Output-Based Pricing System Regulations
SOR/2019-266
ENVIRONMENTAL VIOLATIONS ADMINISTRATIVE MONETARY PENALTIES ACT
GREENHOUSE GAS POLLUTION PRICING ACT
Registration 2019-06-28
Output-Based Pricing System Regulations
P.C. 2019-974 2019-06-27
Her Excellency the Governor General in Council, on the recommendation of the Minister of the Environment, makes the annexed Output-Based Pricing System Regulations pursuant to
(a) sections 192, 193, 198 and 256 of the Greenhouse Gas Pollution Pricing ActFootnote a; and
(b) section 5Footnote b of the Environmental Violations Administrative Monetary Penalties ActFootnote c.
Return to footnote aS.C. 2018, c. 12, s. 186
Return to footnote bS.C. 2018, c. 12, s. 196
Return to footnote cS.C. 2009, c. 14, s. 126
Interpretation
Marginal note:Definition of facility
1 (1) For the purposes of the Act and these Regulations, facility means
(a) all of the following elements that are operated in an integrated way to carry out an industrial activity:
(i) a site, or multiple sites, at which an industrial activity is carried out and the buildings, equipment, and other structures and stationary items located on those sites, and
(ii) any other sites used in conjunction with the industrial activity, including a quarry, tailings pond, wastewater lagoon or pond and landfill; or
(b) the portion of a natural gas transmission pipeline system within a province, used to transmit processed natural gas, of which the pipelines and associated installations or equipment — including compressor stations, storage installations and compressors — are operated in an integrated way, but excludes pipelines, installations or equipment that are used in the local distribution of natural gas and that are downstream of a metering station.
Marginal note:More than one person responsible — paragraph 1(a)
(2) If more than one person is responsible for the elements referred to in subparagraph (1)(a)(i) or (ii) as an owner or otherwise, including having the charge, management or control of, or as the true decision maker with respect to their operations, those elements are only included in the definition of facility if there is at least one person who is responsible for, owns, has the charge management or control of, or is the true decision maker in common.
Marginal note:More than one person responsible — paragraph 1(b)
(3) If more than one person is responsible for the pipelines and associated installations or equipment referred to in paragraph (1)(b) as an owner or otherwise, including having the charge, management or control of, or as the true decision maker with respect to the pipelines and associated installations or equipment, those pipelines and associated installations or equipment are only included in the definition of facility if there is at least one person who is responsible for, owns, has the charge management or control of, or is the true decision maker in common.
Marginal note:Single facility
(4) If two or more facilities referred to in paragraph (b) of the definition facility in subsection (1) within the same province have the same person responsible, or, if they have more than one person responsible, they have at least one person responsible in common, and are operated in an integrated way, they are deemed to be a single facility.
Marginal note:Interpretation
(5) With respect to a facility
(a) any part of a public road or of a railway track that is bordered on both sides by the facility and used to carry out the facility’s industrial activities is deemed to be part of the facility;
(b) for greater certainty, any part of a railway track that is used exclusively to carry out the facility’s industrial activities is part of the facility;
(c) for greater certainty, buildings that are used for legal, administrative or management purposes and that are not located where an industrial activity is carried out are not included for the purposes of the definition of facility; and
(d) if two or more facilities referred to in paragraph (b) of the definition facility in subsection (1), within the same province, have the same person responsible or a person responsible in common and are not operated in an integrated way, they each constitute a separate facility.
Marginal note:Definitions
2 (1) The following definitions apply in these Regulations.
- Act
Act means the Greenhouse Gas Pollution Pricing Act. (Loi)
- authorized official
authorized official means
(a) in respect of a person responsible for a covered facility who is an individual, that individual or another individual who is authorized to act on their behalf;
(b) in respect of a person responsible for a covered facility that is a corporation, an officer of the corporation who is authorized to act on its behalf; and
(c) in respect of a person responsible for a covered facility that is another entity, an individual who is authorized to act on its behalf. (agent autorisé)
- biomass
biomass means plants or plant materials, animal waste or any product made of either of these, including wood and wood products, bio-charcoal, agricultural residues, biologically derived organic matter in municipal and industrial wastes, landfill gas, bio-alcohols, pulping liquor, sludge digestion gas and fuel from animal or plant origin. (biomasse)
- boiler unit
boiler unit has the same meaning as subsection 2(1) of the Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity. (groupe chaudière)
- combustion engine
combustion engine means an engine, other than an engine that is self-propelled or designed to be propelled while performing its function, that
(a) operates according to the Brayton thermodynamic cycle and combusts fossil fuels to produce a net amount of motive power; or
(b) combusts fossil fuels and uses reciprocating motion to convert thermal energy into mechanical work. (moteur à combustion)
- combustion engine unit
combustion engine unit has the same meaning as subsection 2(1) of the Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity. (groupe moteur à combustion)
- Directive 017
Directive 017 means the directive entitled Directive 017: Measurement Requirements for Oil and Gas Operations, published by the Alberta Energy Regulator on December 13, 2018. (directive 017)
- Directive PNG017
Directive PNG017 means the directive entitled Directive PNG017: Measurement Requirements for Oil and Gas Operations, published by the Government of Saskatchewan on August 1, 2017. (directive PNG017)
- dolomitic lime
dolomitic lime means lime derived from limestone that contains equal to or more than 5% magnesium carbonate. (chaux dolomitique)
- electricity generation facility
electricity generation facility means a covered facility, other than one referred to in paragraph 5(2)(c), that generates electricity as its primary industrial activity, that is used to generate electricity from fossil fuels and that is composed of one unit or a group of units. (installation de production d’électricité)
- flaring emissions
flaring emissions means controlled emissions of gases from industrial activities as a result of the combustion of a gas or liquid stream produced at a facility, the purpose of which is not to produce useful heat. It does not include emissions from the flaring of landfill gas. (émissions de torchage)
- gaseous fuel
gaseous fuel means a fossil fuel that is gaseous at a temperature of 15°C and a pressure of 101.325kPa. (combustible gazeux)
- GHG
GHG means greenhouse gas. (version anglaise seulement)
- GHGRP
GHGRP means the document entitled Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program, Canada’s Greenhouse Gas Quantification Requirements, published by the Department of the Environment in 2017. (méthode d’ECCC)
- global warming potential
global warming potential or GWP means the global warming potential set out in column 2 of Schedule 3 to the Act for the greenhouse gas set out in column 1 of that Schedule. (PRP ou potentiel de réchauffement planétaire)
- grey cement
grey cement means a mix composed primarily of clinker that contains more than 0.5% by weight of ferric oxide, gypsum and limestone. (ciment gris)
- HFC
HFC means the hydrofluorocarbons set out in items 6 to 24 of Schedule 3 to the Act. (HFC)
- high-calcium lime
high-calcium lime means lime derived from limestone that contains less than 5% magnesium carbonate. (chaux forte en calcium)
- industrial process emissions
industrial process emissions means emissions from an industrial process that involves a chemical or physical reaction other than combustion and the purpose of which is not to produce useful heat. (émissions liées aux procédés industriels)
- industrial product use emissions
industrial product use emissions means emissions from the use of a product in an industrial process that does not involve a chemical or physical reaction and does not react in the process, including emissions from the use of sulphur hexafluoride (SF6), HFCs and PFCs as cover gases and the use of HFCs and PFCs in a foam-blowing process. (émissions associées à l’utilisation de produits industriels)
- IPCC Guidelines
IPCC Guidelines means the guidelines entitled 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories, published by the Institute for Global Environmental Strategies in 2006. (lignes directrices du GIEC)
- ISO Standard 14065
ISO Standard 14065 means the standard ISO 14065 entitled Greenhouse gases — Requirements for greenhouse gas validation and verification bodies for use in accreditation or other forms of recognition, published by the International Organization for Standardization in 2013. (norme ISO 14065)
- leakage emissions
leakage emissions means uncontrolled emissions. It does not include industrial process emissions and industrial product use emissions. (émissions dues aux fuites)
- liquid fuel
liquid fuel means a fossil fuel that is liquid at a temperature of 15°C and a pressure of 101.325kPa. (combustible liquide)
- natural gas
natural gas means a mixture of hydrocarbons — such as methane, ethane or propane — that is in a gaseous state at a temperature of 15°C and a pressure of 101.325 kPa and that is composed of at least 70% methane by volume or that has a higher heating value that is not less than 35 MJ/standard m3 and not more than 41 MJ/standard m3. It excludes landfill gas, digester gas, refinery gas, blast furnace gas, coke oven gas or gas derived through industrial processes from petroleum coke or coal, including synthetic gas. (gaz naturel)
- on-site transportation emissions
on-site transportation emissions means emissions from registered or unregistered vehicles and other machinery that are used at the facility for the transport of substances, materials, equipment or products used in a production process or for the transport of people, and that are fuelled using fuels delivered in a delivery to which an exemption certificate referred to in subparagraph 36(1)(b)(v) of the Act applies. (émissions liées au transport sur le site)
- PFC
PFC means the perfluorocarbons set out in in items 25 to 33 of Schedule 3 to the Act. (PFC)
- solid fuel
solid fuel means a fossil fuel that is solid at a temperature of 15°C and a pressure of 101.325kPa. (combustible solide)
- speciality lime
speciality lime means lime produced by passing dolomitic lime through a kiln more than once or by adding material to dolomitic lime to change its properties. (chaux spécialisée)
- specified emission type
specified emission type means an emission type listed in subsection 5(1). (type d’émissions visé)
- specified industrial activity
specified industrial activity means, with respect to a covered facility, an industrial activity specified in paragraph 5(2)(a), subparagraphs 5(2)(b)(i) or (ii), or paragraph 5(c), as the case may be. (activité industrielle visée)
- stationary fuel combustion emissions
stationary fuel combustion emissions means emissions from stationary devices that combust solid fuels, liquid fuels, gaseous fuels, or tires or asphalt shingles, whether in whole or in part, for the purpose of producing useful heat. (émissions de combustion stationnaire de combustible)
- thermal energy
thermal energy means useful thermal energy in the form of steam or hot water that is intended to be used for an industrial purpose. (énergie thermique)
- thermal energy to electricity ratio
thermal energy to electricity ratio means, in respect of a unit or equipment that generates electricity, the ratio of the total quantity of thermal energy produced to the total quantity of gross electricity generated by the unit or equipment, not including the quantities from the use of duct burners, in a calendar year and expressed in the same units of measurement. (rapport énergie thermique-électricité)
- total capacity
total capacity means, in respect of a unit or equipment that generates electricity, either
(a) the maximum continuous rating (the maximum net power that can be continuously sustained by a unit or equipment that generates electricity without the use of duct burners, at a temperature of 15˚C and a pressure of 101.325 kPa), expressed in MW of electricity, as most recently reported to a provincial authority of competent jurisdiction or to the electric system operator in the province where the unit or equipment is located, or
(b) if no report has been made, the most electricity that was generated by the unit or equipment during two continuous hours in a calendar year, expressed in MW of electricity. (capacité totale)
- unit
unit means an assembly comprised of a boiler or combustion engine and any other equipment that is physically connected to either, including duct burners and other combustion devices, heat recovery systems, steam turbines, generators and emission control devices, and that generates electricity and, if applicable, produces thermal energy from the combustion of fossil fuels. (groupe)
- venting emissions
venting emissions means controlled emissions that occur due to the design of a facility, to procedures used in the manufacture or processing of a substance or product or to pressure exceeding the capacity of the equipment at the facility. (émissions d’évacuation)
- waste emissions
waste emissions means emissions that result from waste disposal at a facility, including the landfilling of solid waste, the biological treatment or incineration of waste and the flaring of landfill gas. Waste emissions do not include emissions from the combustion of tires or asphalt shingles, whether in whole or in part, to produce useful heat or on-site transportation emissions. (émissions des déchets)
- wastewater emissions
wastewater emissions means emissions resulting from industrial wastewater and industrial wastewater treatment at a facility. (émissions des eaux usées)
- WCI Method
WCI Method means the document entitled Final Essential Requirements of Mandatory Reporting, published on December 17, 2010 by the Western Climate Initiative. (méthode de la WCI)
- white cement
white cement means a mix composed primarily of clinker that contains 0.5% or less by weight of ferric oxide, gypsum and limestone. (ciment blanc)
Marginal note:Incorporation by reference
(2) Unless otherwise indicated, a reference to any document incorporated by reference into these Regulations, except the ISO Standard 14065 and the GHGRP, is incorporated as amended from time to time.
Purpose
Marginal note:Purpose
3 These Regulations implement an output-based pricing system for industrial GHG emissions with respect to covered facilities where industrial activities are engaged in.
Overview
Marginal note:System components
4 These Regulations set out
(a) the manner in which a person responsible for a covered facility must, under Part 2 of the Act, provide a report that sets out the information with respect to the GHG emissions limit and cause the report to be verified;
(b) the methods to quantify the GHGs from a covered facility and the production from each specified industrial activity engaged in at the covered facility;
(c) the manner of determining the covered facility’s GHG emissions limit based on the facility’s production from each specified industrial activity and the applicable output-based standard; and
(d) the manner in which compensation is provided for excess emissions and surplus credits are issued.
Application
Marginal note:Quantification of GHGs
5 (1) Subject to section 22, GHGs must be quantified for the following emission types:
(a) stationary fuel combustion emissions;
(b) industrial process emissions;
(c) industrial product use emissions;
(d) venting emissions;
(e) flaring emissions;
(f) leakage emissions;
(g) on-site transportation emissions;
(h) waste emissions; and
(i) wastewater emissions.
Marginal note:Specified industrial activities
(2) Output-based standards are established under these Regulations for the following industrial activities:
(a) with respect to a covered facility referred to in paragraph (a) of the definition covered facility in section 169 of the Act, the industrial activities set out in column 1 of Schedule 1 that are engaged in at the facility;
(b) with respect to a covered facility referred to in paragraph (b) of the definition covered facility in section 169 of the Act, that in a request submitted under subsection 172(1) of the Act specified as its primary activity
(i) an industrial activity set out in column 1 of Schedule 1, the industrial activities set out in column 1 of Schedule 1 that are engaged in at the facility, or
(ii) an industrial activity other than one set out in column 1 of Schedule 1, the industrial activities – including those set out in column 1 of Schedule 1 – that are engaged in at the facility and that are specified in the notice provided by the Minister that accompanies the covered facility certificate; and
(c) with respect to a covered facility referred to in paragraph (b) of the definition covered facility in section 169 of the Act whose primary activity is something other than an industrial activity, that in a request submitted under subsection 172(1) of the Act specifies an industrial activity, the industrial activities specified in column 1 of Schedule 1 that are engaged in at the facility.
End of designation
Marginal note:Cancellation of designation
6 (1) In accordance with subsection 172(3) of the Act, the Minister may cancel the designation of a covered facility, that was designated on the condition that it would emit at least 10kt of CO2e in any of the three calendar years following the date of first production, if the covered facility has not met that condition as of December 31 of the third calendar year following that date.
Marginal note:Notice
(2) The Minister must provide notice of their intention to cancel the covered facility’s designation to the person responsible for the covered facility at least 30 days before cancelling the designation.
Marginal note:Ceasing to be a covered facility
7 (1) A facility ceases to be a covered facility under the following circumstances:
(a) it has ceased production from all specified industrial activities for five consecutive compliance periods; or
(b) the person responsible for the covered facility makes a request to that effect because it is expected that the specified industrial activities engaged in at the covered facility will cease for at least 12 consecutive months.
Marginal note:Date of cessation
(2) A covered facility ceases to be a covered facility on the following date:
(a) for the purposes of paragraph (1)(a), on December 31 of the fifth consecutive calendar year for which no production is reported in an annual report; and
(b) for the purposes of paragraph (1)(b), on the later of
(i) the 30th day following the date the Minister receives the request from the person responsible for the covered facility, or
(ii) the date the covered facility ceases production.
Marginal note:Cessation of operations during compliance period
(3) In a circumstance in which a facility ceases to be a covered facility before the end of a compliance period, the person who was responsible for that facility must comply with the obligations set out in Division 1 of Part 2 of the Act, including those set out in these Regulations, in respect of the portion of that compliance period during which it was a covered facility.
Covered Facility
Marginal note:Criteria — definition section 169 of Act
8 For the purposes of paragraph (a) of the definition covered facility in section 169 of the Act, the following criteria must be met by a facility that is located in a province or area that is set out in Part 2 of Schedule 1 to the Act:
(a) a report was made, in accordance with a Notice with respect to reporting of greenhouse gases (GHGs) published under section 46 of the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999, in respect of that facility indicating that that facility emitted a quantity of GHGs equal to 50kt or more of CO2e, as one or more facilities as defined in such a notice, for the 2014 calendar year or any subsequent calendar year; and
(b) the primary activity engaged in at the facility is
(i) any of the industrial activities set out in column 1 of Schedule 1, in a province or area, other than Saskatchewan, set out in Part 2 of Schedule 1 to the Act, or
(ii) an industrial activity set out in item 5 or 38, column 1, of Schedule 1, in Saskatchewan.
Compliance Period
Marginal note:Compliance period
9 (1) Subject to subsection (2), a period that begins on January 1 and ends on December 31 for each calendar year, starting in 2019, is specified for the definition compliance period in section 169 of the Act.
Marginal note:Partial compliance period
(2) If a facility becomes a covered facility under the Act after January 1 of a given calendar year, its specified period, for the purposes of the definition compliance period in section 169 of the Act, for that year begins on
(a) the effective date of registration that is indicated in the Minister of National Revenue’s notice under subsection 64(2) of the Act; or
(b) in the case of a covered facility in Prince Edward Island, the date of registration that is specified in the covered facility certificate issued under subsection 171(2) of the Act.
Person Responsible
Marginal note:Person responsible
10 For the purposes of these Regulations, the person responsible for a facility or a covered facility is the person who owns or is otherwise responsible for the facility or covered facility, including the person who has the charge, management or control of the facility or covered facility, or who is the true decision maker with respect to the operations of the facility or covered facility.
