroethylene, methylene chloride, 1,1,1 trichloroethane, carbon tetrachloride and chlorinated fluorocarbons; all spent solvent mixtures and blends used in degreasing containing, before use, a total of 10% or more (by volume) of one or more of the above halogenated solvents or those solvents listed as F002, F004 or F005; and still bottoms from the recovery of those spent solvents and spent solvent mixtures. |
| 2 | F002 | The following spent halogenated solvents: tetrachloroethylene, methylene chloride, trichloroethylene, 1,1,1 trichloroethane, chlorobenzene, 1,1,2 trichloro 1,2,2 trifluoroethane, ortho dichlorobenzene, trichlorofluoromethane and 1,1,2-trichloroethane; all spent solvent mixtures and blends containing, before use, a total of 10% or more (by volume) of one or more of the above halogenated solvents or those listed as F001, F004 or F005; and still bottoms from the recovery of those spent solvents and spent solvent mixtures. |
| 3 | F003 | The following spent non halogenated solvents: xylene, acetone, ethyl acetate, ethyl benzene, ethyl ether, methyl isobutyl ketone, n butyl alcohol, cyclohexanone and methanol; all spent solvent mixtures and blends containing, before use, only the above spent non-halogenated solvents; and all spent solvent mixtures and blends containing, before use, one or more of the above spent non-halogenated solvents, and a total of 10% or more (by volume) of one or more of those solvents listed as F001, F002, F004 or F005; and still bottoms from the recovery of those spent solvents and spent solvent mixtures. |
| 4 | F004 | The following spent non halogenated solvents: cresols, cresylic acid and nitrobenzene; all spent solvent mixtures and blends containing, before use, a total of 10% or more (by volume) of one or more of the above spent non-halogenated solvents or those solvents listed as F001, F002 or F005; and still bottoms from the recovery of these spent solvents and spent solvent mixtures. |
| 5 | F005 | The following spent non halogenated solvents: toluene, methyl ethyl ketone, carbon disulphide, isobutanol, pyridine, benzene, 2-ethoxyethanol and 2-nitropropane; all spent solvent mixtures and blends containing, before use, a total of 10% or more (by volume) of one or more of the above spent non-halogenated solvents or those solvents listed as F001, F002 or F004; and still bottoms from the recovery of those spent solvents and spent solvent mixtures. |
| 6 | F006 | Wastewater treatment sludges from electroplating operations except for the following processes: (1) sulphuric acid anodizing of aluminum; (2) tin plating on carbon steel; (3) zinc plating (on a segregated basis) on carbon steel; (4) aluminum or aluminum zinc plating on carbon steel; (5) cleaning or stripping associated with tin, zinc or aluminum plating on carbon steel; and (6) chemical etching and milling of aluminum. |
| 7 | F007 | Spent cyanide plating bath solutions from electroplating operations. |
| 8 | F008 | Plating bath sludge from the bottom of plating baths from electroplating operations where cyanides are used in the process. |
| 9 | F009 | Spent stripping and cleaning bath solutions from electroplating operations where cyanides are used in the process. |
| 10 | F010 | Quenching bath sludge from oil baths from metal heat treating operations where cyanides are used in the process. |
| 11 | F011 | Spent cyanide solutions from salt bath pot cleaning from metal heat treating operations. |
| 12 | F012 | Quenching wastewater treatment sludge from metal heat treating operations where cyanides are used in the process. |
| 13 | F019 | Wastewater treatment sludge from the chemical conversion coating of aluminum except from zirconium phosphating in aluminum can washing if such phosphating is an exclusive conversion coating process. |
| 14 | F020 | Wastes from the production or manufacturing use (as a reactant, chemical intermediate or component in a formulating process) of tri- or tetrachlorophenol or of intermediates used to produce their pesticide derivatives, excluding wastewater and spent carbon from hydrogen chloride purification and wastes from the production of hexachlorophene from highly purified 2,4,5-trichlorophenol. |
| 15 | F021 | Wastes from the production or manufacturing use (as a reactant, chemical intermediate or component in a formulating process) of pentachlorophenol or of intermediates used to produce its derivatives, excluding wastewater and spent carbon from hydrogen chloride purification. |
| 16 | F022 | Wastes from the manufacturing use (as a reactant, chemical intermediate or component in a formulating process) of tetra-, penta- or hexachlorobenzenes under alkaline conditions, excluding wastewater and spent carbon from hydrogen chloride purification. |
| 17 | F023 | Wastes from the production of materials on equipment previously used for the production or manufacturing use (as a reactant, chemical intermediate or component in a formulating process) of tri- and tetrachlorophenols, excluding wastewater and spent carbon from hydrogen chloride purification and wastes from equipment used only for the production or use of hexachlorophene from highly purified 2,4,5-trichlorophenol. |
| 18 | F024 | Process wastes, including, but not limited to, distillation residues, heavy ends, tars and reactor clean-out wastes from the production of certain chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons by free radical catalyzed processes, those chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons being those having carbon chain lengths ranging from 1 to and including 5, with varying amounts and positions of chlorine substitution, and excluding wastewaters, wastewater treatment sludge, spent catalysts and wastes set out in Schedule 7. |
| 19 | F025 | Condensed light ends, spent filters and filter aids, and spent desiccant wastes from the production of certain chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons, by free radical catalyzed processes, those chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons being those having carbon chain lengths ranging from 1 to and including 5, with varying amounts and positions of chlorine substitution. |
| 20 | F026 | Wastes from the production of materials on equipment previously used for the manufacturing use (as a reactant, chemical intermediate or component in a formulating process) of tetra-, penta- or hexachlorobenzene under alkaline conditions, excluding wastewater and spent carbon from hydrogen chloride purification. |
| 21 | F027 | Discarded unused formulations containing tri-, tetra- or pentachlorophenol or discarded unused formulations containing compounds derived from those chlorophenols, excluding formulations containing hexachlorophene synthesized from prepurified 2,4,5-trichlorophenol as the sole component. |
| 22 | F028 | Residues resulting from incineration or treatment of soil contaminated with wastes listed as F020, F021, F022, F023, F026 or F027. |
| 23 | F032 | Wastewaters, spent formulations from wood preserving processes generated at plants that currently use or have previously used chlorophenolic formulations, process residuals and preservative drippage, except wastewaters that have not come into contact with process contaminants, spent formulations that potentially cross-contaminated wastes from wood preserving processes at plants that do not resume or initiate use of chlorophenolic preservatives, and bottom sediment sludge listed as K001. |
| 24 | F034 | Wastewaters, process residuals, preservative drippage and spent formulations from wood preserving processes generated at plants that use creosote formulations, excluding bottom sediment sludge listed as K001 and wastewaters that have not come into contact with process contaminants. |
| 25 | F035 | Wastewaters, process residuals, preservative drippage and spent formulations from wood preserving processes generated at plants that use inorganic preservatives containing arsenic or chromium, excluding bottom sediment sludge listed as K001 and wastewaters that have not come into contact with process contaminants. |
| 26 | F037 | Petroleum refinery primary oil, water and solids separation sludge; sludge generated from the gravitational separation of oil, water and solids during the storage or treatment of process wastewaters and oil cooling wastewaters from petroleum refineries, including, but not limited to, those generated in oil, water and solids separators, tanks and impoundments, ditches and other conveyances, sumps and stormwater units receiving dry weather flow; sludge generated in stormwater units that do not receive dry weather flow; sludge generated from non-contact once-through cooling waters segregated for treatment from other processes or oily cooling waters; sludge generated in biological treatment units that employ one of the following treatment methods: activated sludge, trickling filter, rotating biological contactor for the continuous accelerated biological oxidation of wastewaters, or high-rate aeration (including sludge generated in one or more additional units after wastewaters have been treated in biological treatment units). Wastes listed as K051 are excluded. |