Annual Report
Marginal note:Content of annual report
11 (1) Subject to subsection (2) and section 16, the report that must be submitted by the person responsible for a covered facility for a compliance period under section 173 of the Act is prepared annually for each covered facility for which they are responsible and includes the information listed in Schedule 2 and the following information:
(a) in respect of a covered facility, other than one referred to in paragraph (b) or (c),
(i) the total quantity of GHGs from the covered facility during the compliance period, expressed in CO2e tonnes, as determined in accordance with section 17, and
(ii) the covered facility’s production during the compliance period, from each specified industrial activity, quantified in accordance with section 31;
(b) in respect of an electricity generation facility,
(i) the total quantity of GHGs from each unit within the covered facility during the compliance period, expressed in CO2e tonnes, as determined in accordance with section 20,
(ii) the sum of the total quantities of GHGs determined under subparagraph (i) for all units within the facility, expressed in CO2e tonnes,
(iii) the production during the compliance period by each unit within the covered facility from each of the industrial activities set out in paragraphs 38(a) to (c), column 1, of Schedule 1 that are engaged in at the unit, separately for each industrial activity, quantified in accordance with section 32, and
(iv) the sum of the production from all of the units within the covered facility during the compliance period, from all of the industrial activities set out in paragraphs 38(a) to (c), column 1, of Schedule 1;
(c) in respect of a covered facility, where the specified industrial activities are both the production of coal by mining coal deposits and, if composed of a unit or a group of units that are registered under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations, the generation of electricity,
(i) the total quantity of GHGs from the covered facility during the compliance period, which is the sum of the total quantity of GHGs from the mining of coal deposits, determined in accordance with section 17, and the total quantities of GHGs from the generation of electricity, determined in accordance with section 20, expressed in CO2e tonnes,
(ii) with respect to the production of coal by mining coal deposits, the production during the compliance period from each specified industrial activity, in accordance with section 31, and
(iii) with respect to the generation of electricity,
(A) the production during the compliance period by each unit within the covered facility from each of the industrial activities set out in paragraphs 38(a) to (c), column 1, of Schedule 1 that are engaged in at the unit, separately for each industrial activity, in accordance with section 32, and
(B) the sum of the production from all of the units within the covered facility during the compliance period, from all of the industrial activities set out in paragraphs 38(a) to (c), column 1, of Schedule 1;
(d) the quantity of GHGs emitted from the covered facility during the compliance period as determined in accordance with section 35, and, if captured and stored CO2 is being subtracted under that section, the total quantity of CO2 captured and stored in a storage project that meets the criteria in subsection 35(2);
(e) the GHG emissions limit applicable to the covered facility for the compliance period, calculated
(i) in respect of a facility referred to in paragraph (a), in accordance with section 36, 36.1 or 36.2,
(ii) in respect of a facility referred to in paragraph (b), in accordance with section 41, 41.1 or 41.2, and
(iii) in respect of a facility referred to in paragraph (c), in accordance with section 42; and
(f) the positive result (corresponding to the quantity of GHGs emitted in excess of the emissions limit) or negative result (corresponding to the difference between the quantity of GHGs emitted and the emissions limit and indicating emissions below the emissions limit) obtained under section 44 for the compliance period, expressed in CO2e tonnes.
Marginal note:Increased electricity generation capacity
(1.1) For the purposes of subparagraph (1)(a)(ii), if section 36.2 applies with respect to a covered facility, the annual report must include the gross quantity of electricity generated that is attributed the capacity added to the equipment and gross quantity of electricity generated that is attributed to the capacity of the equipment before the additional capacity was added, separately, quantified in accordance with section 31 and subsection 36.2(3).
Marginal note:Increased electricity generation capacity
(1.2) For the purposes of subparagraphs 1(b)(iii) and (iv) and (c)(iii), if section 41.2 applies with respect to an electricity generation facility, the annual report must include,
(a) for each unit whose electricity generation capacity from gaseous fuels was increased by 50 MW or more and that has a thermal energy to electricity ratio of less than 0.9, the gross amount of electricity generated during the compliance period by each unit that is attributed to the capacity added to the unit and the gross amount of electricity generated that is attributed to the capacity of the unit before the additional capacity was added, in accordance with section 32 and subsection 41.2(3), separately; and
(b) the sum, from all of the units referred to in paragraph (a), of the gross amount of electricity generated that is attributed to the capacity added to the units and of the gross amount of electricity generated that is attributed to the capacity of the units before the additional capacity was added, separately.
Marginal note:Exception — new covered facilities
(2) Paragraphs (1)(e) and (f) do not apply with respect to a report that must be submitted by the person responsible for a covered facility for which sections 36 to 42 do not apply under section 43.
Marginal note:Additional content – thermal energy
12 (1) If the person responsible for a covered facility sells thermal energy that is produced at the covered facility to other covered facilities or buys thermal energy from any other covered facility, they must include in their annual report
(a) the quantity of thermal energy, expressed in gigajoules, as well as the thermal energy’s temperature and pressure,
(i) sold to another covered facility during the compliance period, as determined by the quantity of thermal energy on sales receipts or by another objective method, or
(ii) bought from another covered facility during the compliance period, as determined by the quantity of thermal energy on sales receipts or by another objective method; and
(b) the ratio of heat from the combustion of fossil fuel to produce that thermal energy, calculated in accordance with section 34.
Marginal note:Additional content – gypsum products
(2) The person responsible for a covered facility where the specified industrial activity set out in item 10, column 1, of Schedule 1 is engaged in, must include in their annual report, the quantity, in tonnes, of each gypsum product that contains at least 70 weight percent of calcium sulphate dihydrate produced during the compliance period.
Marginal note:Additional content – hydrogen gas
(3) If a covered facility where a specified industrial activity set out in items 2, 3, 15 or 29, column 1, of Schedule 1 is engaged in produces hydrogen gas, the person responsible for the covered facility must include in their annual report the quantity of hydrogen gas produced during the compliance period, in tonnes, and the quantity of hydrogen gas sold during the compliance period, in tonnes.
Marginal note:Submission of annual report
13 (1) The person responsible for a covered facility must submit their annual report to the Minister, on or before June 1 of the calendar year following the end of the compliance period for which the annual report is prepared, along with a verification report prepared in accordance with section 52.
Marginal note:Exception
(2) Despite subsection (1), for the compliance period that ends on December 31, 2019, the annual report and the verification report must be submitted to the Minister on or before October 1, 2020.
Marginal note:Account opening
14 The account that the person responsible for the covered facility opens in accordance with subsection 186(1) of the Act is an Output-Based Pricing System account (OBPS account).
Request for Confidentiality
Marginal note:Content of request
15 A request for confidentiality submitted for the purposes of section 254 of the Act must provide the following information:
(a) the information to which the request pertains, clearly identified;
(b) the reason for the request from among those specified in paragraphs 254(a) to (c) of the Act; and
(c) the supporting justification that the information referred to in paragraph (a) has been treated as confidential by the person making the request and is not, and has never been, available to the public.
Quantification
Variation of General Rules
Marginal note:Production of petrochemical products as a by-product
16 (1) The production of a petrochemical product set out in item 17, column 1, of Schedule 1 as a by-product, at a covered facility where an industrial activity, other than one set out in that item is engaged in, is not an industrial activity covered by item 17, column 1, of Schedule 1.
Marginal note:Additional production of natural gas liquids
(2) If natural gas liquids are produced at a covered facility where a specified industrial activity set out in item 3 or 17, column 1, of Schedule 1 is engaged in, the following rules apply:
(a) for the purposes of section 17, the person responsible for the covered facility must quantify the GHGs from the production of natural gas liquids in accordance with the methods applicable to the industrial activity set out in item 3 or 17, as the case may be, column 1, of Schedule 1; and
(b) for the purposes of sections 31, 36 and 36.2, the industrial activity set out in item 4, column 1, of Schedule 1 is deemed not to be engaged in at the covered facility.
Marginal note:Additional production of hydrogen gas
(3) If hydrogen gas is produced at a covered facility where a specified industrial activity set out in item 2, 3, 15 or 29, column 1, of Schedule 1 is engaged in, the following rules apply:
(a) for the purposes of section 17, the person responsible for the covered facility must quantify the GHGs from the production of hydrogen gas in accordance with the method applicable to the industrial activity set out in item 2, 3, 15 or 29, as the case may be, column 1, of Schedule 1; and
(b) for the purposes of sections 31, 36 and 36.2, the industrial activities set out in items 6 and 17, column 1, of Schedule 1 are deemed not to be engaged in at the covered facility.
Marginal note:Additional production of metal tubes
(4) If metal tubes are produced at a covered facility where a specified industrial activity set out in item 19 or 20, column 1, of Schedule 1 is engaged in, the following rules apply:
(a) for the purposes of section 17, the person responsible for the covered facility must quantify the GHGs from the production of metal tubes in accordance with the method applicable to the industrial activity set out in item 19 or 20, as the case may be, column 1, of Schedule 1; and
(b) for the purposes of sections 31, 36 and 36.2, the industrial activity set out in item 22, column 1, of Schedule 1 is deemed not to be engaged in at the covered facility.
Marginal note:Additional production of lime
(5) If lime is produced at a covered facility where a specified industrial activity set out in item 20, column 1, of Schedule 1 is engaged in, the following rules apply:
(a) for the purposes of section 17, the person responsible for the covered facility must quantify the GHGs from the production of lime in accordance with the method applicable to the industrial activity set out in item 20, column 1, of Schedule 1; and
(b) for the purposes of sections 36 and 36.2, the industrial activity set out in item 8, column 1, of Schedule 1 is deemed not to be engaged in at the covered facility.
Marginal note:Additional production of electricity
(6) If electricity is produced at a covered facility where a specified industrial activity set out in item 20, column 1, of Schedule 1 is engaged in, the following rules apply:
(a) for the purposes of section 17, the person responsible for the covered facility must quantify the GHGs from the generation of electricity in accordance with the method applicable to the industrial activity set out in item 20, column 1, of Schedule 1; and
(b) for the purposes of section 36, the industrial activity set out in item 38, column 1, of Schedule 1 is deemed not to be engaged in at the covered facility.
Marginal note:Pyrometallurgical smelting of zinc and lead
(7) If zinc and lead are pyrometallurgically smelted at a covered facility where a specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 23(b), column 1, of Schedule 1 is engaged in, the following rules apply:
(a) for the purposes of section 17, the person responsible for the covered facility must quantify the GHGs from the pyrometallurgical smelting of zinc and lead in accordance with the method applicable to the industrial activity set out in paragraph 23(b), column 1, of Schedule 1; and
(b) for the purposes of sections 31, 36 and 36.2, the industrial activity set out in paragraph 23(c), column 1, of Schedule 1 is deemed not to be engaged in at the covered facility.
Marginal note:Additional production of precious metals
(8) If gold, silver, platinum or palladium is produced at a covered facility where a specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 26(d), column 1, of Schedule 1 is engaged in, the following rules apply:
(a) for the purposes of section 17, the person responsible for the covered facility must quantify the GHGs from the production of those metals in accordance with the method applicable to the industrial activity set out in paragraph 26(d), column 1, of Schedule 1; and
(b) for the purposes of sections 31, 36 and 36.2, the industrial activity set out in paragraph 26(c) or (f), column 1, of Schedule 1 is deemed not to be engaged in at the covered facility.
Marginal note:Additional production of petrochemicals
(9) If a petrochemical product referred to in item 17, column 1, of Schedule 1 is produced at a covered facility where a specified industrial activity set out in item 3 or 4, column 1, of Schedule 1 is engaged in, the following rules apply:
(a) for the purposes of section 17, the person responsible for the covered facility must quantify the GHGs from the production of that petrochemical in accordance with the method applicable to the industrial activity set out in item 3 or 4, as the case may be, column 1, of Schedule 1; and
(b) for the purposes of sections 31, 36 and 36.2, the industrial activity set out in item 17, column 1, of Schedule 1 is deemed not to be engaged in at the covered facility.
Marginal note:Additional production of precious metals
(10) If silver, platinum or palladium is produced at a covered facility where a specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 26(f), column 1, of Schedule 1 is engaged in, the following rules apply:
(a) for the purposes of section 17, the person responsible for the covered facility must quantify the GHGs from the production of those metals in accordance with the method applicable to the industrial activity set out in paragraph 26(f), column 1, of Schedule 1; and
(b) for the purposes of sections 31, 36 and 36.2, the industrial activity set out in paragraph 26(c), column 1, of Schedule 1 is deemed not to be engaged in at the covered facility.
Quantification of GHGs
Marginal note:Total GHGs
17 (1) Subject to subsection (5) and section 18, the total quantity of GHGs from a covered facility other than an electricity generation facility, during a compliance period, expressed in CO2e tonnes, is determined by the formula

where
- Ej
- is the quantity of each GHG type “j” from the covered facility during a compliance period, for each specified emission type, determined in accordance with subsections (2) to (4) or section 19;
- GWPj
- is the global warming potential of the GHG type “j”;
- i
- is the ith specified emission type, where “i” goes from 1 to n and where n is the number of the facility’s specified emission types; and
- j
- is the jth GHG type, where “j” goes from 1 to m and where m is the number of greenhouse gases.
Marginal note:Quantity of each GHG
(2) The quantity of a GHG type “j” from a covered facility during a compliance period for a specified emission type “i” is the sum of the following quantities:
(a) in the case of a GHG from industrial activities set out in items 1 to 37, column 1, of Schedule 1 and also set out in column 2 of the table to the Part of Schedule 3 that is applicable to those industrial activities, from a specified emission type set out in column 1 of that table, the quantities of that GHG calculated in accordance with the requirements of the methods set out in column 3 of that table for that emission type and GHG;
(b) in the case of a GHG from those industrial activities but not set out in column 2 of the table to the part of Schedule 3 that applies to those activities or from a specified emission type not set out in column 1, the quantities of that GHG calculated in accordance with
(i) the GHGRP or the WCI Method, if those methods are applicable to the facility’s industrial activities, or
(ii) the IPCC Guidelines, if the methods referred to in subparagraph (i) are not applicable; and
(c) in the case of a GHG from industrial activities not set out in column 1 of Schedule 1, the quantities of that GHG calculated in accordance with
(i) the GHGRP or the WCI Method, if those methods are applicable to the facility’s industrial activities, or
(ii) the IPCC Guidelines, if the methods referred to in subparagraph (i) are not applicable.
Marginal note:Sampling, analysis and measurement requirements
(3) The sampling, analysis and measurement requirements that apply are
(a) if a GHG is quantified in accordance with paragraph 2(a), the requirements set out in column 4 of the table to the applicable Part of Schedule 3 for the specified emission type set out in column 1 and the GHG set out in column 2; or
(b) if a GHG is quantified in accordance with paragraph 2(b) or (c), the requirements specified in the methods or guidelines used for the purposes of those paragraphs.
Marginal note:Missing data
(4) For the purposes of subsection (2), if, for any reason beyond the control of the person responsible for a covered facility, the data required to quantify the GHGs from a facility are missing for a given period of a compliance period, replacement data for the given period must be calculated in accordance with
(a) if a GHG is quantified in accordance with paragraph 2(a), the requirements set out in column 5 of the table to the applicable Part of Schedule 3 for the specified emission type in column 1 and the GHG set out in column 2; or
(b) if a GHG is quantified in accordance with paragraph 2(b) or (c), the requirements specified in the methods or guidelines used for the purposes of those paragraphs.
Marginal note:Biomass — exclusion of CH4 and N2O
(5) For the purposes of the determination made under subsection (1), the quantities of CH4 and N2O generated from stationary devices that combust biomass for the purpose of producing useful heat are subtracted from the quantities of CH4 and N2O calculated in accordance with subsections (2) to (4) for stationary fuel combustion emissions.
Marginal note:Additional generation of electricity
18 For the purposes of section 17, the quantities of the GHGs for specified emission types from the generation of electricity using fossil fuels by a covered facility — other than covered facilities referred to in paragraphs 5(2)(c) and 11(1)(c) — are calculated in accordance with the methods that are applicable to any of the industrial activities engaged in at the covered facility.
Marginal note:Covered facility referred to in paragraph 5(2)(c)
19 The quantities of the GHGs for specified emission types from a covered facility referred to in paragraph 5(2)(c) are calculated in accordance with
(a) the GHGRP or the WCI Method, if those methods are applicable; or
(b) the IPCC Guidelines, if the methods referred to in paragraph (a) are not applicable.
Marginal note:Total emissions per unit — electricity
20 (1) Subject to subsection (6), with respect to an electricity generation facility, the total quantity of GHGs from each unit within a facility, during a compliance period, expressed in CO2e tonnes, is determined by the formula

where
- Ej
- is the quantity of each GHG type “j” from the unit during a compliance period for each specified emission type determined in accordance with subsections (2) to (5);
- GWPj
- is the global warming potential of the GHG type “j”;
- i
- is the ith specified emission type, where “i” goes from 1 to n and where n is the unit’s number of specified emission types;
- j
- is the jth GHG type, where “j” goes from 1 to m and where m is the number of greenhouse gases.
Marginal note:Quantity of each GHG
(2) The quantity of a GHG type “j” generated by a unit during a compliance period for a specified emission type “i” is the sum of
(a) for CO2, CH4 and N2O from stationary fuel combustion emissions, the quantity of each of those GHGs calculated in accordance with section 1 of Part 38 of Schedule 3 for each unit;
(b) for a GHG set out in column 2 of the table to Part 38 of Schedule 3 for a specified emission type set out in column 1, the quantities of that GHG calculated in accordance the requirements of the methods set out in column 3 of that table for that emission type; and
(c) for a GHG not referred to in paragraph (a) or (b), the quantity of that GHG calculated in accordance with
(i) the GHGRP or the WCI Method, if those methods are applicable, or
(ii) the IPCC Guidelines, if the methods referred to in subparagraph (i) are not applicable.
Marginal note:Apportioning GHGs
(3) For the purposes of paragraph (2)(b) or (c), if the GHGs for a specified emission type referred to in subsection (2) can only be quantified for the facility as a whole, the quantity of those GHGs must be apportioned to the facility’s units on the basis of each unit’s total generation of electricity relative to the facility’s total generation of electricity.
Marginal note:Sampling, analysis and measurement requirements
(4) The sampling, analysis and measurement requirements that apply are
(a) for a GHG quantified in accordance with paragraph (2)(a), the requirements referred to in section 2 of Part 38 of Schedule 3 for each of the units;
(b) for a GHG quantified in accordance with paragraph (2)(b), the requirements set out in column 4 of the table to Part 38 of Schedule 3 for the specified emission type set out in column 1; and
(c) for a GHG quantified in accordance with paragraph (2)(c), the requirements set out in the methods or guidelines used for the purpose of that paragraph.
Marginal note:Missing data
(5) For the purposes of subsection (2), if, for any reason beyond the control of the person responsible for a covered facility, the data required to quantify GHGs from a unit are missing for a given period of a compliance period, replacement data for the given period must be calculated in accordance with
(a) if a GHG is quantified in accordance with paragraph (2)(a), the requirements set out in section 3 of Part 38 of Schedule 3;
(b) if the GHG is quantified in accordance with paragraph (2)(b), the requirements set out in column 5 of the table to Part 38 of Schedule 3 for the specified emission type set out in column 1; and
(c) if the GHGs are quantified in accordance with paragraph (2)(c), the requirements set out in the methods or guidelines used for the purpose of that paragraph.
Marginal note:Biomass — exclusion of CH4 and N2O
(6) For the purposes of the determination made under subsection (1), the quantity of CH4 and N2O generated from stationary devices that combust biomass for the purpose of producing useful heat are subtracted from the quantity of CH4 and N2O calculated in accordance with subsections (2) to (5) for stationary fuel combustion emissions.
Marginal note:Hybrid configuration
21 For the purposes of section 20, if a combustion engine unit and a boiler unit share the same steam turbine, the GHGs from those units are quantified as follows:
(a) with respect to a combustion engine unit, the quantification provisions apply to the assembly comprised of combustion engines and any other equipment connected to them, including the steam turbine that it shares with the boiler unit; and
(b) with respect to a boiler unit, the quantification provisions apply to the assembly comprised of boilers and any other equipment connected to them, including the steam turbine that it shares with the combustion engine unit.
Marginal note:Biomass — exclusion of CO2
22 (1) CO2 from biomass is not included in the quantity of CO2 calculated in accordance with subsections 17(2) to (4) or 20(2) to (5).
Marginal note:Methane
(2) CH4 from venting or leakage emissions from an industrial activity set out in item 1, 2, 4 or 5, column 1, of Schedule 1 is not included in the quantity of CH4 calculated in accordance with subsections 17(2) to (4).
Marginal note:De minimis
23 (1) Subject to subsection (2), the quantity of a GHG for any specified emission type does not need to be included in the determination made under subsections 17(2) to (4) or 20(2) to (5) if the quantity of the GHG, expressed in CO2e tonnes, does not exceed 0.5% of the total quantity of GHGs determined under subsection 17(1) or 20(1).
Marginal note:Limit
(2) The sum of the quantities of GHGs not included under subsection (1) cannot exceed 0.5% of the total quantity of GHGs determined under subsection 17(1) or 20(1).
Marginal note:Rounding
24 Any result from a calculation under subsections 17(1) and 20(1) is to be rounded to the nearest whole number and, if the number is equidistant between two whole consecutive numbers, to the higher number.
Marginal note:Continuous Emissions Monitoring System
25 For the purposes of the GHGRP, if a CEMS is used to quantify GHGs, the person responsible for the covered facility must ensure that the system complies with the requirements of the Reference Method for Source Testing: Quantification of Carbon Dioxide Releases by Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems from Thermal Power Generation, published by the Department of the Environment in June 2012.
Permit To Use an Alternative Method
Marginal note:Alternative method
26 Despite sections 17 and 20, the person responsible for a covered facility may use a method other than a method or guideline required under those sections if they have a permit issued in accordance with section 28.
Marginal note:Application for permit
27 (1) An application for a permit must be submitted to the Minister and must contain the information referred to in Schedule 4.
Marginal note:Certification
(2) The application must be accompanied by a certification, dated and signed by the person responsible for the covered facility or by their authorized official, stating that the information contained in the application is accurate and complete.
Marginal note:Conditions of issuance
28 (1) The Minister must issue the permit to use a quantification method other than one prescribed in these Regulations if
(a) the person responsible for the covered facility establishes that, at the time of the application, it is not technically or economically feasible to use the prescribed method or guideline;
(b) the person responsible for the covered facility demonstrates that the quantification method being proposed is at least as rigorous as the prescribed method or guideline and provides equivalent results to those that would have been obtained from the prescribed method or guideline;
(c) the person responsible for the covered facility provides a plan describing measures that will be taken to enable the use of the prescribed method or guideline and the implementation period for that plan, up to a maximum of two years; and
(d) the requested term of the permit does not exceed the period for which the permit is necessary.
Marginal note:Period of validity
(2) The term of the permit must not exceed 24 months.
Marginal note:Grounds for refusing permit
(3) The Minister must refuse to issue a permit if the Minister has reasonable grounds to believe that the applicant has provided false or misleading information in support of their application.
Marginal note:Renewal
(4) The permit can only be renewed once.
Marginal note:Application for renewal
29 (1) The application for the renewal of a permit must include the information referred to in Schedule 4 and an explanation of the reasons why the plan that was submitted in the initial permit application was not implemented within the period identified in the initial application. The application for renewal must be submitted to the Minister at least 90 days before the expiration of the permit.
Marginal note:Conditions for renewal
(2) The Minister must renew the permit if the conditions set out in subsection 28(1) are met.
Marginal note:Grounds for revocation
30 (1) The Minister must revoke the permit if the Minister has reasonable grounds to believe that the permit holder has provided false or misleading information.
Marginal note:Notice of revocation
(2) Before revoking a permit, the Minister must provide the permit holder with
(a) written reasons for the revocation; and
(b) an opportunity to make written representations in respect of the revocation.
Marginal note:Date of revocation
(3) The revocation of a permit is effective 30 days after the day on which the Minister notifies the permit holder.
Quantification of Production for Specified Industrial Activities
Marginal note:General rule
31 (1) Subject to subsection (4) and section 16, the production from a covered facility, other than an electricity generation facility, from each specified industrial activity during a compliance period is quantified
(a) in the case of production from a specified industrial activity set out in items 1 to 37, column 1, of Schedule 1, in the units of measurement set out in column 2 of Schedule 1 for that industrial activity, and in accordance with any requirements set out in the applicable part of Schedule 3;
(b) in the case of production from a specified industrial activity set out in paragraphs 38(a) to (c), column 1, of Schedule 1, the production is
(i) quantified in whole for the compliance period in accordance with the requirements set out in sections 6 and 7 of Part 38 of Schedule 3, or
(ii) not quantified, in whole or in part, for the compliance period; and
(c) in the case of production from a specified industrial activity not set out in column 1 of Schedule 1, in the units of measurement provided in the request under subsection 172(1) of the Act.
Marginal note:Measuring device
(2) Any measuring device that is used to determine a quantity for the purposes of these Regulations must be
(a) installed, operated, maintained and calibrated in accordance with the manufacturer’s specifications or any applicable generally recognized national or international industry standard; and
(b) maintained to be accurate within ± 5%.
Marginal note:Engineering estimates or mass balance
(3) If it is not possible to directly measure production using a measuring device, it may be quantified using engineering estimates or mass balance.
Marginal note:Transitional provision
(4) For the 2019 calendar year
(a) the production quantified in accordance with paragraphs (1)(a) and (c), must be accurate within ± 5%; and
(b) the production referred to in paragraph (1)(b) may be quantified by the person responsible for the regulated facility in accordance with subsection 9(2) and section 103 of the Greenhouse Gas Emissions Information Production Order, as it read before August 1, 2019.
Marginal note:Electricity generation facility
32 (1) Subject to subsection (2), the gross electricity generated during a compliance period by each unit within the electricity generation facility, from each of the industrial activities set out in paragraphs 38(a) to (c), column 1, of Schedule 1 that is engaged in at the unit, is determined as follows:
(a) if a unit uses only one fossil fuel to generate electricity, in accordance with subsection 4(1) and section 5 of Part 38 of Schedule 3; and
(b) if a unit uses a mixture of fossil fuels or a mixture of biomass and fossil fuels to generate electricity, in accordance with subsections 4(2) and (3) and section 5 of Part 38 of Schedule 3.
Marginal note:Choose not to quantify
(2) The person responsible for the electricity generation facility may choose not to quantify part or all of the quantity of electricity generated from one unit or a group of units.
Marginal note:Rounding
33 Any result from a calculation under subsection 31(1) or section 32 is rounded to three significant figures.
Ratio of Heat
Marginal note:Ratio of heat
34 (1) The ratio of heat from the combustion of fossil fuels during a compliance period is
(a) equal to 1 when the thermal energy is produced from the combustion of only fossil fuels;
(b) for a covered facility not specified in paragraph (c), determined by the following formula when the thermal energy is produced from the combustion of both fossil fuels and biomass:
HF/(HF + B)
where
- HF
- is determined by the formula

where
- QFi
- is the quantity of fossil fuel of type “i” combusted in the facility for the generation of thermal energy during the compliance period, determined in accordance with subsection 7(2) of Part 38 of Schedule 3,
- HHVi
- is the higher heating value of the fossil fuel of type “i” combusted in the facility during the compliance period for the generation of thermal energy in accordance with sections 2.C.1 and 2.C.3 of the GHGRP, and
- i
- is the ith fossil fuel type combusted in the facility during the compliance period, where “i” goes from 1 to n and where n is the number of types of fossil fuels combusted, and
- B
- is determined by the formula
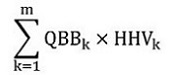
where
- QBBk
- is the quantity of biomass fuel type “k” combusted in the facility for the generation of thermal energy during the compliance period, determined in accordance with subsection 7(2) of Part 38 of Schedule 3 and the WCI Method WCI.214,
- HHVk
- is the higher heating value for biomass fuel type “k” combusted in the facility during the compliance period for the generation of thermal energy in accordance with sections 2.C.1 and 2.C.3 of the GHGRP and the WCI Method WCI.214, and
- k
- is the kth biomass fuel type combusted in the facility during the compliance period, where “k” goes from 1 to m and where m is the number of types of biomass fuels combusted; and
(c) for an electricity generation facility, determined by the following formula when the thermal energy is produced from the combustion of both fossil fuels and biomass:
HF/(HF + B)
where
- HF
- is determined by the formula

where
- QFi
- is the quantity of fossil fuel of type “i” combusted in the facility for the generation of thermal energy during the compliance period, determined in accordance with subsection 4(3) of Part 38 of Schedule 3,
- HHVi
- is the higher heating value of the fossil fuel of type “i” combusted in the facility during the compliance period for the generation of thermal energy determined in accordance with subsection 24(1) of the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations, and
- i
- is the ith fossil fuel type combusted in the facility during the compliance period, where “i” goes from 1 to n and where n is the number of types of fossil fuel combusted, and
- B
- is determined by the formula
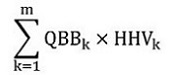
where
- QBBk
- is the quantity of biomass fuel type “k” combusted in the facility for the generation of thermal energy during the compliance period, determined in accordance with subsection 4(3) of Part 38 of Schedule 3,
- HHVk
- is the higher heating value for biomass fuel type “k” combusted in the facility during the compliance period for the generation of thermal energy determined in accordance with subsection 24(1) of the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations, and
- k
- is the kth biomass fuel type combusted in the facility during the compliance period, where “k” goes from 1 to m and where m is the number of types of biomass fuels combusted.
Marginal note:Default ratio of heat
(2) Despite paragraph (1)(b) or (c), if, for any reason beyond the control of the person responsible for a covered facility, the data required to quantify the ratio of heat from the combustion of fossil fuels are missing for a given period during the 2019 calendar year, 1 can be used as the ratio of heat from the combustion of fossil fuels.
Emission of GHGs
Marginal note:Calculation
35 (1) The person responsible for a covered facility must determine the quantity of GHGs that are emitted from the covered facility during a compliance period in accordance with the formula
A – B
where
- A
- is the total quantity of GHGs from the covered facility, expressed in CO2e tonnes, during the compliance period,
(a) in the case of a facility referred to in paragraph 11(1)(a), determined in accordance with section 17,
(b) in the case of a facility referred to in paragraph 11(1)(b), corresponding to the sum referred to in subparagraph 11(1)(b)(ii), and
(c) in the case of a facility referred to in paragraph 11(1)(c), corresponding to the sum referred to in subparagraph 11(1)(c)(i); and
- B
- is the quantity of CO2 captured at the covered facility that is stored during the compliance period in a storage project, determined using the quantification method described in section 1 of the GHGRP, expressed in CO2e tonnes.
Marginal note:Storage requirements
(2) For the purposes of the description of B in subsection (1), the quantity of CO2 may only be included if it has been permanently stored in a storage project that meets the following criteria:
(a) the geological site into which the CO2 is injected is
(i) a deep saline aquifer for the sole purpose of storage of CO2, or
(ii) a depleted oil reservoir for the purpose of enhanced oil recovery; and
(b) the quantity of CO2 stored for the purposes of the project is captured, transported and stored in accordance with the laws applicable to Canada or a province or applicable to the United States or one of its states.
Marginal note:Biomass
(3) The quantity of CO2 from biomass is not included in the amount determined for B in subsection (1).
Marginal note:Deemed emission of CO2
(4) For greater certainty, the quantity of CO2 from a covered facility that has been captured but has not been permanently stored in a storage project that meets the requirements of subsection (2) is deemed to have been emitted by the covered facility and is included in the quantity of GHGs that are emitted from the covered facility.
Emissions Limit
Marginal note:General rule
36 (1) Subject to subsection (2) and sections 16, 36.1, 36.2 and 42, the person responsible for a covered facility, other than an electricity generation facility, must determine the GHG emissions limit that applies to that covered facility for each compliance period, expressed in CO2e tonnes, in accordance with the formula
The summation of the products of Ai and Bi for each specified industrial activity “i”
where
- Ai
- is the covered facility’s production from each specified industrial activity “i” during the compliance period, quantified in accordance with section 31;
- Bi
- is the following output-based standard applicable to the specified industrial activity “i”, as the case may be:
(a) for a specified industrial activity set out in column 1 of Schedule 1 and for which an output-based standard is set out in column 3, that standard,
(b) for a specified industrial activity set out in column 1 of Schedule 1 and for which column 3 sets out that an output-based standard must be calculated in accordance with section 37, the output-based standard calculated in accordance with that section, or
(c) for any specified industrial activity not set out in column 1 of Schedule 1, the output based standard calculated in accordance with section 37; and
- i
- is the ith specified industrial activity where “i” goes from 1 to n where n is the total number of specified industrial activities engaged in at the covered facility.
Marginal note:Ethanol production
(2) For the purposes of subsection (1), the person responsible for a covered facility must not include the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 13(b), column 1, of Schedule 1 unless the covered facility also includes the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 13(a), column 1. The covered facility is deemed to not be engaged in the specified industrial activity set out in item 32, column 1, of that Schedule.
Marginal note:Oilseeds
(3) For the purposes of subsection (1), the person responsible for a covered facility where the specified industrial activity set out in item 31, column 1, of Schedule 1 is engaged in may, for the 2019 calendar year, quantify their production in finished oilseed products and use an output-based standard of 0.0431 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement of production, instead of the production metric set out in column 2 and the output-based standard set out in column 3.
Marginal note:Greater certainty — fertilizer
(4) For greater certainty, if the industrial activity set out in paragraph 29(b), column 1, of Schedule 1 and also either of the industrial activities set out in paragraph 29(c) or (d), column 1, are engaged in at the covered facility, the output-based standard applicable to the industrial activity set out in paragraph 29(b), column 1, applies and the output-based standard applicable to the industrial activity set out in paragraph 29(c) or (d), applies as the case may be.
Marginal note:Output-based standard
(5) For the purposes of subsection (1), if an output-based standard must be calculated, it is calculated once, except in the situation referred to in subsection 39.
Marginal note:New electricity production — gaseous fuel
36.1 (1) Despite subsection 36(1), if a covered facility — other than one referred to in subsection 16(6) — begins generating electricity on or after January 1, 2021 and meets the following criteria, the person responsible for the covered facility must apply, for the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 38(c), column 1, of Schedule 1, the applicable output-based standard, in accordance with subsection (2), for each compliance period, as of the compliance period during which the covered facility began generating electricity:
(a) the electricity is generated from gaseous fuel by equipment that is designed to operate at a thermal energy to electricity ratio of less than 0.9; and
(b) the covered facility has an electricity generation capacity equal to or greater than 50 MW from that equipment.
Marginal note:Decreasing output-based standard
(2) The output-based standard that applies to the industrial activity referred to in paragraph 38(c), column 1, of Schedule 1 is, as the case may be
(a) 370 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for the 2021 compliance period,
(b) 329 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for the 2022 compliance period,
(c) 288 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for the 2023 compliance period,
(d) 247 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for the 2024 compliance period,
(e) 206 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for the 2025 compliance period,
(f) 164 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for the 2026 compliance period,
(g) 123 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for the 2027 compliance period,
(h) 82 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for the 2028 compliance period,
(i) 41 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for the 2029 compliance period, and
(j) 0 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for the 2030 compliance period and subsequent compliance periods.
Marginal note:Increased capacity of electricity generation
36.2 (1) Subject to subsections 16(1) to (5) and (7) to (10), if, on or after January 1, 2021, a covered facility — other than a covered facility referred to in subsection 16(6) — increases its electricity generation capacity from gaseous fuels by 50 MW or more and that increased capacity is from equipment that has a thermal energy to electricity ratio of less than 0.9 and that was added after that date or has had its capacity increased and, the person responsible for the covered facility must determine the covered facility’s GHG emissions limit for each compliance period, as of the compliance period during which the increase occurred, in accordance with subsection (2).