| 27 | F038 | Petroleum refinery secondary (emulsified) oil, water and solids separation sludge; sludge or float generated from the physical or chemical separation of oil, water and solids in process wastewaters and oily cooling wastewaters from petroleum refineries, including, but not limited to, sludge and floats generated in induced air flotation (IAF) units, tanks and impoundments, and in dissolved air flotation (DAF) units; sludge generated in stormwater units that do not receive dry weather flow; sludge generated from non-contact once-through cooling waters segregated for treatment from other processes or oily cooling water; sludge and float generated in biological treatment units that employ one of the following treatment methods: activated sludge, trickling filter, rotating biological contactor for the continuous accelerated biological oxidation of wastewaters, or high-rate aeration (including sludge and float generated in one or more additional units after wastewaters have been treated in a biological treatment unit). Wastes listed as F037, K048 and K051 are excluded. |
| 28 | F039 | Leachate (liquids that percolated through land disposed wastes) resulting from the disposal of more than one waste classified as a hazardous waste by being included in this Schedule. |
PART 2
Hazardous Wastes and Hazardous Recyclable Materials from Specific Sources
| Column 1 | Column 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Item | Identification No. | Description of Hazardous Waste and Hazardous Recyclable Material |
| Wood Preservation | ||
| 1 | K001 | Bottom sediment sludge from the treatment of wastewaters from wood preserving processes that use creosote or pentachlorophenol or both. |
| Inorganic Pigments | ||
| 2 | K002 | Wastewater treatment sludge from the production of chrome yellow and orange pigments. |
| 3 | K003 | Wastewater treatment sludge from the production of molybdate orange pigments. |
| 4 | K004 | Wastewater treatment sludge from the production of zinc yellow pigments. |
| 5 | K005 | Wastewater treatment sludge from the production of chrome green pigments. |
| 6 | K006 | Wastewater treatment sludge from the production of chromeoxide green pigments (anhydrous and hydrated). |
| 7 | K007 | Wastewater treatment sludge from the production of iron blue pigments. |
| 8 | K008 | Oven residue from the production of chromeoxide green pigments. |
| Organic Chemicals | ||
| 9 | K009 | Distillation bottoms from the production of acetaldehyde from ethylene. |
| 10 | K010 | Distillation side cuts from the production of acetaldehyde from ethylene. |
| 11 | K011 | Bottom stream from the wastewater stripper in the production of acrylonitrile. |
| 12 | K013 | Bottom stream from the acetonitrile column in the production of acrylonitrile. |
| 13 | K014 | Bottoms from the acetonitrile purification column in the production of acrylonitrile. |
| 14 | K015 | Still bottoms from the distillation of benzylchloride. |
| 15 | K016 | Heavy ends or distillation residues from the production of carbon tetrachloride. |
| 16 | K017 | Heavy ends (still bottoms) from the purification column in the production of epichlorohydrin. |
| 17 | K018 | Heavy ends from the fractionation column in ethyl chloride production. |
| 18 | K019 | Heavy ends from the distillation of ethylene dichloride in ethylene dichloride production. |
| 19 | K020 | Heavy ends from the distillation of vinyl chloride in vinyl chloride monomer production. |
| 20 | K021 | Aqueous spent antimony catalyst waste from fluoromethanes production. |
| 21 | K022 | Distillation bottom tars from the production of phenol and acetone from cumene. |
| 22 | K023 | Distillation light ends from the production of phthalic anhydride from naphthalene. |
| 23 | K024 | Distillation bottoms from the production of phthalic anhydride from naphthalene. |
| 24 | K025 | Distillation bottoms from the production of nitrobenzene by the nitration of benzene. |
| 25 | K026 | Stripping still tails from the production of methyl ethyl pyridines. |
| 26 | K027 | Centrifuge and distillation residues from toluene diisocyanate production. |
| 27 | K028 | Spent catalyst from the hydrochlorinator reactor in the production of 1,1,1 trichloroethane. |
| 28 | K029 | Waste from the product stream stripper in the production of 1,1,1 trichloroethane. |
| 29 | K030 | Column bottoms or heavy ends from the combined production of trichloroethylene and perchloroethylene. |
| 30 | K083 | Distillation bottoms from aniline production. |
| 31 | K085 | Distillation or fractionating column bottoms from the production of chlorobenzenes. |
| 32 | K093 | Distillation light ends from the production of phthalic anhydride from o xylene. |
| 33 | K094 | Distillation bottoms from the production of phthalic anhydride from o xylene. |
| 34 | K095 | Distillation bottoms from the production of 1,1,1 trichloroethane. |
| 35 | K096 | Heavy ends from the heavy ends columns from the production of 1,1,1 trichloroethane. |
| 36 | K103 | Process residues from aniline extraction from the production of aniline. |
| 37 | K104 | Combined wastewater streams from nitrobenzene and aniline production. |
| 38 | K105 | Separated aqueous stream from the reactor product washing step in the production of chlorobenzene. |
| 39 | K107 | Column bottoms from product separation from the production of 1,1-dimethyl-hydrazine (UDMH) from carboxylic acid hydrazines. |
| 40 | K108 | Condensed column overheads from product separation and condensed reactor vent gases from the production of 1,1-dimethylhydrazine (UDMH) from carboxylic acid hydrazides. |
| 41 | K109 | Spent filter cartridges from product purification from the production of 1,1- dimethylhydrazine (UDMH) from carboxylic acid hydrazides. |
| 42 | K110 | Condensed column overheads from intermediate separation from the production of 1,1-dimethylhydrazine (UDMH) from carboxylic acid hydrazides. |
| 43 | K111 | Product washwaters from the production of dinitrotoluene via nitration of toluene. |
| 44 | K112 | Reaction by-product water from the drying column in the production of toluenediamine via hydrogenation of dinitrotoluene. |
| 45 | K113 | Condensed liquid light ends from the purification of toluenediamine in the production of toluenediamine via hydrogenation of dinitrotoluene. |
| 46 | K114 | Vicinals from the purification of toluenediamine in the production of toluenediamine via hydrogenation of dinitrotoluene. |
| 47 | K115 | Heavy ends from the purification of toluenediamine in the production of toluenediamine via hydrogenation of dinitrotoluene. |
| 48 | K116 | Organic condensate from the solvent recovery column in the production of toluene diisocyanate via phosgenation of toluenediamine. |
| 49 | K117 | Wastewater from the reactor vent gas scrubber in the production of ethylene dibromide via bromination of ethene. |
| 50 | K118 | Spent adsorbent solids from the purification of ethylene dibromide in the production of ethylene dibromide via bromination of ethene. |
| 51 | K136 | Still bottoms from the purification of ethylene dibromide in the production of ethylene dibromide via bromination of ethene. |
| 52 | K140 | Floor sweepings, off-specification product and spent filter media from the production of 2,4,6-tribromophenol. |
| 53 | K149 | Distillation bottoms from the production of alpha- (or methyl-) chlorinated toluenes, ring- chlorinated toluenes, benzoyl chlorides and compounds with mixtures of those functional groups, excluding still bottoms from the distillation of benzyl chloride. |
| 54 | K150 | Organic residuals, excluding spent carbon adsorbent, from the spent chlorine gas and hydrochloric acid recovery processes associated with the production of alpha- (or methyl ) chlorinated toluenes, ring-chlorinated toluenes, benzoyl chlorides and compounds with mixtures of those functional groups. |
| 55 | K151 | Wastewater treatment sludge generated during the treatment of wastewaters from the production of alpha- (or methyl-) chlorinated toluenes, ring-chlorinated toluenes, benzoyl chlorides and compounds with mixtures of those functional groups, excluding neutralization and biological sludge. |
| 56 | K156 | Organic waste (including heavy ends, still bottoms, light ends, spent solvents, filtrates and decantates) from the production of carbamates and carbamoyl oximes, excluding waste generated from the manufacture of 3-iodo-2-propynyl n-butylcarbamate. |
| 57 | K157 | Wastewaters (including scrubber waters, condenser waters, washwaters and separation waters) from the production of carbamates and carbamoyl oximes, excluding wastes generated from the manufacture of 3-iodo-2-propynyl n-butylcarbamate. |