Marginal note:Different output-based standard
(2) The GHG emissions limit that applies to the covered facility for a compliance period, expressed in CO2e tonnes, is determined in accordance with the formula

where
- Ai
- is the production during the compliance period, quantified in accordance with section 31
(a) from each specified industrial activity “i”, except the industrial activity set out in paragraph 38(c), column 1, of Schedule 1, and
(b) from the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 38(c), column 1, of Schedule 1, except from equipment referred to in the descriptions C, E and F;
- Bi
- is the output-based standard applicable to the specified industrial activity “i”, as the case may be:
(a) for a specified industrial activity set out in column 1 of Schedule 1 and for which an output-based standard is set out in column 3, that standard,
(b) for a specified industrial activity set out in column 1 of Schedule 1 and for which column 3 sets out that an output-based standard must be calculated in accordance with section 37, the output-based standard calculated in accordance with that section, or
(c) for any specified industrial activity not set out in column 1 of Schedule 1, the output based standard calculated in accordance with section 37; and
- C
- is the gross amount of electricity generated during the compliance period by the equipment that started generating electricity from gaseous fuels on or after January 1, 2021, designed to operate at a thermal energy to electricity ratio of less than 0.9, from the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 38(c), column 1, of Schedule 1, quantified in accordance with section 31;
- D
- is the output-based standard set out in subsection 36.1(2) that is applicable to the compliance period in question;
- E
- is, for equipment with increased electricity generation capacity and has a thermal energy to electricity ratio of less than 0.9, other than equipment referred to in the description of C, the gross amount of electricity generated during the compliance period attributed to the capacity added to the equipment, from the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 38(c), column 1, of Schedule 1, quantified in accordance with section 31 and subsection (3);
- F
- is, for equipment with increased electricity generation capacity and has a thermal energy to electricity ratio of less than 0.9, other than equipment referred to in the description of C, the gross amount of electricity generated during the compliance period attributed to the capacity of the equipment before the additional capacity was added, from the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 38(c), column 1, of Schedule 1, quantified in accordance with section 31 and subsection (3); and
- G
- is the output-based standard set out in column 3 of part 38 of Schedule 1, that is applicable to the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 38(c), column 1; and
- i
- is the ith specified industrial activity where “i” goes from 1 to n where n is the total number of the covered facility’s specified industrial activities.
Marginal note:Apportionment of electricity generation
(3) For the purposes of the descriptions of E and F in subsection (2), the gross amount of electricity generated by the equipment referred to in those descriptions is apportioned, using engineering estimates, to the equipment’s capacity added to the equipment and to the capacity of the equipment before the additional capacity was added, based on the ratio of the amount of its increased capacity to its total capacity, taking into account the increased capacity.
Marginal note:Increased capacity — rule
(4) For the purposes of subsection (1), the electricity generation capacity of a facility increases by 50 MW or more for a calendar year as of the day on which its electricity generation capacity is 50 MW greater than its electricity generation capacity on December 31, 2020. For greater certainty, any increase in capacity is cumulative.
Marginal note:Presumption
36.3 If the output-based standard set out in subsection 36.1(2) applies to a covered facility’s generation of electricity for a given compliance period, it continues to apply for all subsequent compliance periods even if
(a) for the purposes of section 36.1, the covered facility is not generating electricity from gaseous fuel or the equipment in question has a thermal energy to electricity ratio that is equal to or greater than 0.9; or
(b) for the purposes of section 36.2, the equipment in question is not generating electricity from gaseous fuel or has a thermal energy to electricity ratio that is equal to or greater than 0.9.
Marginal note:Calculated output-based standard
37 (1) Subject to subsection (3) and sections 38 to 40, the output-based standard that is applicable to a specified industrial activity of a covered facility for which an output-based standard must be calculated is determined by the formula
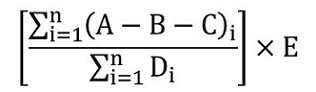
where
- A
- is the total quantity of GHGs from the covered facility for reference year “i”, determined in accordance with section 17, expressed in CO2e tonnes;
- B
- is the allocation for net thermal energy for reference year “i” and is
(a) determined by the formula
0.062 CO2e tonnes/gigajoules × (M − N) × O
where
- M
- is the quantity of thermal energy produced by the covered facility that was sold to another covered facility in reference year “i”, determined by the quantity of thermal energy on sales receipts or by another objective method, expressed in gigajoules,
- N
- is the quantity of thermal energy that was bought from another covered facility in reference year “i”, as determined by the quantity of thermal energy on sales receipts or by another objective method, expressed in gigajoules, and
- O
- is the ratio of heat from the combustion of fossil fuels to produce thermal energy for reference year “i” and is
(a) if M is greater than N, the ratio of heat determined under section 34 for reference year “i” for the covered facility, or
(b) if M is less than N, the ratio of heat determined under section 34 for reference year “i” for the covered facility from which the thermal energy was purchased, or
(b) 0 for all reference years if the quotient obtained by dividing the sum of the results determined under paragraph (a) for each reference year “i” by the number of reference years is less than the quotient obtained by dividing the result of the following formula by the number of reference years:
0.015 × A
- C
- the total quantity of GHGs from all specified industrial activities engaged in at the facility, for reference year “i”, other than the industrial activity for which the output-based standard is being calculated, determined in accordance with sections 17 and 18, for each of those activities;
- D
- is the production from a covered facility from the industrial activity for which the output-based standard is being calculated, for reference year “i”, quantified in accordance with section 31;
- E
- is the GHG emissions reduction factor applicable to the specified industrial activity for which the output-based standard is being calculated and is
(a) 95% for a specified industrial activity set out in paragraphs 7(c), 8(b) and (c), and 20(d), column 1, of Schedule 1,
(b) 90% for a specified industrial activity set out in item 22 and paragraphs 23(a) and 29(d), column 1, of Schedule 1, and
(c) 80% for all other specified industrial activities; and
- i
- is the ith reference year, where “i” goes from 1 to n and where n is the number of reference years, determined in accordance with subsection (2).
Marginal note:Reference years
(2) The reference years applicable to the specified industrial activities set out in column 1 of Schedule 1 that are engaged in at a covered facility for which an emissions limit is calculated for a compliance period are
(a) except for a covered facility referred to in paragraph (b), at the choice of the responsible person, either,
(i) the 2017 and 2018 calendar years, or
(ii) the compliance period; or
(b) for a covered facility for which an emissions limit is being calculated for the first time but for which the person responsible has submitted an annual report under these Regulations for a previous compliance period without including the information referred to in paragraphs 11(1)(e) and (f) in accordance with subsection 11(2), either
(i) the two calendar years preceding the compliance period for which the emissions limit is calculated, if the data are available for those years,
(ii) the calendar year preceding the compliance period for which the emissions limit is calculated, if the data are not available for the two calendar years referred to in (i), or
(iii) the compliance period for which the emissions limit is being calculated, if that data are not available for those preceding calendar years.
Marginal note:Thermal energy allocation
(3) For the purposes of subsection (1), if an output-based standard must be calculated with respect to a covered facility for more than one specified industrial activity, the allocation for net thermal energy can only be deducted from one of those calculations.
Marginal note:Rounding
(4) The result from the calculation under subsection (1) is rounded to three significant figures.
Marginal note:Exception — steel
38 (1) For the purposes of the description of C in subsection 37(1), if the specified industrial activity for which the output-based standard is being calculated is the industrial activity set out in paragraph 20(d), column 1, of Schedule 1 and the covered facility is also engaged in the generation of electricity, the quantity of GHGs from the generation of electricity attributable to the industrial activity set out in that item are not included in the total quantity of GHGs determined for C.
Marginal note:For greater certainty
(2) For greater certainty, the quantity of GHGs from the generation of electricity attributable to the specified industrial activities set out in paragraphs 20(a) to (c), column 1, of Schedule 1 are included in the total quantity of emissions determined for C.
Marginal note:Recalculation of output-based standard
39 If an output-based standard applicable to a specified industrial activity set out in column 1 of Schedule 1 was calculated for a compliance period that started after January 1 of a given year, it must be recalculated in accordance with subsection 37(1) for the next compliance period.
Marginal note:Covered facility — subparagraph 5(2)(b)(ii)
40 Despite section 37, for a specified industrial activity set out in subparagraph 5(2)(b)(ii), other than a specified industrial activity set out in column 1 of Schedule 1, the information provided in the request under subsection 172(1) of the Act is used for the calculation of the output-based standard under subsection 37(1).
Marginal note:Electricity
41 (1) Subject to subsection (2) and sections 41.1 and 41.2, the person responsible for an electricity generation facility must determine the GHG emissions limit that applies to the electricity generation facility for each compliance period, expressed in CO2e tonnes, in accordance with the formula

where
- Aj
- is the gross amount of electricity generated during the compliance period quantified in accordance with section 32, for each unit “i” within the electricity generation facility, from each of the industrial activities set out in paragraphs 38(a) to (c), column 1, of Schedule 1 that is engaged in at the electricity generation facility;
- Bj
- is the output-based standard applicable to each specified industrial activity set out in paragraphs 38(a) to (c), column 1, of Schedule 1 that are engaged in at each unit “i” and that is set out in column 3;
- i
- is the ith unit, where “i” goes from 1 to n and where n is the total number of units within the electricity generation facility generating electricity using fossil fuels; and
- j
- is the jth activity, where “j” goes from 1 to m and where m is the total number of industrial activities set out in paragraphs 38(a) to (c), column 1, of Schedule 1 that are engaged in at the facility.
Marginal note:Output-based standard — exception
(2) The output-based standard applicable to the industrial activity set out in paragraph 38(a), column 1, of Schedule 1 applies to a unit if it generates electricity using liquid or gaseous fuel and it
(a) is registered under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations; and
(b) used solid fuel to generate electricity in 2018.
Marginal note:New electricity production facility — gaseous fuel
41.1 (1) If an electricity generation facility begins generating electricity on or after January 1, 2021 and meets the following criteria, the person responsible for the covered facility must determine the GHG emissions limit that applies to the facility for each compliance period as of the compliance period during which the electricity generation began, in accordance with subsection (2):
(a) at least one unit within the facility generates electricity from gaseous fuels; and
(b) at least one of the units that generates electricity from gaseous fuels within the facility has an electricity generation capacity equal to or greater than 50 MW and is designed to operate at a thermal energy to electricity ratio of less than 0.9.
Marginal note:Different output-based standard
(2) The GHG emissions limit that applies to the electricity generation facility, expressed in CO2e tonnes, is determined for each compliance period in accordance with the formula
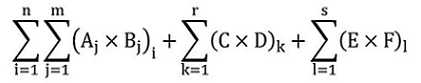
where
- Aj
- is, for each unit “i” within the electricity generation facility that generates electricity from solid fuel or liquid fuel, the gross amount of electricity generated during the compliance period, quantified in accordance with section 32, from the specified industrial activities set out in paragraph 38(a) and (b), column 1, of Schedule 1 that are engaged in at the unit;
- Bj
- the output-based standard applicable to each specified industrial activity set out in paragraphs 38(a) and (b), column 1, of Schedule 1 that the are engaged in at each unit “i” and that is set out in column 3;
- C
- is, for each unit “k” within the electricity generation facility that generates electricity from gaseous fuels, that has an electricity generation capacity equal to or greater than 50 MW and that has a thermal energy to electricity ratio of less than 0.9, the gross amount of electricity generated during the compliance period in accordance with section 32, from the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 38(c), column 1, of Schedule 1 that is engaged in at the unit;
- D
- is the output-based standard applicable and is
(a) 370 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for compliance period 2021,
(b) 329 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for compliance period 2022,
(c) 288 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for compliance period 2023,
(d) 247 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for compliance period 2024,
(e) 206 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for compliance period 2025,
(f) 164 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for compliance period 2026,
(g) 123 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for compliance period 2027,
(h) 82 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for compliance period 2028,
(i) 41 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for compliance period 2029, and
(j) 0 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, for compliance period 2030 and subsequent compliance periods; and
- E
- is, for each unit “l” within the electricity generation facility that generate electricity from gaseous fuels, has an electricity generation capacity of less than 50 MW or a thermal energy to electricity ratio of 0.9 or greater, the gross amount of electricity generated during the compliance period from the specified industrial activity engaged in at the unit set out in paragraph 38(c), column 1, of Schedule 1, quantified in accordance with section 32;
- F
- the output-based standard applicable to each specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 38(c), column 1, of Schedule 1 that are engaged in at each unit “i” and that is set out in column 3;
- i
- is the ith unit, where “i” goes from 1 to n and where n is the total number of units within the electricity generation facility generating electricity using solid fuel or liquid fuel;
- j
- is the jth activity, where “j” goes from 1 to m and where m is the total number of industrial activities set out in paragraphs 38(a) to (b), column 1, of Schedule 1 that is engaged in at the electricity generation facility;
- k
- is the kth unit, where “k” goes from 1 to r and where r is the total number of units within the electricity generation facility, generating electricity using gaseous fuel, that have an electricity generation capacity equal to or greater than 50 MW and a thermal energy to electricity ratio of less than 0.9;
- l
- is the lth unit, where “l” goes from 1 to s and where s is the total number of units within the electricity generation facility, generating electricity using gaseous fuel, that have an electricity generation capacity of less than 50 MW or a thermal energy to electricity ratio of 0.9 or greater.
Marginal note:Increased capacity of electricity generation
41.2 (1) If, on or after January 1, 2021, an electricity generation facility’s electricity generation capacity from gaseous fuels increases by 50 MW or more and that increased capacity is from a unit designed to operate at a thermal energy to electricity ratio of less than 0.9, the person responsible for the covered facility must determine the GHG emissions limit that applies to the facility for each compliance period, as of the compliance period during which the increase occurred, in accordance with subsection (2).
Marginal note:Different output-based standard
(2) The GHG emissions limit that applies to the electricity generation facility, expressed in CO2e tonnes, is determined for each compliance period in accordance with the formula
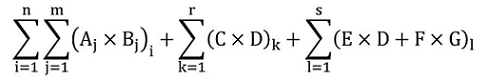
where
- Aj
- is the gross amount of electricity generated during the compliance period, quantified in accordance with section 32, for each of the following units:
(a) for each unit “i” within the electricity generation facility, from each of the specified industrial activities set out in paragraphs 38(a) and (b), column 1, of Schedule 1 that are engaged in at the electricity generation facility,
(b) from the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 38(c), column 1, of Schedule 1 that is engaged in at the unit, for each unit “i” within an electricity generation facility that
(i) was generating electricity prior to the facility’s increase in electricity generation capacity, except units referred to in the description of E or F, and
(ii) that began generating electricity on or after January 1, 2021, if the unit has an electricity generation capacity of less than 50 MW or designed to operate at a thermal energy to electricity ratio equal to or greater than 0.9;
- Bj
- the output-based standard applicable to each of the specified industrial activities set out in paragraphs 38(a) to (c), column 1, of Schedule 1 that are engaged in at each unit “i” and that is set out in column 3;
- C
- is, for each unit “k” within the electricity generation facility that started generating electricity from gaseous fuels on or after January 1, 2021, that has an electricity generation capacity equal to or greater than 50 MW and that has a thermal energy to electricity ratio of less than 0.9, the gross amount of electricity generated during the compliance period quantified in accordance with section 32, from the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 38(c), column 1, of Schedule 1 that is engaged in at the electricity generation facility;
- D
- is the output-based standard set out in the description of D in subsection 41.1(2) that is applicable to the compliance period in question;
- E
- is, for each unit “l” that generated electricity from gaseous fuels within the electricity generation facility prior to the facility’s increase in electricity generation capacity and whose electricity generation capacity was increased by 50 MW or more and whose thermal energy to electricity ratio of less than 0.9, the gross amount of electricity generated during the compliance period that is attributed to the capacity added to a unit, from the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 38(c), column 1, of Schedule 1, quantified in accordance with section 32 and subsection (3);
- F
- is, for each unit “l” that generated electricity from gaseous fuels within the electricity generation facility prior to the facility’s increase in electricity generation capacity and whose electricity generation capacity was increased by 50 MW or more and whose thermal energy to electricity ratio of less than 0.9, the gross amount of electricity generated during the compliance period that is attributed to the capacity of the unit before the additional capacity was added, from the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 38(c), column 1, of Schedule 1, quantified in accordance with section 32 and subsection (3);
- G
- is the output-based standard applicable to the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 38(c), column 1, of Schedule 1 and set out in column 3;
- i
- is the ith unit, where “i” goes from 1 to n and where n is the total number of units within the electricity generation facility generating electricity using fossil fuels, except units referred to in the description of k and l;
- j
- is the jth activity, where “j” goes from 1 to m and where m is the total number of industrial activities set out in paragraphs 38(a) to (c), column 1, of Schedule 1 that are engaged in at the electricity generation facility;
- k
- is the kth unit, where “i” goes from 1 to r and where r is the total number of units within the electricity generation facility that started generating electricity from gaseous fuels on or after January 1, 2021, that have an electricity generation capacity equal to or greater than 50 MW and that have a thermal energy to electricity ratio of less than 0.9; and
- l
- is the lth unit, where “i” goes from 1 to s and where s is the total number of units that generated electricity from gaseous fuels within the electricity generation facility prior to the facility’s increase in electricity generation capacity and whose electricity generation capacity was increased by 50 MW or more and whose thermal energy to electricity ratio of less than 0.9.
Marginal note:Apportionment of electricity generation
(3) For the purposes of the descriptions of E and F in subsection (2), the gross amount of electricity generated by a unit referred to those descriptions is apportioned, using engineering estimates, to the capacity added to the unit and to the capacity of the unit before the additional capacity was added, based on the ratio of its increased capacity to its total capacity, taking into account the increased capacity.
Marginal note:Increased capacity — rule
(4) For the purposes of subsection (1), the electricity generation capacity, from gaseous fuels, of an electricity generation facility increases by 50 MW or more for a calendar year as of the day on which its electricity generation capacity is 50 MW greater than its electricity generation capacity on December 31, 2020. For greater certainty, any increase in a unit’s capacity is cumulative.
Marginal note:Presumption
41.3 For the purposes of sections 41.1 and 41.2, if the output-based standard set out in subsection 41.1(2) applies to a unit or group of units for a compliance period for the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 38(c), column 1, of Schedule 1, that output-based standard will continue to apply to the unit or group of units even if the unit or group of units is not producing electricity from gaseous fuel or has a thermal energy to electricity ratio that is equal to or greater than 0.9.
Marginal note:Coal and electricity
42 The person responsible for a covered facility where the specified industrial activities engaged in are both the production of coal by mining coal deposits and the generation of electricity and that is comprised of a unit or a group of units that are registered under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations must calculate the GHG emissions limit that applies to the covered facility for each compliance period by adding the emissions limit obtained in subsection 36(1) for that compliance period for the specified industrial activity set out in item 25, column 1, of Schedule 1 and the emissions limit determined under section 41 or 41.2 for that compliance period for the specified industrial activities set out in paragraphs 38(a) to (c), column 1, of that Schedule, expressed in CO2e tonnes.
Marginal note:New covered facilities
43 (1) If, on January 1 of a compliance period, a covered facility has not completed two calendar years of production following the date of first production, sections 36 to 42 do not apply to the covered facility for that compliance period.
Marginal note:Primary activity
(2) Subsection (1) only applies to a covered facility whose primary activity is a specified industrial activity.
Marginal note:New electricity generation facility
(3) Subsection (1) does not apply to an electricity generation facility that begins generating electricity on or after January 1, 2021.
Marginal note:Date of production
(4) For the purposes of subsection (1), to determine the date of first production for a covered facility all industrial activities that the facility has previously been or is currently engaged in must be taken into account.
Assessment
Marginal note:Assessment of emissions against emissions limit
44 (1) The person responsible for a covered facility must assess for each compliance period the quantity of GHGs that are emitted from the covered facility during the applicable compliance period against its applicable GHG emissions limit in accordance with the formula
A – B
where
- A
- is the quantity of GHGs that are emitted from the covered facility during the compliance period, expressed in CO2e tonnes, determined in accordance with subsection 35; and
- B
- is the applicable GHG emissions limit for the covered facility for the compliance period, expressed in CO2e tonnes, determined in accordance with sections 36, 36.1, 36.2, 41, 41.1, 41.2 or 42.
Marginal note:New covered facilities
(2) If, on January 1 during a compliance period, the covered facility has not completed two calendar years of production following the date of first production, subsection (1) does not apply to the covered facility for that compliance period.
Marginal note:Primary activity
(3) Subsection (2) only applies to a covered facility whose primary activity is a specified industrial activity.
Marginal note:New electricity generation facility
(4) Subsection (2) does not apply to an electricity production facility that begins generating electricity on or after January 1, 2021.
Marginal note:Date of production
(5) For the purposes of subsection (2), to determine the date of first production for a covered facility all industrial activities that the facility has previously been or is currently engaged in must be taken into account.
Records
Marginal note:Content
45 (1) The person responsible for a covered facility must keep a record of the following information with respect to the covered facility and each unit within it, if applicable, for each compliance period
(a) the total quantity of GHGs from each specified emission type;
(b) the quantity of each GHG from each specified emission type;
(c) all data used for a calculation made under these Regulations, for each specified emission type and GHG, including data used to estimate missing data;
(d) all sampling, analysis and measurement data for each specified emission type and GHG;
(e) the methods used to quantify, sample, analyze and measure each specified emission type;
(f) the methods and data used to quantify production;
(g) the procedural changes made in data collection and calculations and changes to measuring devices used to quantify GHGs or production;
(h) the quantity of each GHG not included in the total quantity of GHGs under section 23 and the relevant specified emission type;
(i) the quantities of CO2 captured, transported or stored expressed in tonnes and the data used to quantify that CO2;
(j) the output-based standard calculated under section 37 for each specified industrial activity and all methods and data used to calculate that output-based standard;
(k) documents that demonstrate the maintenance, calibration and operation of measuring devices was done in accordance with these Regulations;
(l) if the person responsible for a covered facility sells thermal energy that was produced at the covered facility to other covered facilities or buys thermal energy from other covered facilities,
(i) the sales invoices or receipts for the thermal energy bought or sold,
(ii) the name of any covered facility from which thermal energy is bought or to which it is sold and the covered facility certificate number that was issued to the covered facility, and
(iii) the methods and data used to quantify the quantity of thermal energy bought or sold and the data in relation to the ratio of heat from the combustion of fossil fuel;
(m) any errors or omissions identified and the measures taken to correct them, with all supporting data and documentation;
(n) a copy of all permits issue pursuant to section 28; and
(o) documentation that demonstrates that the CO2 was captured, transported and stored in accordance with the laws of Canada or a province or of the United States or one of its States.
Marginal note:CEMS
(2) For each compliance period during which a person responsible for the covered facility uses a continuous emissions monitoring system, they must comply with the record keeping requirements set out in section 8 of the Reference Method for Source Testing: Quantification of Carbon Dioxide Releases by Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems from Thermal Power Generation, published by the Department of the Environment in 2012.
Marginal note:Availability of information
(3) The record must be kept within 30 days after the information becomes available.
Marginal note:Electronic submission
46 (1) Any information that is required to be provided to the Minister under these Regulations with respect to a covered facility must be submitted electronically in the form and format specified by the Minister and must bear the electronic signature of the person responsible for the covered facility or of their authorized official.
Marginal note:Provision on paper
(2) If the Minister has not specified an electronic form and format or if it is not feasible to submit the information in accordance with subsection (1) because of circumstances beyond the control of the person responsible for the covered facility or their authorized official, the information must be submitted on paper, signed by the person responsible for the covered facility or their authorized official, in the form and format specified by the Minister. However, if no form and format has been so specified, it may be in any form and format.
Marginal note:Retention of information
47 (1) The person responsible for a covered facility must retain any record kept under section 45 and a copy of information submitted to the Minister under these Regulations, including any calculations, measurements and other data on which the records or information is based.
Marginal note:Location of records
(2) The records, copies and documents must be retained at the principal place of business in Canada of the person responsible for the covered facility or, on notification to the Minister, at any other place in Canada where they can be inspected.
Marginal note:Relocation of records
(3) If the records, copies or supporting documents are moved, the person responsible for the covered facility must notify the Minister, in writing, of the civic address of the new location within 30 days after the day of the move.
Marginal note:Obligation to notify
48 The person responsible for the covered facility must notify the Minister, in writing, within 30 days after a change to any of the following:
(a) the administrative information set out in sections 1 and 2 of Schedules 2 and 5 and provided to the Minister under these Regulations;
(b) the facility’s perimeter;
(c) the information provided in an application for registration under subsection 171(1) of the Act or in a request for designation under subsection 172(1) of the Act; or
(d) the information provided in an application for a permit under section 27, if the permit is still valid.
Verification Report
Marginal note:Verification body
49 (1) To be authorized to verify an annual report or a corrected report, a third party must
(a) meet the following accreditation requirements:
(i) it is accredited as a verification body to the ISO Standard 14065 by the Standards Council of Canada, the American National Standards Institute or any other accreditation organization that is a member of the International Accreditation Forum,
(ii) it has a scope of accreditation that is sufficient to verify the annual report or the corrected report, and
(iii) it is not suspended by an accreditation organization that issued an accreditation; and
(b) conduct the verification in accordance with ISO Standard 14064-3 published by the International Organization for Standardization in 2006 entitled Greenhouse gases — Part 3: Specification with guidance for the validation and verification of greenhouse gas assertions or published in 2019 entitled Greenhouse gases -- Part 3: Specification with guidance for the verification and validation of greenhouse gas statements, based on their accreditation, by applying methods that allow it to make a determination to a reasonable level of assurance, as defined in that standard, on whether
(i) a material discrepancy exists with respect to the total quantity of GHGs and production reported in the annual report from each specified industrial activity that is used in the calculation of the emissions limit, and
(ii) in the verification body’s opinion, the annual report or corrected report was prepared in accordance with these Regulations.
Marginal note:Material discrepancy
(2) For the purpose of the verification of a covered facility’s annual report or corrected report, a material discrepancy exists when
(a) with respect to GHGs from covered facilities that have emitted a quantity of GHGs of less than 50 kt of CO2e during the compliance period,
(i) in the case of each error or omission respecting GHGs that is identified during the verification and that may be quantified, the result, expressed as a percent, determined by the formula, is equal to or greater than 8%:
A/B × 100
where
- A
- is the absolute value of the overstatement or understatement resulting from the error or omission expressed in CO2e tonnes, and
- B
- is the total quantity of GHGs reported in the annual report or corrected report, expressed in CO2e tonnes, and
(ii) in the case of the aggregate of all errors and omissions respecting GHGs, that are identified during the verification and that may be quantified, the result, expressed as a percent, determined by the formula, is equal to or greater than 8%:
A/B × 100
where
- A
- is the absolute value of the net result of all overstatements and understatements resulting from all errors and omissions, expressed in CO2e tonnes, and
- B
- is the total quantity of GHGs reported in the annual report or corrected report, expressed in CO2e tonnes;
(b) with respect to GHGs from covered facilities that emitted a quantity of GHGs of equal to or greater than 50 kt of CO2e but less than 500 kt during the compliance period,
(i) in the case of each error or omission respecting GHGs that is identified during the verification and that may be quantified, the result, expressed as a percent, determined by the formula, is equal to or greater than 5%:
A/B × 100
where
- A
- is the absolute value of the overstatement or understatement resulting from the error or omission expressed in CO2e tonnes, and
- B
- is the total quantity of GHGs reported in the annual report or corrected report, expressed in CO2e tonnes, and
(ii) in the case of the aggregate of all errors and omissions respecting GHGs that are identified during the verification and that may be quantified, the result, expressed as a percent, determined by the formula, is equal to or greater than 5%:
A/B × 100
where
- A
- is the absolute value of the net result of all overstatements and understatements resulting from all errors and omissions, expressed in CO2e tonnes, and
- B
- is the total quantity of GHGs reported in the annual report or corrected report, expressed in CO2e tonnes;
(c) with respect to GHGs from covered facilities that emitted a quantity of GHGs that is equal to or greater than 500 kt of CO2e during the compliance period,
(i) in the case each single error or omission respecting GHGs that is identified during the verification and that may be quantified, the result, expressed as a percent, determined by the formula, is equal to or greater than 2%:
A/B × 100
where
- A
- is the absolute value of the overstatement or understatement resulting from an error or omission expressed in CO2e tonnes, and
- B
- is the total quantity of GHGs reported in the annual report or corrected report, expressed in CO2e tonnes, and
(ii) in the case of the aggregate of all errors and omissions respecting GHGs that are identified during the verification and that may be quantified, the result, expressed as a percent, determined by the formula, is equal to or greater than 2%:
A/B × 100
where
- A
- is the absolute value of the net result of all overstatements and understatements resulting from all errors and omissions, expressed in CO2e tonnes, and
- B
- is the total quantity of GHGs reported in the annual report or corrected report, expressed in CO2e tonnes; and
(d) with respect to the production from each specified industrial activity that is used in the calculation of the emissions limit, in the case an error or omission respecting the quantification of the production that is identified during the verification and may be quantified, the result, expressed as a percent, determined by the formula is equal to or greater than 5%:
A/B × 100
where
- A
- is the absolute value of the overstatement or understatement resulting from an error or omission expressed in the applicable unit of measure, and
- B
- is the production from specified industrial activity in question that is reported in the annual report or corrected report, expressed in the applicable unit of measure.
Marginal note:Conflict of interest
50 (1) The person responsible for a covered facility must ensure that no real or potential conflict of interest exists between the person and the accredited verification body, including members of the verification team and any individual or corporate entity associated with the verification body, that is a threat to or compromises the verification body’s impartiality that cannot be effectively managed.
Marginal note:Consecutive verifications
(2) The person responsible must not have their annual report verified by a verification body that has verified six consecutive annual reports prepared under these Regulations with respect to the same covered facility, unless three years have elapsed since the last of those reports was verified. However, a corrected report may be verified by the verification body within those three years if it is in relation to an annual report verified by that verification body.
Marginal note:Facility visit
51 (1) Subject to subsection (2), the person responsible for a covered facility must ensure that their covered facility is visited by an accredited verification body in the following situations:
(a) it is the initial verification of the covered facility under these Regulations or by the verification body;
(b) at least three calendar years have passed since the verification body has verified an annual report for the covered facility;
(c) in the last annual report for the covered facility prepared under these Regulations, the verification body made a determination
(i) that a material discrepancy exists with respect to the total quantity of GHGs or production reported in the annual report from a specified industrial activity that is used in the calculation of the emissions limit, or
(ii) that the annual report was not prepared in accordance with these Regulations; or
(d) the verification body is of the opinion a site visit is required.
Marginal note:Other visits
(2) If buildings that are used for legal, administrative or management purposes are not located where an industrial activity is carried out, the person responsible for a covered facility must ensure that the verification body visits those buildings if data or information necessary for verifying an annual report or a corrected report is kept in those buildings.
Marginal note:Content of verification report
52 A verification report is prepared by a verification body in relation to the annual report and corrected report, if applicable, and any related data and information, and includes the information contained in Schedule 5.
Compensation and Compliance Units
Minister’s Intervention
Marginal note:Determination
53 (1) Despite what is set out in a covered facility’s annual report or corrected report for a compliance period, the Minister may establish the emissions limit or determine the quantity of GHGs emitted from the covered facility for the compliance period if
(a) there is a material discrepancy with respect to the total GHGs from the covered facility or the production from one or more specified industrial activity used in the calculation of the emissions limit reported in the annual report or the corrected report; or
(b) the verification statement referred to in paragraph 3(n) of Schedule 5 indicates that it is impossible to determine that a material discrepancy does not exist, or that the annual report or corrected report was prepared in accordance with these Regulations.
Marginal note:Criteria
(2) The Minister is to establish the emissions limit or determine the quantity of GHGs emitted from the covered facility for the compliance period, as the case may be, based on the following:
(a) the annual report and verification report for the compliance period and, if necessary, any previous reports;
(b) any report made in accordance with the Notice with respect to reporting of greenhouse gases (GHGs) published under the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999;
(c) information in respect of industrial activities, in Canada or in other jurisdictions, similar to those of the covered facility, that allows for the determination of production amounts for the covered facility;
(d) accepted quantification methods used to calculate the GHGs from facilities engaged in the same industrial activity or in the same type of industrial activity as the covered facility; and
(e) any other information provided, on the Minister’s request, by the person responsible for the covered facility or the verifier.
Marginal note:Notice
(3) The Minister must notify the person responsible for the covered facility, in writing, of their determination with respect to the emissions limit or the quantity of GHGs emitted from the covered facility established for the compliance period.
Compensation and Issuance of Surplus Credits
Marginal note:Excess emissions
54 For the purposes of subsection 174(1) of the Act, if, during a compliance period, a covered facility emits GHGs in a quantity that exceeds the applicable emissions limit, the compensation to be provided by the person responsible for that facility is to be established based on the quantity of GHGs, expressed in CO2e tonnes, that was emitted in excess of the emissions limit as reported in the annual report submitted for the compliance period or the Minister’s determination under section 53, as the case may be.
Marginal note:Excess emissions charge payment
55 (1) Any compensation that is provided by means of an excess emissions charge payment must be made electronically to the Receiver General for Canada.
Marginal note:Surplus credits
(2) Any compensation that is provided by means of a remittance of surplus credits must be made in the manner set out in section 70.
Marginal note:Other compliance units
(3) Any compensation that is provided by means of a remittance of compliance units other than surplus credits must be made in the manner set out in section 71.
Marginal note:Minimum percentage — charge
56 A minimum of 25% of the compensation that is required under section 174 of the Act must be provided by means of an excess emissions charge payment.
Marginal note:Regular-rate compensation deadline
57 (1) For the purposes of subsection 174(3) of the Act, the regular-rate compensation deadline is December 15 of the calendar year in which the related annual report must be submitted.
Marginal note:Exception
(1.1) Despite subsection (1), for the compliance period that ends on December 31, 2019, the regular-rate compensation deadline is April 15, 2021.
Marginal note:Increased-rate compensation deadline
(2) For the purposes of subsection 174(4) of the Act, the increased-rate compensation deadline is February 15 of the calendar year following the deadline under subsection (1).
Marginal note:Exception
(2.1) Despite subsection (2), for the compliance period that ends on December 31, 2019, the increased-rate compensation deadline is June 15, 2021.
Marginal note:Notice referred to in subsection 53(3)
(3) However, if a notice of determination under subsection 53(3) is issued after October 31 of the year in which the related annual report is due
(a) the regular-rate compensation deadline is 45 days after the day on which the notice is issued; and
(b) the increased-rate compensation deadline is 60 days after the day on which the regular-rate compensation deadline under paragraph (a) expires.
Marginal note:Compensation information
58 A person that is responsible for a covered facility must, at the time compensation is provided, submit to the Minister the following information:
(a) the covered facility certificate number;
(b) the provision of the Act under which the compensation is being provided;
(c) the compliance period for which compensation is being provided;
(d) the quantity of GHGs emitted in excess of the emissions limit in respect of which the compensation is provided, expressed in CO2e tonnes;
(e) the details of any excess emissions charge payment, including
(i) the amount in dollars paid to the Receiver General for Canada,
(ii) the applicable rate, and
(iii) the date of payment;
(f) the details of any surplus credits or offset credits remitted, including, for each type of credit,
(i) the number remitted,
(ii) the date of the remittance transaction,
(iii) the remittance transaction number,
(iv) the serial numbers, and
(v) the date or dates on which they were issued; and
(g) the details of any units or credits, recognized as compliance units, remitted, including
(i) the number remitted,
(ii) the province or territory or program authority referred to in subsection 78(1) that issued the units or credits,
(iii) the date of their retirement,
(iv) the serial numbers assigned to them by the province or territory or program authority referred to in subsection 78(1),
(v) the start date of the offset project for which the unit or credit was issued,
(vi) the year in which the GHG reduction or removal occurred for which the unit or credit was issued,
(vii) the offset protocol applicable to the project for which the unit or credit was issued, including the version number and publication date, and
(viii) the name of the accredited verification body that verified the units or credits.
Marginal note:Surplus credits
59 For the purposes of section 175 of the Act, the number of surplus credits, equivalent to the difference between the emissions limit and the quantity of GHGs emitted from the covered facility, that the Minister issues is based on what is reported in the annual report submitted for the compliance period, provided that no material discrepancy, within the meaning of subsection 49(2), exists with respect to the total quantity of GHGs and the production from each specified industrial activity that is used in the calculation of the emissions limit.
Errors and Omissions
Marginal note:Identification by person responsible
61 The notice submitted under subsection 176(1) of the Act by a person responsible for a covered facility who has become aware of an error or omission in an annual report must indicate whether
(a) the error or omission would have constituted a material discrepancy under subsection 49(2) if it had been identified during the verification of the annual report; and
(b) the aggregate of all errors and omissions would have constituted a material discrepancy under subsection 49(2) if it had been identified during the verification of the annual report.
Marginal note:Corrected report
62 (1) The person responsible for the covered facility must submit to the Minister a corrected report within 60 days after the day on which the notice is submitted or, if the notice indicated that the error or omission, or the aggregate of all errors or omissions, would have constituted a material discrepancy under subsection 49(2), a corrected report, along with a verification report prepared in accordance with section 52, within 90 days after the day on which the notice is submitted.