| 58 | K158 | Bag house dusts and filter or separation solids from the production of carbamates and carbamoyl oximes, excluding wastes generated from the manufacture of 3-iodo-2-propynyl n-butylcarbamate. |
| 59 | K159 | Organics from the treatment of thiocarbamate wastes. |
| 60 | K161 | Purification solids (including filtration, evaporation and centrifugation solids), bag house dust and floor sweepings from the production of dithiocarbamate acids and their salts, excluding substances listed as K125 or K126. |
| Inorganic chemicals | ||
| 61 | K071 | Brine purification sludge from the mercury cell process in chlorine production if separately prepurified brine is not used. |
| 62 | K073 | Chlorinated hydrocarbon wastes from the purification step of the diaphragm cell process using graphite anodes in chlorine production. |
| 63 | K106 | Wastewater treatment sludge from the mercury cell process in chlorine production. |
| Pesticides | ||
| 64 | K031 | By product salts generated in the production of monosodium acid methanearsonate (MSMA) and cacodylic acid. |
| 65 | K032 | Wastewater treatment sludge from the production of chlordane. |
| 66 | K033 | Wastewater and scrub water from the chlorination of cyclopentadiene in the production of chlordane. |
| 67 | K034 | Filter solids from the filtration of hexachlorocyclopentadiene in the production of chlordane. |
| 68 | K035 | Wastewater treatment sludge from the production of creosote. |
| 69 | K036 | Still bottoms from toluene reclamation distillation in the production of disulfoton. |
| 70 | K037 | Wastewater treatment sludge from the production of disulfoton. |
| 71 | K038 | Wastewater from the washing and stripping of phorate production. |
| 72 | K039 | Filter cake from the filtration of diethylphosphorodithioic acid in the production of phorate. |
| 73 | K040 | Wastewater treatment sludge from the production of phorate. |
| 74 | K041 | Wastewater treatment sludge from the production of toxaphene. |
| 75 | K042 | Heavy ends or distillation residues from the distillation of tetrachlorobenzene in the production of 2,4,5 T. |
| 76 | K043 | 2,6 Dichlorophenol waste from the production of 2,4 D. |
| 77 | K97 | Vacuum stripper discharge from the chlordane chlorinator in the production of chlordane. |
| 78 | L098 | Untreated process wastewater from the production of toxaphene. |
| 79 | K099 | Untreated wastewater from the production of 2,4 D. |
| 80 | K123 | Process wastewater, including supernates, filtrates and washwaters, from the production of ethylenebisdithiocarbamic acid and its salts. |
| 81 | K124 | Reactor vent scrubber water from the production of ethylenebisdithiocarbamic acid and its salts. |
| 82 | K125 | Filtration, evaporation and centrifugation solids from the production of ethylenebisdithiocarbamic acid and its salts. |
| 83 | K126 | Baghouse dust and floor sweepings in milling and packaging operations from the production or formulation of ethylenebisdithiocarbamic acid and its salts. |
| 84 | K131 | Wastewater from the reactor and spent sulfuric acid from the acid dryer from the production of methyl bromide. |
| 85 | K132 | Spent absorbent and wastewater separator solids from the production of methyl bromide. |
| Explosives | ||
| 86 | K044 | Wastewater treatment sludge from the manufacturing and processing of explosives. |
| 87 | K045 | Spent carbon from the treatment of wastewater containing explosives. |
| 88 | K046 | Wastewater treatment sludge from the manufacturing, formulation and loading of lead based initiating compounds. |
| 89 | K047 | Pink and red water from the production of TNT. |
| Petroleum refining | ||
| 90 | K048 | Dissolved air flotation (DAF) float from the petroleum refining industry. |
| 91 | K049 | Slop oil emulsion solids from the petroleum refining industry. |
| 92 | K050 | Heat exchanger bundle cleaning sludge from the petroleum refining industry. |
| 93 | K051 | American Petroleum Institute (API) separator sludge from the petroleum refining industry. |
| 94 | K052 | Tanks bottoms (leaded) from the petroleum refining industry. |
| 95 | K169 | Crude oil storage tank sediment from refining petroleum. |
| 96 | K170 | Clarified slurry oil tank sediment and in-line filter or separation solids from refining petroleum. |
| 97 | K171 | Spent hydrotreating catalyst from refining petroleum, including guard beds used to desulfurize feeds to other catalytic reactors, excluding inert support media. |
| 98 | K172 | Spent hydrorefining catalyst from refining petroleum, including guard beds used to desulfurize feeds to other catalytic reactors, excluding inert support media. |
| Iron and steel | ||
| 99 | K061 | Emission control dust and sludge from the primary production of steel in electric furnaces. |
| 100 | K062 | Spent pickle liquor from steel finishing operations of facilities within the iron and steel industry at steel works, blast furnaces (including coke ovens), rolling mills, iron and steel foundries, gray and ductile iron foundries, malleable iron foundries, steel investment foundries or other miscellaneous steel foundries, or at facilities in the electrometallurgical products (except steel) industry, steel wiredrawing and steel nails and spikes industry, coldrolled steel sheet, strip and bars industry or steel pipes and tubes industry. |
| Primary copper | ||
| 101 | K064 | Acid plant blowdown slurry and sludge resulting from the thickening of blowdown slurry from primary copper production. |
| Primary lead | ||
| 102 | K065 | Surface impoundment solids contained in and dredged from surface impoundments at primary lead smelting facilities. |
| Primary zinc | ||
| 103 | K066 | Sludge from treatment of process wastewater and acid plant blowdown from primary zinc production. |
| Primary aluminum | ||
| 104 | K088 | Spent potliners from primary aluminum reduction. |
| Ferroalloys | ||
| 105 | K090 | Emission control dust or sludge from ferrochromiumsilicon production. |
| 106 | K091 | Emission control dust or sludge from ferrochromium production. |
| Secondary lead | ||
| 107 | K069 | Emission control dust and sludge from secondary lead smelting. |
| 108 | K100 | Waste leaching solution from acid leaching of emission control dust and sludge from secondary lead smelting. |
| Veterinary pharmaceuticals | ||
| 109 | K084 | Wastewater treatment sludge from the production of veterinary pharmaceuticals from arsenic or organo arsenic compounds. |
| 110 | K101 | Distillation tar residues from the distillation of aniline based compounds in the production of veterinary pharmaceuticals from arsenic or organo arsenic compounds. |
| 111 | K102 | Residue from the use of activated carbon for decolourization in the production of veterinary pharmaceuticals from arsenic or organo arsenic compounds. |
| Ink formulation | ||
| 112 | K086 | Solvent washes and sludge, caustic washes and sludge or water washes and sludge from cleaning tubs and equipment used in the formulation of ink from pigments, driers, soaps and stabilizers containing chromium and lead. |
| Coking | ||
| 113 | K060 | Ammonia still lime sludge from coking operations. |
| 114 | K087 | Decanter tank tar sludge from coking operations. |
| 115 | K141 | Process residues from the recovery of coal tar, including, but not limited to, collecting sump residues from the production of coke from coal and the recovery of coke by-products produced from coal, excluding those wastes listed as K087. |
| 116 | K142 | Tar storage tank residues from the production of coke from coal or from the recovery of coke by-products produced from coal. |
| 117 | K143 | Process residues from the recovery of light oil, including, but not limited to, those generated in stills, decanters and wash oil recovery units from the recovery of coke by- products produced from coal. |
| 118 | K144 | Wastewater sump residues from light oil refining, including, but not limited to, intercepting or contamination sump sludge from the recovery of coke by-products produced from coal. |
| 119 | K145 | Residues from naphthalene collection and recovery operations from the recovery of coke by-products produced from coal. |
| 120 | K147 | Tar storage tank residues from coal tar refining. |
| 121 | K148 | Residues from coal tar distillation, including, but not limited to, still bottoms. |
SCHEDULE 5(Paragraphs 1(1)(d) and 2(1)(d))
Environmentally Hazardous Substances
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Substance | Concentration by Mass (mg/kg) | |
| 1 | Acetaldehyde | 100.0 |
| 2 | Acetaldehyde ammonia | 100.0 |
| 3 | Acetic acid | 100.0 |
| 4 | Acetic anhydride | 100.0 |
| 5 | Acetone cyanohydrin | 100.0 |
| 6 | Acetyl bromide | 100.0 |
| 7 | Acetyl chloride | 100.0 |
| 8 | Acrolein, stabilized | 100.0 |
| 9 | Acrylonitrile, stabilized | 100.0 |
| 10 | Adipic acid | 100.0 |
| 11 | Allethrin | 100.0 |
| 12 | Allyl alcohol | 100.0 |
| 13 | Allyl chloride | 100.0 |
| 14 | Aluminum sulphate | 100.0 |
| 15 | N-Aminopropylmorpholine | 100.0 |
| 16 | Ammonia | 100.0 |
| 17 | Ammonia solutions | 100.0 |
| 18 | Ammonium acetate | 100.0 |
| 19 | Ammonium benzoate | 100.0 |
| 20 | Ammonium bicarbonate | 100.0 |
| 21 | Ammonium bisulphite | 100.0 |
| 22 | Ammonium carbamate | 100.0 |
| 23 | Ammonium carbonate | 100.0 |
| 24 | Ammonium chloride | 100.0 |
| 25 | Ammonium citrate, dibasic | 100.0 |
| 26 | Ammonium oxalate | 100.0 |
| 27 | Ammonium sulphamate | 100.0 |
| 28 | Ammonium sulphide | 100.0 |
| 29 | Ammonium tartrate | 100.0 |
| 30 | Ammonium thiocyanate | 100.0 |
| 31 | Ammonium thiosulphate | 100.0 |
| 32 | Amyl acetates | 100.0 |
| 33 | Aniline | 100.0 |
| 34 | Antimony pentachloride | 100.0 |
| 35 | Antimony potassium tartrate | 100.0 |
| 36 | Antimony tribromide | 100.0 |
| 37 | Antimony trichloride | 100.0 |
| 38 | Antimony trioxide | 100.0 |
| 39 | Benzidine | 100.0 |
| 40 | Benzoic acid | 100.0 |
| 41 | Benzonitrile | 100.0 |
| 42 | Benzoyl chloride | 100.0 |
| 43 | Benzyl chloride | 100.0 |
| 44 | Beryllium chloride | 100.0 |
| 45 | Butyl acetates | 100.0 |
| 46 | n-Butylamine | 100.0 |
| 47 | n-Butyl phthalate | 100.0 |
| 48 | Calcium hypochlorite | 100.0 |
| 49 | Captan | 100.0 |
| 50 | Carbon disulphide | 100.0 |
| 51 | Chlordecone | 100.0 |
| 52 | 2-Chlorophenol | 100.0 |
| 53 | Chlorosulphonic acid (with or without sulphur trioxide) | 100.0 |
| 54 | Cobaltous bromide | 100.0 |
| 55 | Cobaltous formate | 100.0 |
| 56 | Cobaltous sulphamate | 100.0 |
| 57 | Copper-based pesticides (all forms) | 100.0 |
| 58 | Copper chloride | 100.0 |
| 59 | Coumaphos | 100.0 |
| 60 | Creosote | 100.0 |
| 61 | Crotonaldehyde | 100.0 |
| 62 | Cupric acetate | 100.0 |
| 63 | Cupric oxalate | 100.0 |
| 64 | Cupric sulphate | 100.0 |
| 65 | Cupric sulphate, ammoniated | 100.0 |
| 66 | Cupric tartrate | 100.0 |
| 67 | Cyclohexane | 100.0 |
| 68 | Dichlobenil | 100.0 |
| 69 | Dichlone | 100.0 |
| 70 | 1,1-Dichloro-2,2-di-(p-chlorophenyl) ethane | 100.0 |
| 71 | Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane | 100.0 |
| 72 | 2,2-Dichloroethyl ether | 100.0 |
| 73 | Dichloropropene | 100.0 |
| 74 | 2,2-Dichloropropionic acid | 100.0 |
| 75 | Dichlorvos | 100.0 |
| 76 | Dicofol | 100.0 |
| 77 | Diethylamine | 100.0 |
| 78 | Dimethylamine | 100.0 |
| 79 | Dinitrobenzenes | 100.0 |
| 80 | Dinitrophenol | 100.0 |
| 81 | Dinitrotoluenes (excluding 2,4-dinitrotoluene) | 100.0 |
| 82 | Disulfoton | 100.0 |
| 83 | Endosulfan | 100.0 |
| 84 | Epichlorohydrin | 100.0 |
| 85 | Ethion | 100.0 |
| 86 | Ethylbenzene | 100.0 |
| 87 | Ethylenediamine | 100.0 |
| 88 | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid | 100.0 |
| 89 | Ethylene dibromide | 100.0 |
| 90 | Ethylene dichloride | 100.0 |
| 91 | Ferric ammonium citrate | 100.0 |
| 92 | Ferric ammonium oxalate | 100.0 |
| 93 | Ferric chloride | 100.0 |
| 94 | Ferric nitrate | 100.0 |
| 95 | Ferric sulphate | 100.0 |
| 96 | Ferrous ammonium sulphate | 100.0 |
| 97 | Ferrous chloride | 100.0 |
| 98 | Ferrous sulphate | 100.0 |
| 99 | Formaldehyde | 100.0 |
| 100 | Formic acid | 100.0 |
| 101 | Fumaric acid | 100.0 |
| 102 | Furfural | 100.0 |
| 103 | Hexachlorocyclopentadiene | 100.0 |
| 104 | Isobutyl acetate | 100.0 |
| 105 | Isobutylamine | 100.0 |
| 106 | Isobutyric acid | 100.0 |
| 107 | Isoprene | 100.0 |
| 108 | Kelthane | 100.0 |
| 109 | Mercaptodimethur | 100.0 |
| 110 | Methyl bromide and ethylene dibromide mixtures | 100.0 |
| 111 | Methyl methacrylate | 100.0 |
| 112 | Methylamine | 100.0 |
| 113 | Mevinphos | 100.0 |
| 114 | Mexacarbate | 100.0 |
| 115 | Naled | 100.0 |
| 116 | Naphthalene | 100.0 |
| 117 | Naphthenic acid | 100.0 |
| 118 | Nickel ammonium sulphate | 100.0 |
| 119 | Nickel chloride | 100.0 |
| 120 | Nickel hydroxide | 100.0 |
| 121 | Nickel sulphate | 100.0 |
| 122 | Nitrophenols (o-, m-, p-) | 100.0 |
| 123 | Nitrotoluenes, (o-, m-, p-) | 100.0 |
| 124 | Organotin compounds (all forms) | 100.0 |
| 125 | Organotin Pesticides (all forms) | 100.0 |
| 126 | Oxalates, water soluble | 100.0 |
| 127 | Paraformaldehyde | 100.0 |
| 128 | Phencapton | 100.0 |
| 129 | Phenol | 100.0 |
| 130 | Phosphorus | 100.0 |
| 131 | Phosphorus oxychloride | 100.0 |
| 132 | Phosphorus pentasulphide | 100.0 |
| 133 | Phosphorus trichloride | 100.0 |
| 134 | Polychlorinated biphenyls | 50.0 |
| 135 | Potassium permanganate | 100.0 |
| 136 | Propargite | 100.0 |
| 137 | Propionic acid | 100.0 |
| 138 | Propionic anhydride | 100.0 |
| 139 | Propylene dichloride | 100.0 |
| 140 | Propylene oxide | 100.0 |
| 141 | Pyrethrins | 100.0 |
| 142 | Quinoline | 100.0 |
| 143 | Resorcinol | 100.0 |
| 144 | Silver nitrate | 100.0 |
| 145 | Sodium bisulphite | 100.0 |
| 146 | Sodium dodecylbenzene sulphonate (branched chain) | 100.0 |
| 147 | Sodium hydrogen sulphite | 100.0 |
| 148 | Sodium hydrosulphide | 100.0 |
| 149 | Sodium methylate | 100.0 |
| 150 | Sodium phosphate, dibasic | 100.0 |
| 151 | Sodium phosphate, tribasic | 100.0 |
| 152 | Strychnine or Strychnine mixtures | 100.0 |
| 153 | Strychnine salts or Strychnine salt mixtures | 100.0 |
| 154 | Styrene | 100.0 |
| 155 | Sulphur monochloride | 100.0 |
| 156 | Tetrachloroethane | 100.0 |
| 157 | Tetraethyl Pyrophosphate | 100.0 |
| 158 | Thallium sulphate | 100.0 |
| 159 | Thiram | 100.0 |
| 160 | Titanium sulphate | 100.0 |
| 161 | Toluene | 100.0 |
| 162 | Triazine Pesticides | 100.0 |
| 163 | Trichlorphon | 100.0 |
| 164 | Triethylamine | 100.0 |
| 165 | Trimethylamine | 100.0 |
| 166 | Vanadium pentoxide, non-fused form | 100.0 |
| 167 | Vanadyl sulphate | 100.0 |
| 168 | Vinyl acetate | 100.0 |
| 169 | Xylenes | 100.0 |
| 170 | Xylenols | 100.0 |
| 171 | Zinc acetate | 100.0 |
| 172 | Zinc ammonium chloride | 100.0 |
| 173 | Zinc carbonate | 100.0 |
| 174 | Zinc chloride | 100.0 |
| 175 | Zinc formate | 100.0 |
| 176 | Zinc phenolsulphonate | 100.0 |
| 177 | Zinc phosphide | 100.0 |
| 178 | Zinc sulphate | 100.0 |
| 179 | Zirconium sulphate | 100.0 |
SCHEDULE 6(Paragraphs 1(1)(e) and 2(1)(e) and subparagraphs 2(2)(e)(ii) and 8(j)(v))
Hazardous Constituents Controlled Under Leachate Test and Regulated Limits
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hazardous Constituent Code No. | Hazardous Constituents (synonyms and descriptors) | Concentration(mg/L) | |
| 1 | L32 | Aldicarb | 0.009 |
| 2 | L3 | Aldrin + Dieldrin | 0.070 |
| 3 | L4 | Arsenic | 2.500 |
| 4 | L33 | Atrazine + N dealkylated metabolites | 0.500 |
| 5 | L34 | Azinphos methyl | 2.000 |
| 6 | L5 | Barium | 100.000 |
| 7 | L35 | Bendiocarb | 4.000 |
| 8 | L36 | Benzene | 0.500 |
| 9 | L37 | Benzo(a)pyrene | 0.001 |
| 10 | L6 | Boron | 500.000 |
| 11 | L38 | Bromoxynil | 0.500 |
| 12 | L7 | Cadmium | 0.500 |
| 13 | L8 | Carbaryl/Sevin/1 Naphthyl N methyl carbamate | 9.000 |
| 14 | L39 | Carbofuran | 9.000 |
| 15 | L40 | Carbon tetrachloride (Tetrachloromethane) | 0.5000 |
| 16 | L41 | Chloramines | 300.000 |
| 17 | L9 | Chlordane | 0.700 |
| 18 | L42 | Chlorobenzene (Monochlorobenzene) | 8.000 |
| 19 | L43 | Chloroform | 10.000 |
| 20 | L44 | Chlorpyrifos | 9.000 |
| 21 | L10 | Chromium | 5.000 |
| 22 | L45 | Cresol (Mixture — total of all isomers, when isomers cannot be differentiated) | 200.000 |
| 23 | L46 | m Cresol | 200.000 |
| 24 | L47 | o Cresol | 200.000 |
| 25 | L48 | p Cresol | 200.000 |
| 26 | L49 | Cyanazine | 1.000 |
| 27 | L11 | Cyanide | 20.000 |
| 28 | L2 | 2,4 D / (2,4 Dichlorophenoxy)acetic acid | 10.000 |
| 29 | L50 | 2,4 DCP / (2,4 Dichlorophenol) | 90.000 |
| 30 | L12 | DDT (total isomers) | 3.000 |
| 31 | L13 | Diazinon/Phosphordithioic acid, o,o diethyl o (2 isopropyl 6 methyl 4 pyrimidinyl) ester | 2.000 |
| 32 | L51 | Dicamba | 12.000 |
| 33 | L52 | 1,2 Dichlorobenzene (o Dichlorobenzene) | 20.00 |
| 34 | L53 | 1,4 Dichlorobenzene (p Dichlorobenzene) | 0.50 |
| 35 | L54 | 1,2 Dichloroethane (Ethylene dichloride) | 5.0 |
| 36 | L55 | 1,1 Dichloroethylene (Vinylidene chloride) | 1.40 |
| 37 | L56 | Dichloromethane (also see — methylene chloride) | 5.00 |
| 38 | L57 | Diclofop methyl | 0.90 |
| 39 | L58 | Dimethoate | 2.00 |
| 40 | L59 | 2,4 Dinitrotoluene | 0.13 |
| 41 | L60 | Dinoseb | 1.00 |
| 42 | L70 | Diquat | 7.00 |
| 43 | L71 | Diuron | 15.00 |
| 44 | L14 | Endrin | 0.02 |
| 45 | L15 | Fluoride | 150.00 |
| 46 | L72 | Glyphosate | 28.00 |
| 47 | L16 | Heptachlor + Heptachlor epoxide | 0.30 |
| 48 | L73 | Hexachlorobenzene | 0.13 |
| 49 | L74 | Hexachlorobutadiene | 0.50 |
| 50 | L75 | Hexachloroethane | 3.00 |
| 51 | L17 | Lead | 5.00 |
| 52 | L18 | Lindane | 0.40 |
| 53 | L76 | Malathion | 19.00 |
| 54 | L19 | Mercury | 0.10 |
| 55 | L20 | Methoxychlor/1,1,1 Trichloro 2,2 bis(p methoxyphenyl) ethane | 90.00 |
| 56 | L77 | Methyl ethyl ketone / Ethyl methyl ketone | 200.00 |
| 57 | L21 | Methyl Parathion | 0.70 |
| 58 | L78 | Methylene chloride / Dichloromethane | 5.00 |
| 59 | L79 | Metolachlor | 5.00 |
| 60 | L80 | Metribuzin | 8.00 |
| 61 | L81 | Nitrate | 4500.00 |
| 62 | L22 | Nitrate + Nitrite | 1000.000 |
| 63 | L23 | Nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) | 40.00 |
| 64 | L24 | Nitrite | 320.00 |