Marginal note:Content
(2) The corrected report must include the following information:
(a) a description of the corrections made to the annual report;
(b) the circumstances that led to the error or omission and the reasons why the error or omission was not previously detected;
(c) a description of the measures implemented, or to be implemented, to avoid future errors or omissions of the same type;
(d) the quantity of GHGs to which the detected error or omission corresponds, if corrected;
(e) the production to which the detected error or omission corresponds, if corrected;
(f) the result of the calculation under section 64;
(g) in the case of a covered facility other than one referred to in paragraph (h) or (i)
(i) the quantity of each GHG from the covered facility, expressed in CO2e tonnes, for each emission type determined in accordance with subsections 17(2) to (4), if corrected,
(ii) the total quantity of GHGs determined in accordance with section 17, if corrected,
(iii) the quantity of GHGs emitted and the quantity of CO2 that is captured and stored, determined in accordance with section 35, if corrected, and
(iv) the quantity of production quantified in accordance with section 31, if corrected;
(g.1) in the case of a covered facility to which section 36.2 applies, the information referred subsection 11(1.1), if corrected;
(h) in the case of an electricity generation facility
(i) the quantity of each GHG from the covered facility, expressed in CO2e tonnes, for each emission type, if corrected,
(ii) the total quantity of GHGs from each unit within the facility, determined in accordance with section 20, if corrected, and the sum of those GHGs from all units within the covered facility during the compliance period, if corrected,
(iii) the quantity of GHGs emitted and the quantity of CO2 that is captured and stored, determined in accordance with section 35, if corrected, and
(iv) the gross quantity of electricity generated by each unit within the facility, quantified in accordance with section 32, if corrected.
(i) in respect of a covered facility where both the specified industrial activity of producing coal by mining coal deposits and, if comprised of a unit or a group of units that are registered under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations, the generation of electricity are engaged in,
(i) the quantity of each GHG from the covered facility, expressed in CO2e tonnes, from each specified emission type, if corrected,
(ii) the total quantity of GHGs from mining of coal deposits, determined in accordance with section 17, and the total quantities of GHGs from the generation of electricity, determined in accordance with section 20, if corrected,
(iii) the quantity of GHGs emitted and the quantity of CO2 that is captured and stored, determined in accordance with section 35, if applicable, if corrected, and
(iv) the production quantified for each specified industrial activity engaged at the facility, the corrected production by each unit within the covered facility for each of the industrial activities set out in paragraphs 38(a) to (c), column 1, of Schedule 1 during the compliance period and the corrected sum of the production from all of the units, if corrected;
(i.i) in the case of a covered facility to which section 41.2 applies, the information referred to in subsection 11(1.2), if corrected;
(j) any change to the result obtained under section 44; and
(k) any other correction made to the information in the annual report.
Marginal note:Identification by the Minister
63 (1) Subsection 62(2) applies to a report that is required by the Minister under subsection 177(2) of the Act and the report must be submitted to the Minister within the following period:
(a) in the case of a corrected report, 60 days after the day on which the Minister required it; and
(b) in the case of a verified corrected report, 90 days after the day on which the Minister required it.
Marginal note:Verification report
(2) The corrected report submitted under paragraph (1)(b) must be submitted with a verification report prepared in accordance with section 52.
Marginal note:Change in obligations
64 For the purposes of section 178 of the Act, the revised compensation to be paid or remitted or number of surplus credits to be issued, as the case may be, is equal to the difference between the result obtained in accordance with the calculation under section 44, and reported in the annual report, and the result that is reported in the corrected report.
Marginal note:Revised compensation
65 (1) For the purposes of paragraph 178(1)(a) of the Act, any revised compensation is to be provided by means of an excess emissions charge payment or a remittance of compliance units. Revised compensation is to be provided if the difference specified in section 64 is greater than, or equal to, 500 CO2e tonnes.
Marginal note:Issuance of surplus credits
(2) For the purposes of paragraph 178(1)(b) of the Act, the Minister may issue to a person that is responsible for a covered facility a number of surplus credits that is equivalent to the difference between
(a) the number of surplus credits calculated based on the corrected report and the number of surplus credits issued under section 175 of Act based on the annual report; or
(b) the applicable emissions limit and the quantity of GHGs emitted from the facility that are reported in the corrected report.
Marginal note:Excess Surplus credits issued
66 (1) If a corrected report shows that an excess number of surplus credits was issued to the person responsible for a covered facility and the credits in question remain in an account in the tracking system that is linked to the covered facility, the Minister must revoke the excess credits without notice. The revocation is effective as of the date on which the corrected report is submitted.
Marginal note:Insufficient surplus credits in account
(2) If any of the excess surplus credits are no longer in an account in the tracking system that is linked to the covered facility, the person responsible for the facility must, within the compensation deadlines set out in subsections 69(1) and (2), make up the amount owed by
(a) remitting to the Minister other surplus credits in accordance with section 70;
(b) remitting to the Minister other compliance units in accordance with section 71; or
(c) making an excess emissions charge payment in accordance with section 55.
Marginal note:Charge
67 An excess emissions charge payment made for the purposes of subsection 65(1) must be made in the manner set out in section 55.
Marginal note:Surplus credits
68 (1) Any revised compensation that is provided by the remittance of surplus credits must be made in the manner set out in section 70.
Marginal note:Other compliance units
(2) Any revised compensation that is provided by the remittance of compliance units other than surplus credits must be made in the manner set out in section 71.
Marginal note:Regular-rate compensation deadline
69 (1) For the purposes of revised compensation, the regular rate referred to in subsection 174(3) of the Act applies for a period of 45 days after the day on which the corrected report is submitted.
Marginal note:Increased-rate compensation deadline
(2) If compensation is not provided in full by the deadline set out in subsection (1), the increased rate referred to in subsection 174(4) of the Act applies for a period of 60 days after that deadline.
Marginal note:Other compensation deadlines
(3) If a corrected report is submitted to the Minister in respect of a compliance period for which the regular-rate compensation deadline set out in subsection 57(1) or (1.1) has not expired, the compensation deadline in respect of that compliance period is the later of
(a) the compensation deadlines set out in subsection 57(1), (1.1), (2) or (2.1), as the case may be, and
(b) the compensation deadlines under subsection (1) or (2), as the case may be.
Remittance of Compliance Units
Marginal note:Surplus credits
70 Any surplus credit may be remitted to the Minister for the purposes of subsection 174(1) or paragraph 178(1)(a) of the Act if the credit was issued no more than five calendar years before the remittance.
Marginal note:Other compliance units
71 Any recognized unit or credit or offset credit may be remitted to the Minister for the purposes of subsection 174(1) or paragraph 178(1)(a) of the Act if the unit or credit, as the case may be, was issued for GHG reductions or removals that occurred no more than eight calendar years before the remittance.
Suspension and Revocation
Marginal note:Suspension
72 (1) For the purposes of subsection 180(1) of the Act, the Minister may suspend a surplus credit or offset credit in an account if the Minister has reasonable grounds to believe that the credit
(a) was already used;
(b) was issued on the basis of false or misleading information; or
(c) is no longer valid.
Marginal note:Notice
(2) The Minister must, without delay, notify the holder of the account of the suspension of the credit, the reasons for the suspension and the date on which it takes effect.
Marginal note:Response
(3) The holder of the account may, within 30 days after the day on which the Minister’s notice under subsection (2) is issued, submit to the Minister their reasons why the credit should not be suspended.
Marginal note:Revocation
73 The Minister must, after the period set out in subsection 72(3), thoroughly review the reasons for the suspension and notify the holder of the account that
(a) if the Minister determines that the reasons for the suspension are well-founded, the surplus credit or offset credit is revoked; or
(b) the suspension of the credit is lifted.
Marginal note:Request for cancellation
74 A request under subsection 180(2) of the Act to cancel a surplus credit or offset credit must be made to the Minister in writing and include the serial number of the credit to be cancelled.
Issuance Error or Invalidity
Marginal note:Application of subsection 181(1) of the Act
75 (1) If the Minister requires a person, under subsection 181(1) of the Act, to remit a compliance unit, the Minister must provide the person a notice indicating the reason for the remittance, the number of compliance units to be remitted and the deadline by which the remittance is to be made.
Marginal note:Manner of remittance
(2) The compliance units remitted to the Minister under subsection 181(2) of the Act must
(a) in the case surplus credits, have been issued within five calendar years before the deadline indicated in the notice provided under subsection (1); and
(b) in the case of recognized units or credits or offset credits, have been issued for GHG reductions or removals that occurred within the eight calendar years before the deadline indicated in the notice provided under subsection (1).
Tracking System
Marginal note:Accounts for participants
76 For the purposes of subsection 186(1) of the Act, any person, other than a person responsible for a covered facility, who wishes to open an account in the tracking system must notify the Minister in writing. The Minister must send to the person the conditions related to the use of that account in accordance with subsection 186(2) of the Act.
Marginal note:Notice of closure
77 (1) If an account has been inactive for more than seven years, the Minister may give 60 days’ notice to the holder of the account of the Minister’s intent to close the account.
Marginal note:Closing of account
(2) If the holder of the account fails to request that the account remain open before the expiry of the 60 days, the Minister may close the account under subsection 186(3) of the Act.
Recognized Units or Credits
Marginal note:Compliance unit
78 (1) A unit or credit is to be recognized as a compliance unit if it is issued
(a) by a province or territory or by a program authority on behalf of a province or territory; and
(b) under an offset protocol and offset program that is set out on the list published on the Department of the Environment’s website.
Marginal note:Offset programs
(2) In establishing the list of offset programs, the Minister must ensure that each one includes the following elements:
(a) rules regarding governance, oversight and enforcement;
(b) rules regarding registration and renewal of projects;
(c) rules regarding the establishment of periods within which units or credits may be issued;
(d) rules regarding who is entitled to the credit or unit for the GHG reductions or removals;
(e) measures to ensure that GHG reductions and removals are additional and permanent and that reversal risks have been mitigated;
(f) measures to ensure that, for a GHG reduction or removal of one CO2e tonne, no more than one credit or unit is issued and the unit or credit is not used more than once;
(g) publicly available information on projects, protocols and units or credits; and
(h) a requirement that, prior to the issuance of a unit or credit, there be a verification by a third party in accordance with procedures that allow them to determine with a reasonable level of assurance that the associated project meets the requirements of the protocol and program.
Marginal note:Offset protocols
(3) In establishing the list of offset protocols recognized under a program referred to in subsection (2), the Minister must verify that each protocol ensures that
(a) the reduction or removal is with respect to a GHG;
(b) the reduction or removal is not subject to carbon pollution pricing;
(c) the GHG reduction or removal is quantified using scientifically-established methods that allow for
(i) the calculation of the quantity of GHG emissions or removals for each GHG source, sink and reservoir,
(ii) the quantification of reversals,
(ii.1) the assessment of leakage risks,
(iii) the calculation of the quantity of GHG reductions or removals that would not have occurred in comparison with the baseline scenario, and
(iv) the use of conservative quantification assumptions and approaches;
(c.1) the baseline scenario used reflects the most recent data available, any legal requirements and current practices with respect to the activity that is the subject of the protocol;
(d) best practices are used for
(i) data gathering and management,
(ii) record keeping,
(iii) the ongoing monitoring of offset projects, including permanence, and
(iv) quality assurance and quality control; and
(e) the GHG global warming potentials used in calculations are less than or equal to those set out in column 2 of Schedule 3 to the Act.
Marginal note:Recognized unit or credit
(4) A recognized unit or credit must, at the time of its remittance to the Minister,
(a) be valid;
(b) have been issued in respect of a project that uses a protocol referred to in subsection (3);
(c) have been issued in respect of a project located in Canada that began in 2017 or later; and
(d) have been verified by a verification body that
(i) is accredited as a verification body to the ISO Standard 14065 by the Standards Council of Canada, the American National Standards Institute or any other accreditation organization that is a member of the International Accreditation Forum, and
(ii) is not suspended by the accreditation organization that issued its accreditation.
Transitional Provisions
Marginal note:Subsection 12(3)
79 For the 2019 calendar year, despite subsection 12(3), if a covered facility where a specified industrial activity set out in items 2 or 3, column 1, of Schedule 1 is engaged in produces hydrogen gas, the person responsible for the covered facility must include in their annual report the information referred to in that subsection if it is available.
Marginal note:Application
80 Section 8 of the Greenhouse Gas Emissions Information Production Order, as it read immediately before August 1, 2019, continues to apply, with any necessary modifications, with respect to a person responsible for a covered facility where an industrial activity set out in Schedule 1 to these Regulations is engaged in until January 1, 2020.
Marginal note:Records
81 (1) Any records kept in accordance with section 11 of the Greenhouse Gas Emissions Information Production Order, as it read immediately before August 1, 2019, during the period beginning on January 1, 2019 and ending on August 1, 2019, are deemed to be records kept for the purposes of subsection 45(1) of these Regulations.
Marginal note:Alternative method
(2) For the 2019 calendar year, if a person responsible for a covered facility used an alternative sampling, measurement or analysis method for a specified emission type in accordance with section 8 of the Greenhouse Gas Emissions Information Production Order, as it read before August 1, 2019, they must keep a record of a description of that method.
Marginal note:Clinker
82 For the 2019 calendar year, despite paragraph 31(1)(a) of these Regulations, the production from a covered facility with respect to the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 7(a), column 1, of Schedule 1 of these Regulations may be quantified under paragraph 36(c) of the Greenhouse Gas Emissions Information Production Order, as it read immediately before August 1, 2019. If the production is quantified under the Order, it cannot be used in the calculation of the emissions limit under subsection 36(1) of these Regulations.
Marginal note:Glass containers
83 For the 2019 calendar year, despite paragraph 31(1)(a) and subsection 36(1) of these Regulations, the production from a covered facility with respect to the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 9(a), column 1, of Schedule 1 to these Regulations may be quantified in accordance with section 103.2 of the Greenhouse Gas Emissions Information Production Order, as it read before August 1, 2019.
Marginal note:High value chemicals
84 For the 2019 calendar year, despite paragraph 31(1)(a) of these Regulations, the production from a facility with respect to the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 17(a), column 1, of Schedule 1 to these Regulations may be quantified in accordance with section 103.36 of the Greenhouse Gas Emissions Information Production Order, as it read before August 1, 2019.
Marginal note:Isopropyl alcohol
85 For the 2019 calendar year, despite subparagraph 11(1)(a)(ii) of these Regulations, the person responsible for the covered facility is not required to quantify the production from the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 3(c), column 1, of Schedule 1.
Marginal note:Pulp and Paper
85.1 (1) For the 2019 calendar year, despite paragraph 31(1)(a) and subsection 36(1) of these Regulations, the production from a covered facility with respect to the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 36(c), column 1, of Schedule 1 to these Regulations may be quantified in accordance with section 102 of the Greenhouse Gas Emissions Information Production Order, as it read before August 1, 2019. In that case, the output-based standards that apply are
(a) 0.203 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, in the case of a facility equipped with a recovery boiler, lime kiln or pulping digester, and
(b) 0.184 CO2e tonnes per unit of measurement, in the case of a facility not equipped with a recovery boiler, lime kiln or pulping digester.
Marginal note:Reporting
(2) For the 2019 calendar year, if a covered facility where the specified industrial activity set out in paragraph 36(c), column 1, of Schedule 1 to these Regulations is engaged in quantifies production in accordance with subsection (1), the annual report must include the quantity of specialty products produced, in tonnes, if that information is available.
Amendments to the Environmental Administrative Monetary Penalties Regulations
86 [Amendments]
87 [Amendments]
88 [Amendments]
89 [Amendments]
90 [Amendments]
91 [Amendments]
92 [Amendments]
Coming into Force
Marginal note:January 1, 2019
93 (1) Subject to subsections (2) to (6), these Regulations are deemed to have come into force on January 1, 2019.
Marginal note:July 1, 2019
(2) These Regulations apply in Yukon and Nunavut on July 1, 2019.
Marginal note:January 1, 2020
(3) Sections 26 to 30 and subsections 31(2) and (3) come into force on January 1, 2020.
Marginal note:August 1, 2019
(4) Subsection 45(2) of these Regulations comes into force on August 1, 2019.
Marginal note:February 16, 2023
(5) Section 56 comes into force on February 16, 2023.
Marginal note:February 16, 2021
(6) Section 76 comes into force on February 16, 2021.