| 65 | L82 | Nitrobenzene | 2.00 |
| 66 | L83 | Paraquat | 1.00 |
| 67 | L26 | Parathion | 5.00 |
| 68 | L84 | Pentachlorophenol | 6.00 |
| 69 | L85 | Phorate | 0.20 |
| 70 | L86 | Picloram | 19.00 |
| 71 | L100 | Polychlorinated dibenzo dioxins and furans | 0.0000015 TEQ |
| 72 | L87 | Pyridine | 5.00 |
| 73 | L27 | Selenium | 1.00 |
| 74 | L88 | Simazine | 1.00 |
| 75 | L89 | 2,4,5 T (2,4,5 Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid) | 28.00 |
| 76 | L1 | 2,4,5 TP/ Silvex/ 2 (2,4,5 Trichlorophenoxy)propionic acid | 1.00 |
| 77 | L90 | Temephos | 28.00 |
| 78 | L91 | Terbufos | 0.10 |
| 79 | L92 | Tetrachloroethylene | 3.00 |
| 80 | L93 | 2,3,4,6 Tetrachlorophenol / (2,3,4,6 TeCP) | 10.00 |
| 81 | L29 | Toxaphene | 0.50 |
| 82 | L94 | Triallate | 23.00 |
| 83 | L95 | Trichloroethylene | 5.00 |
| 84 | L96 | 2,4,5 Trichlorophenol / (2,4,5 TCP) | 400.00 |
| 85 | L97 | 2,4,6 Trichlorophenol / (2,4,6 TCP) | 0.50 |
| 86 | L98 | Trifluralin | 4.50 |
| 87 | L30 | Trihalomethanes — Total (also see — Chloroform) | 10.00 |
| 88 | L31 | Uranium | 10.00 |
| 89 | L99 | Vinyl chloride | 0.20 |
SCHEDULE 7(Paragraphs 1(1)(f) and 2(1)(f), subparagraphs 8(j)(v)and 38(1)(a)(iii) and Schedule 4)
PART 1
Acute Hazardous Waste and Hazardous Recyclable Material Chemicals
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Identification No. | Description of Hazardous Waste or Hazardous Recyclable Material | |
| 1 | P026 | 1-(o-Chlorophenyl)thiourea |
| 2 | P081 | 1,2,3-Propanetriol, trinitrate |
| 3 | P042 | 1,2-Benzenediol,4-[1-hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl]- |
| 4 | P067 | 1,2-Propylenimine |
| 5 | P185 | 1,3-Dithiolane-2-carboxaldehyde, 2,4-dimethyl-, O-[(methylamino)-carbonyl]oxime |
| 6 | P004 | 1,4,5,8-Dimethanonaphthalene,1,2,3,4,10,10-hexa-chloro-1,4,4a,5,8,8a,-hexahydro-, (1alpha,4alpha,4abeta,5alpha,8alpha,8abeta) |
| 7 | P060 | 1,4,5,8-Dimethanonaphthalene,1,2,3,4,10,10-hexa-chloro-1,4,4a,5,8,8a-hexahydro-, (1alpha,4alpha,4abeta,5beta,8beta,8abeta)- |
| 8 | P002 1 | Acetyl-2-thiourea |
| 9 | P048 | 2,4-Dinitrophenol |
| 10 | P051 | 2,7:3,6-Dimethanonaphth [2,3-b]oxirene, 3,4,5,6,9,9-hexachloro-1a,2,2a,3,6,6a,7,7a-octahydro-, (1aalpha,2beta,2abeta,3alpha,6alpha,6 abeta,7beta,7aalpha)-, and metabolites |
| 11 | P037 | 2,7:3,6-Dimethanonaphth[2,3-b]oxirene,3,4,5,6,9,9-hexachloro-1a,2,2a,3,6,6a,7,7a-octahydro-, (1aalpha,2beta,2aalpha,3beta,6beta,6aalpha,7beta,7aalpha)-[b]oxirene, 3,4,5,6,9,9-hexachloro- |
| 12 | P045 | 2-Butanone, 3,3-dimethyl-1-methylthio)-, O-[methylamino)carbonyl]oxime |
| 13 | P034 | 2-Cyclohexyl-4,6-dinitrophenol |
| 14 | P001 | 2H-1-Benzopyran-2-one, 4-hydroxy-3-(3-oxo-1-phenylbutyl)-, and salts, when present at concentrations greater than 0.3% |
| 15 | P069 | 2-Methyllactonitrile |
| 16 | P017 | 2-Propanone, 1-bromo- |
| 17 | P005 | 2-Propen-1-ol |
| 18 | P003 | 2-Propenal |
| 19 | P102 | 2-Propyn-1-ol |
| 20 | P007 | 3(2H)-Isoxazolone, 5-(aminomethyl)- |
| 21 | P027 | 3-Chloropropionitrile |
| 22 | P202 | 3-Isopropylphenyl N-methylcarbamate |
| 23 | P047 | 4,6-Dinitro-o-cresol, and salts |
| 24 | P059 | 4,7-Methano-1H-indene, 1,4,5,6,7,8,8-heptachloro-3a,4,7,7a-tetrahydro- |
| 25 | P008 | 4-Aminopyridine |
| 26 | P008 | 4-Pyridinamine |
| 27 | P007 | 5-(Aminomethyl)-3-isoxazolol |
| 28 | P050 | 6,9-Methano-2,4,3-benzodioxathiepin, 6,7,8,9,10,10-hexachloro-1,5,5a,6,9,9a-hexahydro-, 3-oxide |
| 29 | P127 | 7-Benzofuranol, 2,3-dihydro-2,2-dimethyl-, methylcarbamate |
| 30 | P088 | 7-Oxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2,3-dicarboxylic acid |
| 31 | P023 | Acetaldehyde, chloro- |
| 32 | P057 | Acetamide, 2-fluoro- |
| 33 | P002 | Acetamide, N-(aminothioxomethyl)- |
| 34 | P058 | Acetic acid, fluoro-, sodium salt |
| 35 | P003 | Acrolein |
| 36 | P070 | Aldicarb |
| 37 | P203 | Aldicarb sulfone |
| 38 | P004 | Aldrin |
| 39 | P005 | Allyl alcohol |
| 40 | P046 | alpha,a-Dimethylphenethylamine |
| 41 | P072 | alpha-Naphthylthiourea |
| 42 | P006 | Aluminum phosphide |
| 43 | P009 | Ammonium picrate |
| 44 | P119 | Ammonium vanadate |
| 45 | P099 | Argentate(1-), bis(cyano-C)-, potassium |
| 46 | P010 | Arsenic acid H3AsO4 |
| 47 | P012 | Arsenic oxide As2O3 |
| 48 | P011 | Arsenic oxide As2O5 |
| 49 | P011 | Arsenic pentoxide |
| 50 | P012 | Arsenic trioxide |
| 51 | P038 | Arsine, diethyl- |
| 52 | P036 | Arsonous dichloride, phenyl- |
| 53 | P054 | Aziridine |
| 54 | P067 | Aziridine, 2-methyl- |
| 55 | P013 | Barium cyanide |
| 56 | P024 | Benzenamine, 4-chloro- |
| 57 | P077 | Benzenamine, 4-nitro- |
| 58 | P028 | Benzene, (chloromethyl)- |
| 59 | P046 | Benzeneethanamine, alpha,alpha-dimethyl- |
| 60 | P014 | Benzenethiol |
| 61 | P188 | Benzoic acid, 2-hydroxy-, compd with (3aS-cis)-1,2,3,3a,8,8a-hexahydro-1,3a,8-trimethylpyrrolo[2,3-b]indol-5-yl methylcarbamate ester (1:1) |
| 62 | P028 | Benzyl chloride |
| 63 | P015 | Beryllium powder |
| 64 | P017 | Bromoacetone |
| 65 | P018 | Brucine |
| 66 | P021 | Calcium cyanide |
| 67 | P021 | Calcium cyanide Ca(CN)2 |
| 68 | P189 | Carbamic acid, [(dibutylamino)-thio]methyl-, 2,3-dihydro-2,2-dimethyl-7-benzofuranyl ester |
| 69 | P191 | Carbamic acid, dimethyl-, 1-[(dimethyl-amino)carbonyl]-5-methyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl ester |
| 70 | P190 | Carbamic acid, methyl-, 3-methylphenyl ester |
| 71 | P192 | Carbamic acid,dimethyl-,3-methyl-1-(1methylethyl)-1H-pyrazol-5-yl ester |
| 72 | P127 | Carbofuran |
| 73 | P022 | Carbon disulfide |
| 74 | P095 | Carbonic dichloride |
| 75 | P189 | Carbosulfan |
| 76 | P023 | Chloroacetaldehyde |
| 77 | P029 | Copper cyanide |
| 78 | P029 | Copper cyanide Cu(CN) |
| 79 | P030 | Cyanides (soluble cyanide salts), not otherwise specified |
| 80 | P031 | Cyanogen |
| 81 | P033 | Cyanogen chloride |
| 82 | P033 | Cyanogen chloride (CN)Cl |
| 83 | P016 | Dichloromethyl ether |
| 84 | P036 | Dichlorophenylarsine |
| 85 | P037 | Dieldrin |
| 86 | P038 | Diethylarsine |
| 87 | P041 | Diethyl-p-nitrophenyl phosphate |
| 88 | P043 | Diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP) |
| 89 | P044 | Dimethoate |
| 90 | P191 | Dimetilan |
| 91 | P020 | Dinoseb |
| 92 | P085 | Diphosphoramide, octamethyl- |
| 93 | P111 | Diphosphoric acid, tetraethyl ester |
| 94 | P039 | Disulfoton |
| 95 | P049 | Dithiobiuret |
| 96 | P050 | Endosulfan |
| 97 | P088 | Endothall |
| 98 | P051 | Endrin |
| 99 | P051 | Endrin, and metabolites |
| 100 | P042 | Epinephrine |
| 101 | P031 | Ethanedinitrile |
| 102 | P194 | Ethanimidothioc acid, 2-(dimethylamino)-N-[[(methylamino)carbonyl]oxy]-2-oxo-, methyl ester |
| 103 | P066 | Ethanimidothioic acid, N-[[(methylamino)carbonyl]oxy]-, methyl ester |
| 104 | P101 | Ethyl cyanide |
| 105 | P054 | Ethyleneimine |
| 106 | P097 | Famphur |
| 107 | P056 | Fluorine |
| 108 | P057 | Fluoroacetamide |
| 109 | P058 | Fluoroacetic acid, sodium salt |
| 110 | P198 | Formetanate hydrochloride |
| 111 | P197 | Formparanate |
| 112 | P065 | Fulminic acid, mercury(2+) salt |
| 113 | P059 | Heptachlor |
| 114 | P062 | Hexaethyl tetraphosphate |
| 115 | P068 | Hydrazine, methyl- |
| 116 | P116 | Hydrazinecarbothioamide |
| 117 | P063 | Hydrocyanic acid |
| 118 | P063 | Hydrogen cyanide |
| 119 | P096 | Hydrogen phosphide |
| 120 | P060 | Isodrin |
| 121 | P192 | Isolan |
| 122 | P196 | Manganese, bis(dimethylcarbamodithioato-S,S′)- |
| 123 | P196 | Manganese dimethyl dithiocarbamate |
| 124 | P202 | M-Cumenyl methylcarbamate |
| 125 | P065 | Mercury fulminate |
| 126 | P092 | Mercury, (acetato-O)phenyl- |
| 127 | P082 | Methanamine, N-methyl-N-nitroso- |
| 128 | P064 | Methane, isocyanato- |
| 129 | P016 | Methane, oxybis[chloro- |
| 130 | P112 | Methane, tetranitro- |
| 131 | P118 | Methanethiol, trichloro- |
| 132 | P197 | Methanimidamide, N,N-dimethyl-N′-[2-methyl-4-[[(methylamino)carbonyl]oxy]phenyl]- |
| 133 | P198 | Methanimidamide, N,N-dimethyl-N′-[3-[[(methylamino)-carbonyl]oxy]phenyl]-, monohydrochloride |
| 134 | P199 | Methiocarb |
| 135 | P066 | Methomyl |
| 136 | P068 | Methyl hydrazine |
| 137 | P064 | Methyl isocyanate |
| 138 | P071 | Methyl parathion |
| 139 | P190 | Metolcarb |
| 140 | P128 | Mexacarbate |
| 141 | P073 | Nickel carbonyl |
| 142 | P073 | Nickel carbonyl Ni(CO)4, (T-4)- |
| 143 | P074 | Nickel cyanide |
| 144 | P074 | Nickel cyanide Ni(CN)2 |
| 145 | P075 | Nicotine, and salts |
| 146 | P076 | Nitric oxide |
| 147 | P078 | Nitrogen dioxide |
| 148 | P076 | Nitrogen oxide NO |
| 149 | P078 | Nitrogen oxide NO2 |
| 150 | P081 | Nitroglycerine |
| 151 | P082 | N-Nitrosodimethylamine |
| 152 | P084 | N-Nitrosomethylvinylamine |
| 153 | P040 | O,O-Diethyl O-pyrazinyl phosphorothioate |
| 154 | P085 | Octamethylpyrophosphoramide |
| 155 | P087 | Osmium oxide OsO4,(T-4)- |
| 156 | P087 | Osmium tetroxide |
| 157 | P194 | Oxamyl |
| 158 | P089 | Parathion |
| 159 | P024 | p-Chloroaniline |
| 160 | P020 | Phenol, 2-(1-methylpropyl)-4,6-dinitro- |
| 161 | P009 | Phenol, 2,4,6-trinitro-, ammonium salt |
| 162 | P048 | Phenol, 2,4-dinitro- |
| 163 | P034 | Phenol, 2-cyclohexyl-4,6-dinitro- |
| 164 | P047 | Phenol, 2-methyl-4,6-dinitro-, and salts |
| 165 | P202 | Phenol, 3-(1-methylethyl)-, methylcarbamate |
| 166 | P201 | Phenol, 3-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl)-, methylcarbamate |
| 167 | P199 | Phenol, (3,5-dimethyl-4-(methylthio)-, methylcarbamate |
| 168 | P128 | Phenol, 4-(dimethylamino)-3,5-dimethyl-, methylcarbamate (ester) |
| 169 | P092 | Phenylmercury acetate |
| 170 | P093 | Phenylthiourea |
| 171 | P094 | Phorate |
| 172 | P095 | Phosgene |
| 173 | P096 | Phosphine |
| 174 | P041 | Phosphoric acid, diethyl 4-nitrophenyl ester |
| 175 | P094 | Phosphorodithioic acid, O,O-diethyl S-[(ethylthio)methyl] ester |
| 176 | P039 | Phosphorodithioic acid, O,O-diethyl S-[2-(ethylthio)ethyl] ester |
| 177 | P044 | Phosphorodithioic acid, O,O-dimethylS-[2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl] ester |
| 178 | P043 | Phosphorofluoridic acid, bis(1-methylethyl) ester |
| 179 | P071 | Phosphorothioic acid, O,O,-dimethyl O-(4-nitrophenyl) ester |
| 180 | P089 | Phosphorothioic acid, O,O-diethyl O-(4-nitrophenyl) ester |
| 181 | P040 | Phosphorothioic acid, O,O-diethyl O-pyrazinyl ester |
| 182 | P097 | Phosphorothioic acid, O-[4-[(dimethylamino)sulfonyl]phenyl] O,O-r dimethyl ester |
| 183 | P188 | Physostigmine salicylate |
| 184 | P204 | Physostigmine |
| 185 | P110 | Plumbane, tetraethyl- |
| 186 | P077 | p-Nitroaniline |
| 187 | P098 | Potassium cyanide |
| 188 | P098 | Potassium cyanide K(CN) |
| 189 | P099 | Potassium silver cyanide |
| 190 | P201 | Promecarb |
| 191 | P203 | Propanal, 2-methyl-2-(methyl-sulfonyl)-, O-[(methylamino)carbonyl]oxime |
| 192 | P070 | Propanal, 2-methyl-2-(methylthio)-, O-[(methylamino)carbonyl]oxime |
| 193 | P101 | Propanenitrile |
| 194 | P069 | Propanenitrile, 2-hydroxy-2-methyl- |
| 195 | P027 | Propanenitrile, 3-chloro- |
| 196 | P102 | Propargyl alcohol |
| 197 | P075 | Pyridine, 3-(1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)-, (S)-, and salts |
| 198 | P204 | Pyrrolo[2,3-b]indol-5-ol,1,2,3,3a,8,8a-hexahydro-1,3a,8- trimethyl-, methylcarbamate (ester), (3aS-cis)- |
| 199 | P114 | Selenious acid, dithallium(1+) salt |
| 200 | P103 | Selenourea |
| 201 | P104 | Silver cyanide |
| 202 | P104 | Silver cyanide Ag(CN) |
| 203 | P105 | Sodium azide |
| 204 | P106 | Sodium cyanide |
| 205 | P106 | Sodium cyanide Na(CN) |
| 206 | P108 | Strychnidin-10-one, and salts |
| 207 | P018 | Strychnidin-10-one, 2,3-dimethoxy- |
| 208 | P108 | Strychnine, and salts |
| 209 | P115 | Sulfuric acid, dithallium(1+) salt |
| 210 | P110 | Tetraethyl lead |
| 211 | P111 | Tetraethyl pyrophosphate |
| 212 | P109 | Tetraethyldithiopyrophosphate |
| 213 | P112 | Tetranitromethane |
| 214 | P062 | Tetraphosphoric acid, hexaethyl ester |
| 215 | P113 | Thallic oxide |
| 216 | P113 | Thallium oxide Tl2O3 |
| 217 | P114 | Thallium(I) selenite |
| 218 | P115 | Thallium(I) sulfate |
| 219 | P109 | Thiodiphosphoric acid, tetraethyl ester |
| 220 | P045 | Thiofanox |
| 221 | P049 | Thioimidodicarbonic diamide [(H2N)C(S)]2NH |
| 222 | P014 | Thiophenol |
| 223 | P116 | Thiosemicarbazide |
| 224 | P026 | Thiourea, (2-chlorophenyl)- |
| 225 | P072 | Thiourea, 1-naphthalenyl- |
| 226 | P093 | Thiourea, phenyl- |
| 227 | P185 | Tirpate |
| 228 | P123 | Toxaphene |
| 229 | P118 | Trichloromethanethiol |
| 230 | P119 | Vanadic acid, ammonium salt |
| 231 | P120 | Vanadium oxide V2O5 |
| 232 | P120 | Vanadium pentoxide |
| 233 | P084 | Vinylamine, N-methyl-N-nitroso- |
| 234 | P001 | Warfarin, and salts, when present at concentrations greater than 0.3% |
| 235 | P121 | Zinc cyanide |
| 236 | P121 | Zinc cyanide Zn(CN)2 |
| 237 | P122 | Zinc phosphide Zn3P2, when present at concentrations greater than 10% |
| 238 | P205 | Zinc, bis(dimethylcarbamodithioato-S,S′)-, |
| 239 | P205 | Ziram |
PART 2
Hazardous Waste and Hazardous Recyclable Material Chemicals
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Identification No. | Description of Hazardous Waste or Hazardous Recyclable Material | |
| 1 | U021 | [1,1-Biphenyl]-4,4-diamine |
| 2 | U073 | [1,1′-Biphenyl]-4,4′-diamine, 3,3′-dichloro- |
| 3 | U091 | [1,1′-Biphenyl]-4,4′-diamine, 3,3′-dimethoxy- |
| 4 | U095 | [1,1′-Biphenyl]-4,4′-diamine, 3,3′-dimethyl- |
| 5 | U208 | 1,1,1,2-Tetrachloroethane |
| 6 | U209 | 1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane |
| 7 | U227 | 1,1,2-Trichloroethane |
| 8 | U078 | 1,1-Dichloroethylene |
| 9 | U098 | 1,1-Dimethylhydrazine |
| 10 | U207 | 1,2,4,5-Tetrachlorobenzene |
| 11 | U085 | 1,2:3,4-Diepoxybutane |
| 12 | U069 | 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, dibutyl ester |
| 13 | U088 | 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, diethyl ester |
| 14 | U102 | 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, dimethyl ester |
| 15 | U107 | 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, dioctyl ester |
| 16 | U028 | 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, bis(2-ethylhexyl) ester |
| 17 | U202 | 1,2-Benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one, 1,1-dioxide, and salts |
| 18 | U066 | 1,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane |
| 19 | U079 | 1,2-Dichloroethylene |
| 20 | U099 | 1,2-Dimethylhydrazine |
| 21 | U109 | 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine |
| 22 | U155 | 1,2-Ethanediamine, N,N-dimethyl-N′-2-pyridinyl-N′-(2-thienylmethyl)- |
| 23 | U193 | 1,2-Oxathiolane, 2,2-dioxide |
| 24 | U142 | 1,3,4-Metheno-2H-cyclobuta[cd]pentalen-2-one, 1,1a,3,3a,4,5,5,5a,5b,6-decachlorooctahydro- |
| 25 | U234 | 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene |
| 26 | U182 | 1,3,5-Trioxane, 2,4,6-trimethyl- |
| 27 | U201 | 1,3-Benzenediol |
| 28 | U364 | 1,3-Benzodioxol-4-ol, 2,2-dimethyl-, |
| 29 | U278 | 1,3-Benzodioxol-4-ol, 2,2-dimethyl-, methyl carbamate |
| 30 | U141 | 1,3-Benzodioxole, 5-(1-propenyl)- |
| 31 | U203 | 1,3-Benzodioxole, 5-(2-propenyl)- |
| 32 | U090 | 1,3-Benzodioxole, 5-propyl- |
| 33 | U128 | 1,3-Butadiene, 1,1,2,3,4,4-hexachloro- |
| 34 | U130 | 1,3-Cyclopentadiene, 1,2,3,4,5,5-hexachloro- |
| 35 | U084 | 1,3-Dichloropropene |
| 36 | U190 | 1,3-Isobenzofurandione |
| 37 | U186 | 1,3-Pentadiene |
| 38 | U193 | 1,3-Propane sultone |
| 39 | U074 | 1,4-Dichloro-2-butene |
| 40 | U108 | 1,4-Diethyleneoxide |
| 41 | U108 | 1,4-Dioxane |
| 42 | U166 | 1,4-Naphthalenedione |
| 43 | U166 | 1,4-Naphthoquinone |
| 44 | U172 | 1-Butanamine, N-butyl-N-nitroso- |
| 45 | U031 | 1-Butanol |
| 46 | U011 | 1H-1,2,4-Triazol-3-amine |
| 47 | U186 | 1-Methylbutadiene |
| 48 | U167 | 1-Naphthalenamine |
| 49 | U279 | 1-Naphthalenol, methylcarbamate |
| 50 | U194 | 1-Propanamine |
| 51 | U111 | 1-Propanamine, N-nitroso-N-propyl- |
| 52 | U110 | 1-Propanamine, N-propyl- |
| 53 | U235 | 1-Propanol, 2,3-dibromo-, phosphate (3:1) |
| 54 | U140 | 1-Propanol, 2-methyl- |
| 55 | U243 | 1-Propene, 1,1,2,3,3,3-hexachloro- |
| 56 | U084 | 1-Propene, 1,3-dichloro- |
| 57 | U085 | 2,2-Bioxirane |
| 58 | T140 | 2,3,4,6-Tetrachlorophenol |
| 59 | U237 | 2,4-(1H,3H)-Pyrimidinedione, 5-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]- |
| 60 | T140 | 2,4,5-T |
| 61 | T140 | 2,4,5-Trichlorophenol |
| 62 | U408 | 2,4,6-Tribromophenol |
| 63 | T140 | 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol |
| 64 | U240 | 2,4-D, salts and esters |
| 65 | U081 | 2,4-Dichlorophenol |
| 66 | U101 | 2,4-Dimethylphenol |
| 67 | U105 | 2,4-Dinitrotoluene |
| 68 | U197 | 2,5-Cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione |
| 69 | U147 | 2,5-Furandione |
| 70 | U082 | 2,6-Dichlorophenol |
| 71 | U106 | 2,6-Dinitrotoluene |
| 72 | U236 | 2,7-Naphthalenedisulfonic acid, 3,3′-[(3,3′-dimethyl[1,1′-biphenyl]-4,4′-diyl)bis(azo)bis[5-amino-4-hydroxy]-, tetrasodium salt |
| 73 | U005 | 2-Acetylaminofluorene |
| 74 | U159 | 2-Butanone |
| 75 | U160 | 2-Butanone, peroxide |
| 76 | U053 | 2-Butenal |
| 77 | U074 | 2-Butene, 1,4-dichloro- |
| 78 | U143 | 2-Butenoic acid, 2-methyl-, 7-[[2,3-dihydroxy-2-(1-methoxyethyl)-3-methyl-1-oxobutoxy]methyl]-2,3,5,7a-tetrahydro-1H-pyrrolizin-1-yl ester, [1S-[1alpha(Z), 7(2S*,3R*), 7aalpha]]- |
| 79 | U042 | 2-Chloroethyl vinyl ether |
| 80 | U125 | 2-Furancarboxaldehyde |
| 81 | U058 | 2H-1,3,2-Oxazaphosphorin-2-amine, N,N-bis(2-chloroethyl)tetrahydro-, 2-oxide |
| 82 | U248 | 2H-1-Benzopyran-2-one, 4-hydroxy-3-(3-oxo-1-phenyl-butyl)-, and salts, when present at concentrations of 0.3% or less |
| 83 | U116 | 2-Imidazolidinethione |
| 84 | U168 | 2-Naphthalenamine |
| 85 | U171 | 2-Nitropropane |
| 86 | U191 | 2-Picoline |
| 87 | U002 | 2-Propanone |
| 88 | U007 | 2-Propenamide |
| 89 | U009 | 2-Propenenitrile |
| 90 | U152 | 2-Propenenitrile, 2-methyl- |
| 91 | U008 | 2-Propenoic acid |
| 92 | U118 | 2-Propenoic acid, 2-methyl-, ethyl ester |
| 93 | U162 | 2-Propenoic acid, 2-methyl-, methyl ester |
| 94 | U113 | 2-Propenoic acid, ethyl ester |
| 95 | U073 | 3,3′-Dichlorobenzidine |