SCHEDULE 1(Subsection 5(2), paragraph 8(b), subparagraphs 11(1)(b)(iii) and (iv), clauses 11(1)(c)(iii)(A) and (B), subsections 12(2) and (3) and 16(1) to (8), paragraphs 17(2)(a) and (c), subsections 22(2), 31(1), 32(1), 36(1) to (4), 36.1(1) and (2), 36.2(2) and 37(1) and (2), sections 38 to 40, subsections 41(1) and (2), 41.1(2) and 41.2(2), section 42, subparagraph 62(2)(i)(iv), section 2 of Part 4 of Schedule 3, sections 1 and 2 of Part 7 of Schedule 3 and subparagraphs 3(g)(ii) and 3(h)(iii) of Schedule 5)Industrial Activities and Output-based Standards
TABLE
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Activity | Units of Measurement | Output-based standard (CO2e tonnes/unit of measurement) | Applicable Part of Schedule 3 | |
| Oil and Gas Production | ||||
| 1 | Bitumen and other crude oil production — other than bitumen extracted from surface mining — by a covered facility other than a covered facility referred to in item 3 | |||
| barrels of light crude oil | 0.0159 | Part 1 | |
| barrels of bitumen and heavy crude oil | 0.0544 | Part 1 | |
| 2 | Upgrading of bitumen or heavy oil to produce synthetic crude oil | barrels of synthetic crude oil | 0.0408 | Part 2 |
| 3 | Processing of crude oil or secondary petroleum products at a covered facility that has a combined annual volume of gasoline, diesel fuel and lubricant basestock produced that is greater than 40% of its annual volume of liquid petroleum products produced | |||
| complexity-weighted barrels | 0.00420 | Part 3 | |
| kilolitres of lubricant basestock | 0.295 | Part 3 | |
| tonnes of isopropyl alcohol | calculated in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations | Part 3 | |
| 4 | Processing of natural gas and production of | |||
| 100 000 cubic metres of pipeline-transmission- quality natural gas at a temperature of 15°C and a pressure of 101.325 kPa | 10.6 | Part 4 | |
| cubic metres of propane and butane combined at a temperature of 15°C and at an equilibrium pressure | 0.0301 | Part 4 | |
| 5 | Transmission of processed natural gas by a facility referred to in paragraph (b) of the definition facility in subsection 1(1) of these Regulations | Megawatt hours (MWh) | 0.393 | Part 5 |
| 6 | Production of hydrogen gas using steam hydrocarbon reforming or partial oxidation of hydrocarbons | Tonnes of hydrogen gas | 9.84 | Part 6 |
| Mineral Processing | ||||
| 7 | Production of clinker and cement | |||
| tonnes of clinker | 0.799 | Part 7 | |
| tonnes of grey cement | 0.733 | Part 7 | |
| tonnes of white cement | calculated in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations | Part 7 | |
| 8 | Production of lime from limestone using a kiln | |||
| tonnes of high- calcium lime produced and lime kiln dust sold | 1.20 | Part 8 | |
| tonnes of dolomitic lime produced and lime kiln dust sold | calculated in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations | Part 8 | |
| tonnes of speciality lime produced | calculated in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations | Part 8 | |
| 9 | Production of glass, including glass wool insulation, using a furnace, | |||
| tonnes of packed glass | 0.370 | Part 9 | |
| tonnes of glass | calculated in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations | Part 9 | |
| 10 | Production of gypsum products that contain at least 70 weight percent of calcium sulphate dihydrate | tonnes of gypsum products that contain at least 70 weight percent calcium sulphate dihydrate | calculated in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations | Part 10 |
| 11 | Production of mineral wool insulation, excluding glass wool insulation | tonnes of mineral wool insulation | calculated in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations | Part 11 |
| 12 | Production of brick or other products made from clay or shale using a kiln | tonnes of brick and other products made from clay or shale using a kiln | 0.223 | Part 12 |
| Chemicals | ||||
| 13 | Production of grain ethanol for use as fuel and secondary production of ethanol for industrial use | |||
| kilolitres of absolute ethanol | 0.321 | Part 13 | |
| kilolitres of absolute ethanol | 0.728 | Part 13 | |
| 14 | Production of furnace black in any form, including pellets and powders, using thermal oxidation or thermal decomposition of hydrocarbons | tonnes of furnace black | 2.08 | Part 14 |
| 15 | Production of 2-methylpenta-methylenediamine (MPMD) | tonnes of MPMD | 4.65 | Part 15 |
| 16 | Production of nylon 6 or nylon 6,6, as the case may be | |||
| tonnes of nylon resins | 0.480 | Part 16 | |
| tonnes of nylon fibres | 0.711 | Part 16 | |
| 17 | Production of the following petrochemicals from petroleum and liquefied natural gas or from feedstocks derived from petroleum: | |||
| tonnes of high-value chemicals from steam cracking | 0.652 | Part 17 | |
| tonnes of aromatic cyclic hydrocarbons | 0.694 | Part 17 | |
| tonnes of higher olefins | 0.954 | Part 17 | |
| tonnes of hydrocarbon solvents | 1.14 | Part 17 | |
| tonnes of styrene | 0.925 | Part 17 | |
| tonnes of polyethylene | 0.164 | Part 17 | |
| Pharmaceuticals | ||||
| 18 | Production of vaccines for human or animal use | litres of vaccine | Calculated in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations | Part 18 |
| Iron, Steel and Metal Tubes | ||||
| 19 | Production of steel from feedstock that comes primarily from scrap iron or steel, except the production of metal ingots or the production, using a mould, of metal products of a specific shape or design to produce the intended use of which when in that form is dependent in whole or in part on its shape or design, of | |||
| tonnes of cast steel | 0.124 | Part 19 | |
| tonnes of rolled steel | 0.0937 | Part 19 | |
| 20 | Production of iron or steel from smelted iron ore or production of metallurgical coke | |||
| tonnes of coke | 0.597 | Part 20 | |
| tonnes of iron | 1.46 | Part 20 | |
| tonnes of steel | 0.164 | Part 20 | |
| tonnes of steel | Calculated in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations | Part 20 | |
| 21 | Production of iron ore pellets from iron ore concentrate, of | |||
| tonnes of flux pellets | 0.0990 | Part 21 | |
| tonnes of pellets other than flux pellets | 0.0560 | Part 21 | |
| 22 | Production of metal tubes | tonnes of metal tubes | Calculated in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations | Part 22 |
| Mining and Ore Processing | ||||
| 23 | Smelting or refining, from feedstock that comes primarily from ore, of at least one of the following base metals: | |||
| tonnes of copper anodes | calculated in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations | Part 23 | |
| tonnes of lead and lead alloys | 2.45 | Part 23 | |
| tonnes of zinc and lead | 0.856 | Part 23 | |
| tonnes of nickel matte | 0.843 | Part 23 | |
| tonnes of base metal produced | 1.70 | Part 23 | |
| tonnes of copper cathodes | calculated in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations | Part 23 | |
| 24 | Production of potash from the mining and refining of potash ore using | |||
| tonnes of potash containing at least 90% potassium chloride | 0.232 | Part 24 | |
| tonnes of potash containing at least 90% potassium chloride | 0.0382 | Part 24 | |
| 25 | Production by mining coal deposits | |||
| tonnes of thermal coal | calculated in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations | Part 25 | |
| tonnes of metallurgical coal | 0.0499 | Part 25 | |
| 26 | Production of metal or diamonds from the mining or milling of ore or kimberlite | |||
| tonnes of iron in ore | 0.0169 | Part 26 | |
| tonnes of uranium in ore concentrate | 9.26 | Part 26 | |
| kilograms of silver, platinum and palladium | Calculated in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations | Part 26 | |
| tonnes of base metals in ore concentrate | 0.643 | Part 26 | |
| carats of diamond | 0.0172 | Part 26 | |
| kilograms of gold | 7.71 | Part 26 | |
| 27 | Calcining of coal to produce char | Tonnes of char | Calculated in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations | Part 27 |
| 28 | Production of activated carbon from coal | Kilograms of activated carbon | Calculated in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations | Part 28 |
| Nitrogen Fertilizers | ||||
| 29 | Production of nitrogen-based fertilizer, including | |||
| tonnes of nitric acid | 0.331 | Part 29 | |
| tonnes of ammonia | 1.82 | Part 29 | |
| tonnes of urea liquor | 0.162 | Part 29 | |
| tonnes of ammonium phosphate | Calculated in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations | Part 29 | |
| Food Processing | ||||
| 30 | Industrial processing of potatoes for human or animal consumption | Tonnes of potatoes used as raw material | 0.0728 | Part 30 |
| 31 | Industrial processing of oilseeds for human or animal consumption | Tonnes of oilseed used as raw material | 0.0481 | Part 31 |
| 32 | Production of ethanol from distillation for use in the production of alcoholic beverages | Kilolitres of absolute alcohol | 1.11 | Part 32 |
| 33 | Processing of corn through wet milling | Tonnes of corn used as raw material | 0.0991 | Part 33 |
| 34 | Production of citric acid | Tonnes of anhydrous citric acid | 0.479 | Part 34 |
| 35 | Production of refined sugar from raw cane sugar | Tonnes of refined sugar | 0.102 | Part 35 |
| Pulp and Paper | ||||
| 36 | Production of pulp and other products | |||
| tonnes of finished product | 0.203 | Part 36 | |
| tonnes of finished product | 0.184 | Part 36 | |
| tonnes of specialty product | Calculated in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations | Part 36 | |
| Automotive | ||||
| 37 | Main assembly of four-wheeled self-propelled vehicles that are designed for use on highways and that have a gross vehicle weight rating of less than 4 536 kg (10,000 pounds) | Number of vehicles | 0.216 | Part 37 |
| Electricity Generation | ||||
| 38 | Generation of electricity | |||
| gigawatt hours (GWh) |
| Part 38 | |
| gigawatt hours (GWh) | 550 | Part 38 | |
| gigawatt hours (GWh) | 370 | Part 38 | |
SCHEDULE 2(Subsection 11(1))Content of Annual Report on Emissions and Production
1 Information with respect to the person responsible for the covered facility:
(a) an indication as to whether they own or are otherwise responsible for the covered facility, including having the charge, management or control of the facility, or are the true decision maker with respect to the facility’s operations;
(b) their name (including any trade name or other name used by them) and civic address;
(c) the name, title, civic and postal addresses, telephone number and, if any, email address of their authorized official;
(d) the name, title, civic and postal addresses, telephone number and, if any, email address of a contact person, if different from the authorized official; and
(e) the federal Business Number assigned to them by the Canada Revenue Agency, if any.
2 Information with respect to the covered facility:
(a) its name and the civic address of its physical location, if any;
(b) its latitude and longitude coordinates in decimal degrees or degrees, minutes and seconds, except for a covered facility referred to in paragraph (b) of the definition of facility in subsection 1(1) of these Regulations;
(c) its six-digit North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) Canada code;
(d) the covered facility certificate number that was issued to it;
(e) if applicable, the National Pollutant Release Inventory (NPRI) identification number assigned to it for the purposes of the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999 and its Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program identification number; and
(f) in the case of an electricity generation facility or a covered facility referred to in paragraph 11(1)(c) that is composed, in part, of a unit or a group of units,
(i) the unique name for each unit,
(ii) the unit’s registration number under the Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity, if any, and
(iii) the unit’s registration number under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations, if any.
3 The quantity of each GHG for the compliance period, expressed in tonnes, for each of the following emission types:
(a) stationary fuel combustion emissions;
(b) industrial process emissions;
(c) industrial product use emissions;
(d) venting emissions;
(e) flaring emissions;
(f) leakage emissions;
(g) on-site transportation emissions;
(h) waste emissions; and
(i) wastewater emissions.
4 The quantities of CH4 and N2O that are subtracted under subsection 17(5) or 20(6) of these Regulations from the total CH4and N2O, expressed in tonnes, separately.
5 A list of the methods used to calculate, sample, measure and analyze each specified emission type and GHG for the compliance period.
6 If a covered facility uses a continuous emissions monitoring system and has captured or stored CO2, the quantity of CO2 captured during the compliance period.
7 If CO2 was captured, stored and deducted from the total quantity of GHGs under section 35 of these Regulations, the following information,
(a) a statement that indicates whether the CO2 was stored in accordance with the requirements set out in subsection 35(2) of these Regulations;
(b) the type of geological storage site used, among those set out in paragraph 35(2)(a) of these Regulations;
(c) the latitude and longitude coordinates in decimal degrees or degrees, minutes and seconds, of the storage site; and
(d) the name and address of the owner or the operator of the storage site, if they are different than those of the person responsible for the covered facility.
8 The output-based standard for each of the specified industrial activities engaged in at the covered facility and, for a calculated output-based standard, the data used to calculate that standard.
9 The method used to determine the covered facility’s production from each of the specified industrial activities engaged in at the facility.
10 With respect to thermal energy that is sold or bought, in addition to the information required in section 12 of these Regulations:
(a) the name of each covered facility from which thermal energy was bought and the covered facility certificate number that was issued to it; and
(b) the name of each covered facility to which thermal energy was sold and the covered facility certificate number that was issued to it.
11 With respect to a facility that produces cement,
(a) in addition to the tonnes of grey cement, the tonnes of clinker, gypsum and limestone that the grey cement contains, separately; and
(b) in addition to the tonnes of white cement, the tonnes of clinker, gypsum and limestone that the white cement contains, separately.
12 With respect to a facility that produces petrochemicals, the quantity of hydrogen gas produced during the compliance period, in tonnes, the quantity of hydrogen gas sold, in tonnes, and the concentration of the hydrogen gas sold, expressed in weight percentage.
13 With respect to a facility that produces metal from the mining of ore
(a) in addition to the total quantity of silver, platinum and palladium, in kilograms, combined, each of those metals separately, and;
(b) in addition to the combined total of base metals, in tonnes combined, each of those base metals in ore concentrate, in tonnes, separately.
14 With respect to an electricity generation facility composed of a unit referred to in subsection 41(2) of these Regulations, a statement indicating whether solid fuel was used by the unit to generate electricity in 2018 and whether additional liquid or gaseous fuel was used in that same year, if that information is available.
15 With respect to a covered facility for which part or all of the electricity generated from fossil fuels is not quantified, a list of the units or equipment from which the electricity is generated but not quantified.
16 With respect to a covered facility referred to in section 36.2 or 41.2 of these Regulations, with respect to the units or equipment whose electricity generation capacity has been increased during a compliance period,
(a) the total capacity and thermal energy to electricity ratio of the unit or equipment prior to its capacity being increased;
(b) the total capacity and thermal energy to electricity ratio of the unit or equipment subsequent to its capacity being increased; and
(c) the date of completion of any modifications made to the unit or equipment to increase its capacity.
17 With respect to an electricity generation facility referred to in section 41.1 of these Regulations, the total capacity and thermal energy to electricity ratio of each unit within the facility that generates electricity from gaseous fuels.
SCHEDULE 3(Subsections 17(2) to (4), and 20(2), (4) and (5), paragraphs 31(1)(a) and (b), subsection 32(1), paragraphs 34(1)(b) and (c) and Schedule 1)Quantification Requirements
PART 1Bitumen and Other Crude Oil Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | Directive 017 or Directive PNG017 | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Flaring emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.363(k) | Directive 017 or Directive PNG017 | WCI Method WCI.365 |
| 3 | Wastewater emissions from | ||||
| CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| CH4 | WCI Method WCI.203(h) | WCI Method WCI.204(h) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| 4 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 2Bitumen and Heavy Oil Upgrading
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | Directive 017 or Directive PNG017 | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions from | ||||
| CO2 | WCI Method WCI.133 | WCI Method WCI.134 | WCI Method WCI.135 | |
| CO2 | WCI Method WCI.203(d) | WCI Method WCI.204(d) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(a) | WCI Method WCI.204(a) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| 3 | Flaring emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(e) | WCI Method WCI.204(e) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 4 | Venting emissions from | ||||
| CO2 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(b) | WCI Method WCI.204(b) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| CO2 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(k) | WCI Method WCI.204(b) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| 5 | Wastewater emissions from | ||||
| CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| CH4 | WCI Method WCI.203(h) | WCI Method WCI.204(h) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| 6 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 3Petroleum Refining
DIVISION 1Quantification of Emissions
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Venting emissions from | ||||
| CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(b) | WCI Method WCI.204(b) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| CO2, and CH4 | WCI Method WCI.203(c) | WCI Method WCI.204(c) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| CH4 | WCI Method WCI.203(m) | WCI Method WCI.204(m) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| 3 | Industrial process emissions from | ||||
| CO2 | WCI Method WCI.133 | WCI Method WCI.134 | WCI Method WCI.135 | |
| CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(a) | WCI Method WCI.204(a) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| CO2 | WCI Method WCI.203(d) | WCI Method WCI.204(d) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(j) | WCI Method WCI.204(i) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| 4 | Flaring emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(e) | WCI Method WCI.204(e) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 5 | Leakage emissions | CH4 | WCI Method WCI.203(i) | WCI Method WCI.203(i) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 6 | Wastewater emissions from | ||||
| CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| CH4 | WCI Method WCI.203(h) | WCI Method WCI.204(h) | WCI Method WCI.205 | |
| 7 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
DIVISION 2Quantification of Production
1 (1) Direct-only complexity weighted barrels (direct-only CWB) is quantified in accordance with the method outlined in the directive entitled CAN-CWB Methodology for Regulatory Support: Public Report, published by Solomon Associates in January 2014.
(2) In the method referred to in subsection (1),
(a) the value of “Sales and Exports of Steam and Electricity” must be set to zero;
(b) the value of “EC Reported CO2e Site Emissions” excludes
(i) the emissions associated with electricity generated at the covered facility, and
(ii) the emissions associated with steam generated but not used by the covered facility;
(c) the value of “Deemed Indirect CO2e Emissions from imported electricity”
(i) includes emissions associated with electricity that is generated and used at the covered facility, and
(ii) is calculated using 0.420 tonnes of CO2e per MWh of electricity bought;
(d) the value of “Deemed Indirect CO2e Emissions from imported steam” is equal to 0; and
(e) the value of the “CWB factor” used to calculate hydrogen generation, in all cases, is 5.7.
PART 4Natural Gas Processing
DIVISION 1Quantification of Emissions
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | Directive 017 or Directive PNG017 | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions from acid gas removal | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.363 (c) | WCI Method WCI.364 | WCI Method WCI.365 |
| 3 | Flaring emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.363(k) | Directive 017 or Directive PNG017 | WCI Method WCI.365 |
| 4 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
DIVISION 2Quantification of Production
1 The combined quantity, in cubic metres, of propane and butane set out in paragraph 4(b), column 2, of the table to Schedule 1 is the sum of the quantity of propane, in cubic metres, at a temperature of 15°C and at an equilibrium pressure and the quantity of butane at a temperature of 15°C and at an equilibrium pressure, in cubic metres.
PART 5Natural Gas Transmission
DIVISION 1Quantification of Emissions
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Flaring emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.353(d) | Directive 017 or Directive PNG017 | WCI Method WCI.355 |
DIVISION 2Quantification of Production
1 (1) Production by the covered facility, expressed in MWh, is the sum of the amounts determined by the following formula for each of the drivers operated by the covered facility:
Px × Lx× Hx
where
- P
- is the rated brake power of driver “x”, expressed in megawatts;
- L
- is the actual annual average percent load of driver “x”, or, if the actual annual average percent load is unavailable, the percentage determined by the formula:
rpmavg /rpmmax
where
- rpmavg
- is the actual annual average speed during operation of driver “x”, expressed in revolutions per minute, and
- rpmmax
- is the maximum rated speed of driver “x”, expressed in revolutions per minute;
- H
- is the number of hours during the compliance period that driver “x” was operated; and
(2) The following definitions apply in this section.