| 96 | U091 | 3,3′-Dimethoxybenzidine |
| 97 | U095 | 3,3′-Dimethylbenzidine |
| 98 | U148 | 3,6-Pyridazinedione, 1,2-dihydro- |
| 99 | U157 | 3-Methylcholanthrene |
| 100 | U164 | 4(1H)-Pyrimidinone, 2,3-dihydro-6-methyl-2-thioxo- |
| 101 | U158 | 4,4′-Methylenebis(2-chloroaniline) |
| 102 | U036 | 4,7-Methano-1H-indene, 1,2,4,5,6,7,8,8-octachloro-2,3,3a,4,7,7a-hexahydro- |
| 103 | U030 | 4-Bromophenyl phenyl ether |
| 104 | U049 | 4-Chloro-o-toluidine, hydrochloride |
| 105 | U161 | 4-Methyl-2-pentanone |
| 106 | U059 | 5,12-Naphthacenedione,8-acetyl-10-[(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy)-alpha-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,8,11-trihydroxy-1-methoxy-, (8S-cis)- |
| 107 | U181 | 5-Nitro-o-toluidine |
| 108 | U094 | 7,12-Dimethylbenz[a]anthracene |
| 109 | U367 | 7-Benzofuranol, 2,3-dihydro-2,2-dimethyl- |
| 110 | U394 | A2213 |
| 111 | U001 | Acetaldehyde |
| 112 | U034 | Acetaldehyde, trichloro- |
| 113 | U187 | Acetamide, N-(4-ethoxyphenyl)- |
| 114 | U005 | Acetamide, N-9H-fluoren-2-yl- |
| 115 | U112 | Acetic acid ethyl ester |
| 116 | T140 | Acetic acid, (2,4,5-trichlorophenoxy)- |
| 117 | U240 | Acetic acid, (2,4-dichlorophenoxy)-, salts and esters |
| 118 | U144 | Acetic acid, lead(2+) salt |
| 119 | U214 | Acetic acid, thallium(1+) salt |
| 120 | U002 | Acetone |
| 121 | U003 | Acetonitrile |
| 122 | U004 | Acetophenone |
| 123 | U006 | Acetyl chloride |
| 124 | U007 | Acrylamide |
| 125 | U008 | Acrylic acid |
| 126 | U009 | Acrylonitrile |
| 127 | U096 | alpha,alpha-Dimethylbenzylhydroperoxide |
| 128 | U167 | alpha-Naphthylamine |
| 129 | U011 | Amitrole |
| 130 | U012 | Aniline |
| 131 | U136 | Arsinic acid, dimethyl- |
| 132 | U014 | Auramine |
| 133 | U015 | Azaserine |
| 134 | U010 | Azirino[2,3_3,4]pyrrolo[1,2-a]indole-4,7-dione, 6-amino-8-[[(aminocarbonyl)oxy]methyl]-1,1a,2,8,8a,8b-hexahydro-8a-methoxy-5-methyl-, [1aS-(1aalpha,8beta,8aalpha,8balpha)]- |
| 135 | U280 | Barban |
| 136 | U278 | Bendiocarb |
| 137 | U364 | Bendiocarb phenol |
| 138 | U271 | Benomyl |
| 139 | U018 | Benz[a]anthracene |
| 140 | U094 | Benz[a]anthracene, 7,12-dimethyl- |
| 141 | U016 | Benz[c]acridine |
| 142 | U157 | Benz[j]aceanthrylene, 1,2-dihydro-3-methyl- |
| 143 | U017 | Benzal chloride |
| 144 | U192 | Benzamide, 3,5-dichloro-N-(1,1-dimethyl-2-propynyl)- |
| 145 | U012 | Benzenamine |
| 146 | U328 | Benzenamine, 2-methyl- |
| 147 | U222 | Benzenamine, 2-methyl-, hydrochloride |
| 148 | U181 | Benzenamine, 2-methyl-5-nitro- |
| 149 | U014 | Benzenamine, 4,4-carbonimidoylbis[N,N-dimethyl- |
| 150 | U158 | Benzenamine, 4,4-methylenebis[2-chloro- |
| 151 | U049 | Benzenamine, 4-chloro-2-methyl-,hydrochloride |
| 152 | U353 | Benzenamine, 4-methyl- |
| 153 | U093 | Benzenamine, N,N-dimethyl-4-(phenylazo)- |
| 154 | U019 | Benzene |
| 155 | U055 | Benzene, (1-methylethyl)- |
| 156 | U017 | Benzene, (dichloromethyl)- |
| 157 | U023 | Benzene, (trichloromethyl)- |
| 158 | U247 | Benzene, 1,1-(2,2,2-trichloroethylidene)bis[4- methoxy- |
| 159 | U207 | Benzene, 1,2,4,5-tetrachloro- |
| 160 | U070 | Benzene, 1,2-dichloro- |
| 161 | U234 | Benzene, 1,3,5-trinitro- |
| 162 | U071 | Benzene, 1,3-dichloro- |
| 163 | U223 | Benzene, 1,3-diisocyanatomethyl- |
| 164 | U072 | Benzene, 1,4-dichloro- |
| 165 | U030 | Benzene, 1-bromo-4-phenoxy- |
| 166 | U105 | Benzene, 1-methyl-2,4-dinitro- |
| 167 | U106 | Benzene, 2-methyl-1,3-dinitro- |
| 168 | U037 | Benzene, chloro- |
| 169 | U239 | Benzene, dimethyl- |
| 170 | U127 | Benzene, hexachloro- |
| 171 | U056 | Benzene, hexahydro- |
| 172 | U220 | Benzene, methyl- |
| 173 | U169 | Benzene, nitro- |
| 174 | U183 | Benzene, pentachloro- |
| 175 | U185 | Benzene, pentachloronitro- |
| 176 | U061 | Benzene, 1,1-(2,2,2-trichloroethylidene)bis[4-chloro- |
| 177 | U060 | Benzene, 1,1-(2,2-dichloroethylidene)bis[4-chloro- |
| 178 | U038 | Benzeneacetic acid, 4-chloro-alpha-(4-chlorophenyl)-alpha-hydroxy-, ethyl ester |
| 179 | U035 | Benzenebutanoic acid, 4-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]- |
| 180 | U221 | Benzenediamine, ar-methyl- |
| 181 | U020 | Benzenesulfonic acid chloride |
| 182 | U020 | Benzenesulfonyl chloride |
| 183 | U021 | Benzidine |
| 184 | U022 | Benzo[a]pyrene |
| 185 | U064 | Benzo[rst]pentaphene |
| 186 | U023 | Benzotrichloride |
| 187 | U047 | beta-Chloronaphthalene |
| 188 | U168 | beta-Naphthylamine |
| 189 | U225 | Bromoform |
| 190 | U136 | Cacodylic acid |
| 191 | U032 | Calcium chromate |
| 192 | U280 | Carbamic acid, (3-chlorophenyl)-, 4-chloro-2-butynyl ester |
| 193 | U409 | Carbamic acid, [1,2-phenylenebis (iminocarbonothioyl)]bis-, dimethyl ester |
| 194 | U271 | Carbamic acid, [1-[(butylamino)carbonyl]-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]-, methyl ester |
| 195 | U372 | Carbamic acid, 1H-benzimidazol-2-yl,methyl ester |
| 196 | U238 | Carbamic acid, ethyl ester |
| 197 | U178 | Carbamic acid, methylnitroso-, ethyl ester |
| 198 | U373 | Carbamic acid, phenyl-, 1-methylethyl ester |
| 199 | U097 | Carbamic chloride, dimethyl- |
| 200 | U114 | Carbamodithioic acid, 1,2-ethanediylbis-, salts and esters |
| 201 | U389 | Carbamothioic acid, bis(1-methylethyl)-, S-(2,3,3-trichloro-2-propenyl)ester |
| 202 | U062 | Carbamothioic acid, bis(1-methylethyl)-S-(2,3-dichloro-2-propenyl) ester |
| 203 | U387 | Carbamothioic acid, dipropyl-, S-(phenylmethyl) ester |
| 204 | U279 | Carbaryl |
| 205 | U372 | Carbendazim |
| 206 | U367 | Carbofuran phenol |
| 207 | U033 | Carbon oxyfluoride |
| 208 | U211 | Carbon tetrachloride |
| 209 | U215 | Carbonic acid, dithallium(1+) salt |
| 210 | U033 | Carbonic difluoride |
| 211 | U156 | Carbonochloridic acid, methyl ester |
| 212 | U034 | Chloral |
| 213 | U035 | Chlorambucil |
| 214 | U036 | Chlordane, alpha and gamma isomers |
| 215 | U026 | Chlornaphazin |
| 216 | U037 | Chlorobenzene |
| 217 | U038 | Chlorobenzilate |
| 218 | U044 | Chloroform |
| 219 | U046 | Chloromethyl methyl ether |
| 220 | U032 | Chromic acid H2CrO4, calcium salt |
| 221 | U050 | Chrysene |
| 222 | U051 | Creosote |
| 223 | U052 | Cresol (cresylic acid) |
| 224 | U053 | Crotonaldehyde |
| 225 | U055 | Cumene |
| 226 | U246 | Cyanogen bromide (CN)Br |
| 227 | U056 | Cyclohexane |
| 228 | U129 | Cyclohexane, 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexachloro-, (1alpha,2alpha,3beta,4alpha,5alpha,6beta)- |
| 229 | U057 | Cyclohexanone |
| 230 | U058 | Cyclophosphamide |
| 231 | U059 | Daunomycin |
| 232 | U060 | DDD |
| 233 | U061 | DDT |
| 234 | U206 | D-Glucose, 2-deoxy-2-[[(methylnitrosoamino)-carbonyl]amino]- |
| 235 | U062 | Diallate |
| 236 | U063 | Dibenz[a,h]anthracene |
| 237 | U064 | Dibenzo[a,i]pyrene |
| 238 | U069 | Dibutyl phthalate |
| 239 | U075 | Dichlorodifluoromethane |
| 240 | U025 | Dichloroethyl ether |
| 241 | U027 | Dichloroisopropyl ether |
| 242 | U024 | Dichloromethoxy ethane |
| 243 | U088 | Diethyl phthalate |
| 244 | U395 | Diethylene glycol, dicarbamate |
| 245 | U028 | Diethylhexyl phthalate |
| 246 | U089 | Diethylstilbestrol |
| 247 | U090 | Dihydrosafrole |
| 248 | U102 | Dimethyl phthalate |
| 249 | U103 | Dimethyl sulfate |
| 250 | U092 | Dimethylamine |
| 251 | U097 | Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride |
| 252 | U107 | Di-n-octyl phthalate |
| 253 | U111 | Di-n-propylnitrosamine |
| 254 | U110 | Dipropylamine |
| 255 | U041 | Epichlorohydrin |
| 256 | U001 | Ethanal |
| 257 | U404 | Ethanamine, N,N-diethyl- |
| 258 | U174 | Ethanamine, N-ethyl-N-nitroso- |
| 259 | U208 | Ethane, 1,1,1,2-tetrachloro- |
| 260 | U226 | Ethane, 1,1,1-trichloro- |
| 261 | U209 | Ethane, 1,1,2,2-tetrachloro- |
| 262 | U227 | Ethane, 1,1,2-trichloro- |
| 263 | U024 | Ethane, 1,1′-[methylenebis(oxy)]bis[2-chloro- |
| 264 | U076 | Ethane, 1,1-dichloro- |
| 265 | U117 | Ethane, 1,1′-oxybis- |
| 266 | U025 | Ethane, 1,1′-oxybis[2-chloro- |
| 267 | U067 | Ethane, 1,2-dibromo- |
| 268 | U077 | Ethane, 1,2-dichloro- |
| 269 | U131 | Ethane, hexachloro- |
| 270 | U184 | Ethane, pentachloro- |
| 271 | U218 | Ethanethioamide |
| 272 | U394 | Ethanimidothioic acid, 2-(dimethylamino)-N-hydroxy-2-oxo-, methyl ester |
| 273 | U410 | Ethanimidothioic acid, N,N′-[thiobis[(methylimino)carbonyloxy]]bis-, dimethyl ester |
| 274 | U173 | Ethanol, 2,2′-(nitrosoimino)bis- |
| 275 | U395 | Ethanol, 2,2′-oxybis-, dicarbamate |
| 276 | U359 | Ethanol, 2-ethoxy- |
| 277 | U004 | Ethanone, 1-phenyl- |
| 278 | U042 | Ethene, (2-chloroethoxy)- |
| 279 | U078 | Ethene, 1,1-dichloro- |
| 280 | U079 | Ethene, 1,2-dichloro-, (E)- |
| 281 | U043 | Ethene, chloro- |
| 282 | U210 | Ethene, tetrachloro- |
| 283 | U228 | Ethene, trichloro- |
| 284 | U112 | Ethyl acetate |
| 285 | U113 | Ethyl acrylate |
| 286 | U238 | Ethyl carbamate (urethane) |
| 287 | U117 | Ethyl ether |
| 288 | U118 | Ethyl methacrylate |
| 289 | U119 | Ethyl methanesulfonate |
| 290 | U067 | Ethylene dibromide |
| 291 | U077 | Ethylene dichloride |
| 292 | U359 | Ethylene glycol monoethyl ether |