- driver
driver means an electric motor, reciprocating engine or turbine used to drive a compressor. (conducteur)
- rated brake power
rated brake power means the maximum brake power of a driver as specified by its manufacturer either on its nameplate or otherwise. (puissance au frein nominale)
PART 6Hydrogen Gas Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.133 | WCI Method WCI.134 | WCI Method WCI.135 |
| 3 | Flaring emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(e) | WCI Method WCI.204(e) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 4 | Leakage emissions | CH4 | WCI Method WCI.203(i) | WCI Method WCI.203(i) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 5 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 7Cement and Clinker Production
DIVISION 1Quantification of Emissions
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions | CO2 | GHGRP 4.A | GHGRP 4.B | GHGRP 4.C |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
DIVISION 2Quantification of Production
1 The quantity of clinker set out in paragraph 7(a), column 2, of Schedule 1 refers only to clinker that is transported out of the facility.
2 The quantity of grey cement and white cement set out in paragraphs 7(b) and (c), column 2, of Schedule 1 refers only to cement produced from clinker that was produced at that facility and that has not been transported out of the facility.
PART 8Lime Manufacturing
DIVISION 1Quantification of Emissions
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions | CO2 | GHGRP 3.A | GHGRP 3.B | GHGRP 3.C |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
DIVISION 2Quantification of Production
1 The quantity of dolomitic lime does not include the dolomitic lime used in the production of speciality lime.
PART 9Glass Manufacturing
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.143 | WCI Method WCI.144 | WCI Method WCI.145 |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 10Gypsum Product Manufacturing
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 11Mineral Wool Insulation Manufacturing
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.183 | WCI Method WCI.184 | WCI Method WCI.185 |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 12Brick Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.183 | WCI Method WCI.184 | WCI Method WCI.185 |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 13Ethanol Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 14Furnace Black Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in able 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.303(b) | WCI Method WCI.304(b) | WCI Method WCI.305 |
| 3 | Venting emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.303(a)(3) | WCI Method WCI.304(a) | WCI Method WCI.305 |
| 4 | Leakage emissions | CH4 | WCI Method WCI.303(a)(4) | WCI Method WCI.304(a) | WCI Method WCI.305 |
| 5 | Industrial product use emissions | SF6 and PFCs | WCI Method WCI.233 | WCI Method WCI.234 | WCI Method WCI.235 |
| 6 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 152–methylpentamethylenediamine (MPMD) Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.133 | WCI Method WCI.134 | WCI Method WCI.135 |
| 3 | Industrial product use emissions | SF6 and PFCs | WCI Method WCI.233 | WCI Method WCI.234 | WCI Method WCI.235 |
| 4 | Flaring emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(e) | WCI Method WCI.204(e) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 5 | Leakage emissions | CH4 | WCI Method WCI.203(i) | WCI Method WCI.203(i) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 6 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 16Nylon Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 17Petrochemicals Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.303(b) | WCI Method WCI.304(b) | WCI Method WCI.305 |
| 3 | Venting emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.303(a)(3) | WCI Method WCI.304(a) | WCI Method WCI.305 |
| 4 | Flaring emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | WCI Methods WCI.303(a)(1), (a)(2) and (c) | WCI Method WCI.304(a) | WCI Method WCI.305 |
| 5 | Leakage emissions | CH4 | WCI Method WCI.303(a)(4) | WCI Method WCI.304(a) | WCI Method WCI.305 |
| 6 | Wastewater emissions | CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 7 | Industrial product use emissions | SF6 and PFCs | WCI Method WCI.233 | WCI Method WCI.234 | WCI Method WCI.235 |
| 8 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 18Vaccine Production
DIVISION 1Quantification of Emissions
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Leakage emissions | SF6 | WCI Method WCI.233 | WCI Method WCI.234 | WCI Method WCI.235 |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
DIVISION 2Quantification of Production
1 Production is quantified at the end of the formulation step of the manufacturing process, in litres of vaccine, as follows:
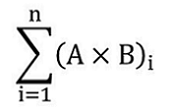
where:
- A
- is the capacity of each tank “i” that is used to combine ingredients at that step, expressed in litres;
- B
- is the number of batches produced in tank “i”; and
- i
- is the ith tank where “i” goes from 1 to n where n is the total number tanks used to combine ingredients.
PART 19Scrap-based Steel Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions from | ||||
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.5 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.6 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.9 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 20Integrated Steel Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions from | ||||
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.2 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.3 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.7 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.5 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.8 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.9 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.6 | GHGRP 6.C.1 | GHGRP 6.D | |
| 3 | Wastewater emissions | CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI. 205 |
| 4 | Industrial product use emissions | SF6 and PFCs | WCI Method WCI.233 | WCI Method WCI.234 | WCI Method WCI. 235 |
| 5 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 21Iron Ore Pelletizing
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions (induration furnace) | CO2 | GHGRP 6.A.1 | GHGRP 6.C | GHGRP 6.D |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 22Metal Tube Manufacturing
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 23Base Metal Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4, and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions from | ||||
| CO2 | WCI Method WCI.163 | WCI Method WCI.164 | WCI Method WCI.165 | |
| CO2 | WCI Method WCI.243 | WCI Method WCI.244 | WCI Method WCI.245 | |
| CO2 | WCI Method WCI.263 | WCI Method WCI.264 | WCI Method WCI.265 | |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 24Potash Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 25Coal Mining
1 For the purpose of item 2 of Table 1 to this Part, the CH4 leakage emissions from surface coal mining are quantified by multiplying the quantity of coal extracted by the applicable emission factor set out in column 3 of Table 2 to this Part according to the province of extraction set out in column 1 and the coal type set out in column 2 of Table 2.
TABLE 1
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Leakage emissions from | ||||
| CH4 | WCI Method WCI.103 | WCI Method WCI.104 | WCI Method WCI.105 | |
| CH4 | WCI Method WCI.253 | WCI Method WCI.254 | WCI Method WCI.255 | |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
TABLE 2
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Province | Coal Type | Emission Factor (tonnes of CH4/ tonnes of coal | |
| 1 | Nova Scotia | Bituminous | 7 x 10–5 |
| 2 | New Brunswick | Bituminous | 7 x 10–5 |
| 3 | Saskatchewan | Lignite | 7 x 10–5 |
| 4 | Alberta | Bituminous | 5.5 x 10–4 |
| 5 | Alberta | Sub-bituminous | 2 x 10–4 |
| 6 | British Columbia | Bituminous | 8.6 x 10–4 |
PART 26Production of Metals or Diamonds
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c , 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 27Char Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set outin Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 28Activated Carbon Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 29Nitrogen-based Fertilizer Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions from | ||||
| N2O | WCI Method WCI.313 | WCI Method WCI.314 | WCI Method WCI.315 | |
| CO2 | WCI Method WCI.83 | WCI Method WCI.84 | WCI Method WCI.85 | |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 30Industrial Potato Processing
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Wastewater emissions | CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 31Industrial Oilseed Processing
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Wastewater emissions | CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 32Alcohol Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Wastewater emissions | CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 33Wet Corn Milling
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Wastewater emissions | CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 34Citric Acid Production
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 35Sugar Refining
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
PART 36Pulp and Paper Production
DIVISION 1Quantification of Emissions
1 For the purposes of the table to this Division, GHGs from stationary fuel combustion emissions from biomass fuels may be quantified using equations 2-1, 2-2, 2-3, 2-7, 2-8, 2-9, 2-13, 2-14 or 2-18 of the GHGRP, if applicable.
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions from | ||||
| CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except,
| GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D | |
| CO2, CH4 and N2O | For fossil fuels, GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in Table 2-6 of 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O, and for pulping liquor, WCI Method WCI.213(c)Footnote for Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types(a) | For fossil fuels, GHGRP 2.C and for pulping liquor, WCI Method WCI.214 | GHGRP 2.D and WCI Method WCI.215 | |
| CO2 | GHGRP 2.A | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D | |
| CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.B, except,
| GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D | |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions: addition of carbonate compound into a lime kiln | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.213(d) | Direct measurement of quantity of carbonate compounds used or indirect measurement using quantity of carbonate compounds according to the quantity on the delivery invoices | WCI Method WCI.215 |
| 3 | Wastewater emissions | CH4 and N2O | WCI Method WCI.203(g) | WCI Method WCI.204(g) | WCI Method WCI.205 |
| 4 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
Return to footnote (a)For the combustion of biomass fuels where CH4 and N2O emission factors are not prescribed, the IPCC Guidelines must be used to estimate those emissions.
DIVISION 2Quantification of Production
1 (1) Production by the covered facility is quantified in tonnes of finished product or tonnes of specialty product, as follows:
(a) in the case of pulp, including dissolving pulp for viscose,
(i) if the moisture content exceeds 10%, the weight of the pulp is adjusted so that its moisture content does not exceed 10%, and
(ii) if the moisture content is equal to or less than 10%, the weight of the pulp without adjustment; and
(b) in the case of a finished product or specialty product referred to in subsection (3) derived directly from pulp or the pulping process, the weight of the product or, if it has been machine dried, its weight after it has been dried.
(2) A finished product referred to in paragraph (1)(b) does not include pulping liquor, wood waste, non-condensable gases, sludge, tall oil, turpentine, biogas, steam, water or products that are used in the production process.
(3) For the purposes of paragraph (1)(b), a specialty product means abrasive paper base, food grade grease resistant paper, packaging waxed paper base, paper for medical applications, napkin paper for commercial use, towel paper for commercial or domestic use, bath paper for domestic use and facial paper for domestic use.
PART 37Automotive Production
DIVISION 1Quantification of Emissions
Quantification of GHGs from Certain Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Stationary fuel combustion emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A and 2.B, except, for diesel, instead of the emission factors set out in table 2-6 of section 2.B, use 0.133 kg/kL for CH4 and 0.4 kg/kL for N2O | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
| 2 | Industrial product use emissions | HFCs | WCI Method WCI.43(d) | WCI Method WCI.44 | WCI Method WCI.45 |
| 3 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
DIVISION 2Quantification of Production
1 Production is the number of four-wheeled self-propelled vehicles that are designed for use on a highway and that have a gross vehicle weight rating of less than 4 536 kg (10,000 pounds) assembled during a compliance period.
PART 38Electricity Generation
DIVISION 1Quantification of Emissions
Stationary Fuel Combustion Emissions
1 (1) CO2, CH4 and N2O from stationary fuel combustion emissions must be quantified by unit in accordance with the following:
(a) for CO2,
(i) in the case of any unit that has obtained a registration number under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations, sections 20 to 26 of those Regulations,
(ii) in the case of any unit that has not obtained a registration number under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations and that generates electricity from the combustion of natural gas, sections 12 to 18 of the Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity, and
(iii) in the case of any other unit, GHGRP 2.A; and
(b) for CH4 and N2O, in the case of all units, GHGRP 2.B.
(2) For the purposes of paragraph (1)(b), for the stationary combustion of diesel, the following emission factors must be used instead of those set out in Table 2-6 to section 2.B of the GHGRP:
(a) for CH4, 0.133 kg/kL; and
(b) for N2O, 0.4 kg/kL.
2 The following sampling, analysis and measurement requirements apply to stationary fuel combustion emissions for each unit:
(a) for CO2,
(i) in the case of any unit that has obtained a registration number under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations, section 27 of those Regulations,
(ii) in the case of any unit that has not obtained a registration number under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations and that generates electricity from the combustion of natural gas, section 19 of the Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity, and
(iii) in the case of any other unit, GHGRP 2.C; and
(b) for CH4 and N2O, in the case of all units, GHGRP 2.C.
3 Replacement data for stationary fuel combustion emissions must be calculated for each unit in accordance with the following:
(a) for CO2,
(i) in the case of any unit that has obtained a registration number under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations, section 28 of those Regulations,
(ii) in the case of any unit that has not obtained a registration number under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations and that generates electricity from the combustion of natural gas, section 20 of the Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity, and
(iii) in the case of any other unit, GHGRP 2.D; and
(b) for CH4 and N2O, in the case of all units, GHGRP 2.D.
Emissions from Other Specified Emission Types
Quantification of GHGs from Other Specified Emission Types
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specified Emission Types | GHGs | Method for Calculating GHGs | Sampling, Analysis and Measurement Requirements | Method for Estimating Missing Analytical Data | |
| 1 | Leakage emissions from coal storage | CH4 | WCI Method WCI.103 | WCI Method WCI.104 | WCI Method WCI.105 |
| 2 | Industrial process emissions from acid gas scrubbers and acid gas reagent | CO2 | WCI Method WCI.43(c) | WCI Method WCI.44 | WCI Method WCI.45 |
| 3 | Industrial product use emissions from | ||||
| SF6 and PFCs | WCI Method WCI.233 | WCI Method WCI.234 | WCI Method WCI.235 | |
| HFCs | WCI Method WCI.43(d) | WCI Method WCI.44 | WCI Method WCI.45 | |
| 4 | On-site transportation emissions | CO2, CH4 and N2O | GHGRP 2.A.1.c, 2.A.1.d, 2.A.2.e and 2.B | GHGRP 2.C | GHGRP 2.D |
DIVISION 2Quantification of Production — Main Industrial Activity
4 (1) Subject to section 5, if a unit uses only one fossil fuel to generate electricity, production of electricity must be quantified in GWh of gross electricity generated by the unit, measured at the electrical terminals of the generators of each unit using meters that comply with the requirements of the Electricity and Gas Inspection Act and the Electricity and Gas Inspection Regulations.
(2) Subject to section 5, if a unit uses a mixture of fossil fuels or a mixture of biomass and fossil fuels to generate electricity, the gross electricity generated by the unit is to be determined separately for the gaseous fuels, liquid fuels and solid fuels in accordance with the following formula and expressed in GWh:

where
- GU
- is the gross quantity of electricity generated by the unit during a compliance period, as measured at the electrical terminals of the generators of the unit using meters that comply with the requirements of the Electricity and Gas Inspection Act and the Electricity and Gas Inspection Regulations, expressed in GWh;
- HFFk
- is determined in accordance with the following formula, calculated separately for gaseous fuels, liquid fuels and solid fuels type “k”:

where
- QFFj
- is the quantity of gaseous, liquid or solid fuel, as the case may be, type “j” combusted in the unit to generate electricity during the compliance period, determined in accordance with subsection (3),
- HHVj
- is the higher heating value of the gaseous, liquid or solid fuel, as the case may be, type “j” combusted in the unit, determined in accordance with subsection 24(1) of the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations, and
- j
- is the jth fossil fuel type combusted in the unit, where “j” goes from 1 to m and where m is the number of types of gaseous, liquid or solid fuel combusted, as the case may be, combusted; and
- HB
- is determined in accordance with the formula
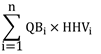
where:
- QBi
- is the quantity of biomass fuel type “i” combusted in the unit to generate electricity during the compliance period, determined in accordance with the subsection (3),
- HHVi
- is the higher heating value for the biomass fuel type “i” combusted in the unit, is determined in accordance with subsection 24(1) of the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations, and
- i
- is the ith biomass fuel type combusted in the unit, where “i” goes from 1 to n and where n is the number of types of biomass fuels combusted.
(3) The quantity of fuel for QFFj or QBi is determined on the following basis:
(a) for a solid fuel, the mass of the fuel combusted, on a wet or dry basis, expressed in tonnes and measured by a measuring device;
(b) for a liquid fuel, the volume of the fuel combusted, expressed in kL and measured using a flow meter; and
(c) for a gaseous fuel, the volume of the fuel combusted, expressed in standard cubic metres and measured using a flow meter.
5 If a combustion engine unit and a boiler unit share the same steam turbine, the quantity of electricity generated by a given unit is determined in accordance with subsection 11(2) of the Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity.
DIVISION 3Additional Industrial Activity – Quantification of Production
6 If a covered facility uses only one fossil fuel to generate electricity, production of electricity is quantified in GWh of gross electricity generated through the use of fossil fuels.
7 (1) If a covered facility uses a mixture of fossil fuels or a mixture of biomass and fossil fuels to generate electricity, the gross electricity generated by the facility is to be determined separately for the gaseous fuels, liquid fuels and solid fuels in accordance with the following formula and expressed in GWh:

where
- GU
- is the gross quantity of electricity generated by the covered facility during the compliance period, expressed in GWh;
- HFFk
- is determined in accordance with the following formula, calculated separately for gaseous fuels, liquid fuels and solid fuels type “k”:

where
- QFFj
- is the quantity of gaseous, liquid or solid fuel, as the case may be, type “j” combusted in the facility for electricity generation during the compliance period, determined under subsection (2) and in accordance with section 2.C.2 of the GHGRP 2.C.2,
- HHVj
- is the higher heating value of the gaseous, liquid or solid fuel, as the case may be, type “j” combusted in the facility for electricity generation determined in accordance with sections 2.C.1 and 2.C.3 of the GHGRP, and
- j
- is the jth fossil fuel type combusted in the facility, where “j” goes from 1 to m and where m is the number of types of gaseous, liquid or solid fuels combusted, as the case may be; and
- HB
- is determined in accordance with the formula
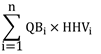
where
- QBi
- is the quantity of biomass fuel type “i” combusted in the facility for electricity generation during the compliance period, determined in accordance with subsection (2) and with section 2.C.2 of the GHGRP and the WCI Method WCI.214,
- HHVi
- is the higher heating value for each biomass fuel type “i” combusted in the facility for electricity generation in accordance with sections 2.C.1 and 2.C.3. of the GHGRP and the WCI Method WCI.214, and
- i
- is the ith biomass fuel type combusted in the facility, where “i” goes from 1 to n and where n is the number of types of biomass fuels combusted.
(2) The quantity of fuel for QFFj and QBi is determined on the following basis:
(a) for a solid fuel, the mass of the fuel combusted, on a wet or dry basis, expressed in tonnes and measured in accordance with section 2.C.2 of the GHGRP;
(b) for a liquid fuel, the volume of the fuel combusted, expressed in kL and measured in accordance with section 2.C.2. of the GHGRP; and
(c) for a gaseous fuel, the volume of the fuel combusted, expressed in standard cubic metres and measured in accordance with section 2.C.2 of the GHGRP 2.C.2.
SCHEDULE 4(Subsections 27(1) and 29(1))Information to Include in Application for Permit
1 Information with respect to the applicant:
(a) their name, civic and postal addresses in Canada, telephone number and, if any, email address; and
(b) the name, title, civic and postal addresses in Canada, telephone number and, if any, email address of their authorized official.
2 The covered facility certificate number that was issued to the covered facility for which the application is being submitted.
3 Details with respect to
(a) each prescribed method or guideline that cannot be used;
(b) the specified emission type and GHG; and
(c) the requirement that cannot be met.
4 Information establishing that, at the time of the application, it is not