| 293 | U115 | Ethylene oxide |
| 294 | U114 | Ethylenebisdithiocarbamic acid, salts and esters |
| 295 | U116 | Ethylenethiourea |
| 296 | U076 | Ethylidene dichloride |
| 297 | U120 | Fluoranthene |
| 298 | U122 | Formaldehyde |
| 299 | U123 | Formic acid |
| 300 | U124 | Furan |
| 301 | U213 | Furan, tetrahydro- |
| 302 | U125 | Furfural |
| 303 | U124 | Furfuran |
| 304 | U206 | Glucopyranose, 2-deoxy-2-(3-methyl-3-nitrosoureido)-, D- |
| 305 | U126 | Glycidylaldehyde |
| 306 | U163 | Guanidine, N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitroso- |
| 307 | U127 | Hexachlorobenzene |
| 308 | U128 | Hexachlorobutadiene |
| 309 | U130 | Hexachlorocyclopentadiene |
| 310 | U131 | Hexachloroethane |
| 311 | U132 | Hexachlorophene |
| 312 | U243 | Hexachloropropene |
| 313 | U133 | Hydrazine |
| 314 | U098 | Hydrazine, 1,1-dimethyl- |
| 315 | U086 | Hydrazine, 1,2-diethyl- |
| 316 | U099 | Hydrazine, 1,2-dimethyl- |
| 317 | U109 | Hydrazine, 1,2-diphenyl- |
| 318 | U134 | Hydrofluoric acid |
| 319 | U134 | Hydrogen fluoride |
| 320 | U135 | Hydrogen sulfide |
| 321 | U135 | Hydrogen sulfide H2S |
| 322 | U096 | Hydroperoxide, 1-methyl-1-phenylethyl- |
| 323 | U137 | Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene |
| 324 | U140 | Isobutyl alcohol |
| 325 | U141 | Isosafrole |
| 326 | U142 | Kepone |
| 327 | U143 | Lasiocarpine |
| 328 | U144 | Lead acetate |
| 329 | U145 | Lead phosphate |
| 330 | U146 | Lead subacetate |
| 331 | U146 | Lead, bis(acetato-O)tetrahydroxytri- |
| 332 | U129 | Lindane |
| 333 | U150 | L-Phenylalanine, 4-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]- |
| 334 | U015 | L-Serine, diazoacetate (ester) |
| 335 | U147 | Maleic anhydride |
| 336 | U148 | Maleic hydrazide |
| 337 | U149 | Malononitrile |
| 338 | U071 | m-Dichlorobenzene |
| 339 | U150 | Melphalan |
| 340 | U151 | Mercury |
| 341 | U152 | Methacrylonitrile |
| 342 | U092 | Methanamine, N-methyl- |
| 343 | U029 | Methane, bromo- |
| 344 | U045 | Methane, chloro- |
| 345 | U046 | Methane, chloromethoxy- |
| 346 | U068 | Methane, dibromo- |
| 347 | U080 | Methane, dichloro- |
| 348 | U075 | Methane, dichlorodifluoro- |
| 349 | U138 | Methane, iodo- |
| 350 | U211 | Methane, tetrachloro- |
| 351 | U225 | Methane, tribromo- |
| 352 | U044 | Methane, trichloro- |
| 353 | U121 | Methane, trichlorofluoro- |
| 354 | U119 | Methanesulfonic acid, ethyl ester |
| 355 | U153 | Methanethiol |
| 356 | U154 | Methanol |
| 357 | U155 | Methapyrilene |
| 358 | U247 | Methoxychlor |
| 359 | U154 | Methyl alcohol |
| 360 | U029 | Methyl bromide |
| 361 | U045 | Methyl chloride |
| 362 | U156 | Methyl chlorocarbonate |
| 363 | U226 | Methyl chloroform |
| 364 | U159 | Methyl ethyl ketone (MEK) |
| 365 | U160 | Methyl ethyl ketone peroxide |
| 366 | U138 | Methyl iodide |
| 367 | U161 | Methyl isobutyl ketone |
| 368 | U162 | Methyl methacrylate |
| 369 | U068 | Methylene bromide |
| 370 | U080 | Methylene chloride |
| 371 | U164 | Methylthiouracil |
| 372 | U010 | Mitomycin C |
| 373 | U163 | MNNG |
| 374 | U086 | N,N′-Diethylhydrazine |
| 375 | U026 | Naphthalenamine, N,N′-bis(2-chloroethyl)- |
| 376 | U165 | Naphthalene |
| 377 | U047 | Naphthalene, 2-chloro- |
| 378 | U031 | n-Butyl alcohol |
| 379 | U217 | Nitric acid, thallium(1+) salt |
| 380 | U169 | Nitrobenzene |
| 381 | U173 | N-Nitrosodiethanolamine |
| 382 | U174 | N-Nitrosodiethylamine |
| 383 | U172 | N-Nitrosodi-n-butylamine |
| 384 | U176 | N-Nitroso-N-ethylurea |
| 385 | U177 | N-Nitroso-N-methylurea |
| 386 | U178 | N-Nitroso-N-methylurethane |
| 387 | U179 | N-Nitrosopiperidine |
| 388 | U180 | N-Nitrosopyrrolidine |
| 389 | U194 | n-Propylamine |
| 390 | U087 | O,O-Diethyl S-methyl dithiophosphate |
| 391 | U048 | o-Chlorophenol |
| 392 | U070 | o-Dichlorobenzene |
| 393 | U328 | o-Toluidine |
| 394 | U222 | o-Toluidine hydrochloride |
| 395 | U115 | Oxirane |
| 396 | U041 | Oxirane, (chloromethyl)- |
| 397 | U126 | Oxiranecarboxyaldehyde |
| 398 | U182 | Paraldehyde |
| 399 | U197 | p-Benzoquinone |
| 400 | U039 | p-Chloro-m-cresol |
| 401 | U072 | p-Dichlorobenzene |
| 402 | U093 | p-Dimethylaminoazobenzene |
| 403 | U183 | Pentachlorobenzene |
| 404 | U184 | Pentachloroethane |
| 405 | U185 | Pentachloronitrobenzene (PCNB) |
| 406 | T140 | Pentachlorophenol |
| 407 | U161 | Pentanol, 4-methyl- |
| 408 | U187 | Phenacetin |
| 409 | U188 | Phenol |
| 410 | U411 | Phenol, 2-(1-methylethoxy)-, methylcarbamate |
| 411 | T140 | Phenol, 2,3,4,6-tetrachloro- |
| 412 | T140 | Phenol, 2,4,5-trichloro- |
| 413 | T140 | Phenol, 2,4,6-trichloro- |
| 414 | U081 | Phenol, 2,4-dichloro- |
| 415 | U101 | Phenol, 2,4-dimethyl- |
| 416 | U082 | Phenol, 2,6-dichloro- |
| 417 | U048 | Phenol, 2-chloro- |
| 418 | U089 | Phenol, 4,4′-(1,2-diethyl-1,2-ethenediyl)bis-, (E)- |
| 419 | U039 | Phenol, 4-chloro-3-methyl- |
| 420 | U170 | Phenol, 4-nitro- |
| 421 | U052 | Phenol, methyl- |
| 422 | T140 | Phenol, pentachloro- |
| 423 | U132 | Phenol, 2,2′-methylenebis[3,4,6-trichloro- |
| 424 | U145 | Phosphoric acid, lead(2+) salt (2:3) |
| 425 | U087 | Phosphorodithioic acid, O,O-diethyl S-methyl ester |
| 426 | U189 | Phosphorus sulfide |
| 427 | U190 | Phthalic anhydride |
| 428 | U179 | Piperidine, 1-nitroso- |
| 429 | U170 | p-Nitrophenol |
| 430 | U192 | Pronamide |
| 431 | U066 | Propane, 1,2-dibromo-3-chloro- |
| 432 | U083 | Propane, 1,2-dichloro- |
| 433 | U027 | Propane, 2,2′-oxybis[2-chloro- |
| 434 | U171 | Propane, 2-nitro- |
| 435 | U149 | Propanedinitrile |
| 436 | T140 | Propanoic acid, 2-(2,4,5-0 trichlorophenoxy)- |
| 437 | U373 | Propham |
| 438 | U411 | Propoxur |
| 439 | U083 | Propylene dichloride |
| 440 | U387 | Prosulfocarb |
| 441 | U353 | p-Toluidine |
| 442 | U196 | Pyridine |
| 443 | U191 | Pyridine, 2-methyl- |
| 444 | U180 | Pyrrolidine, 1-nitroso- |
| 445 | U200 | Reserpine |
| 446 | U201 | Resorcinol |
| 447 | U202 | Saccharin, and salts |
| 448 | U203 | Safrole |
| 449 | U204 | Selenious acid |
| 450 | U204 | Selenium dioxide |
| 451 | U205 | Selenium sulfide |
| 452 | U205 | Selenium sulfide SeS2 |
| 453 | T140 | Silvex (2,4,5-TP) |
| 454 | U206 | Streptozotocin |
| 455 | U189 | Sulfur phosphide |
| 456 | U103 | Sulfuric acid, dimethyl ester |
| 457 | U210 | Tetrachloroethylene |
| 458 | U213 | Tetrahydrofuran |
| 459 | U216 | Thallium chloride TlCl |
| 460 | U214 | Thallium(I) acetate |
| 461 | U215 | Thallium(I) carbonate |
| 462 | U216 | Thallium(I) chloride |
| 463 | U217 | Thallium(I) nitrate |
| 464 | U218 | Thioacetamide |
| 465 | U410 | Thiodicarb |
| 466 | U153 | Thiomethanol |
| 467 | U244 | Thioperoxydicarbonic diamide[(H2N)C(S)]2S2, tetramethyl- |
| 468 | U409 | Thiophanate-methyl |
| 469 | U219 | Thiourea |
| 470 | U244 | Thiram |
| 471 | U220 | Toluene |
| 472 | U223 | Toluene diisocyanate |
| 473 | U221 | Toluenediamine |
| 474 | U389 | Triallate |
| 475 | U228 | Trichloroethylene |
| 476 | U121 | Trichloromonofluoromethane |
| 477 | U404 | Triethylamine |
| 478 | U235 | Tris(2,3-dibromopropyl) phosphate |
| 479 | U236 | Trypan blue |
| 480 | U237 | Uracil mustard |
| 481 | U176 | Urea, N-ethyl-N-nitroso- |
| 482 | U177 | Urea, N-methyl-N-nitroso- |
| 483 | U043 | Vinyl chloride |
| 484 | U248 | Warfarin, and salts, when present at concentrations of 0.3% or less |
| 485 | U239 | Xylene |
| 486 | U200 | Yohimban-16-carboxylic acid,11,17-dimethoxy-18-[(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy]-, methyl ester,(3beta,16beta,17alpha,18beta,20alpha)- |
| 487 | U249 | Zinc phosphide Zn3P2, when present at concentrations of 10% or less |
SCHEDULE 8(Subparagraph 2(2)(e)(i))
Excluded Materials
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Slags, skimmings and dross containing precious metals, copper or zinc for further refining |
| 2 | Platinum group metal (PGM) automobile catalysts |
| 3 | Electronic scrap such as circuit boards, electronic components and wires that are suitable for base or precious metal recovery |
| 4 | Brass in the form of turnings, borings and choppings |
SCHEDULE 9(Section 4)
Movement Document
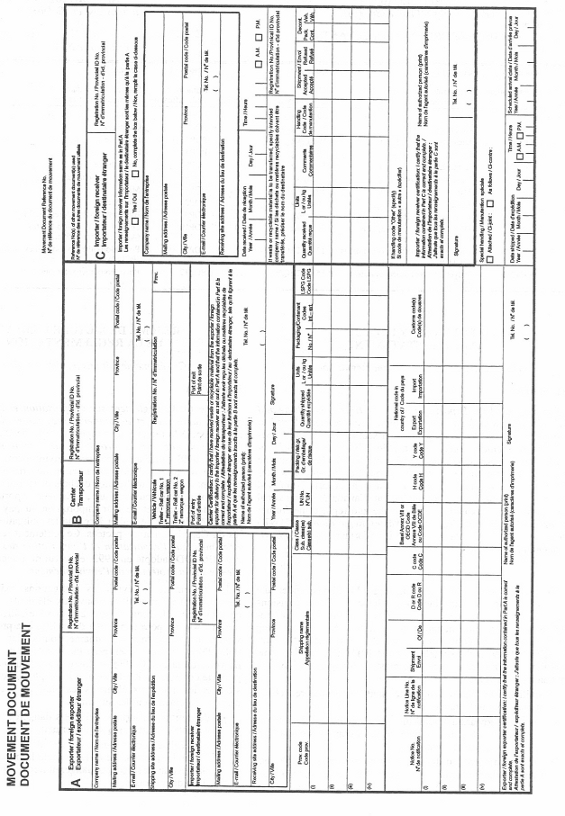
SCHEDULE 10(Paragraphs 8(k) and 38(1)(b))
Persistent Organic Pollutants
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Identification No. | Persistent Organic Pollutant | Concentration | |
| 1 | POP1 | Aldrin | 50 mg/kg |
| 2 | POP2 | Chlordane | 50 mg/kg |
| 3 | POP3 | Dieldrin | 50 mg/kg |
| 4 | POP4 | Endrin | 50 mg/kg |
| 5 | POP5 | Heptachlor | 50 mg/kg |
| 6 | POP6 | Hexachlorobenzene | 50 mg/kg |
| 7 | POP7 | Mirex | 50 mg/kg |
| 8 | POP8 | Toxaphene | 50 mg/kg |
| 9 | POP9 | Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCB) | 50 mg/kg |
| 10 | POP10 | DDT (1,1,1-Trichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane) | 50 mg/kg |
| 11 | POP11 | Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDD) | 15 µg TEQ/kg |
| 12 | POP12 | Polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDF) | 15 µg TEQ/kg |
- Date modified: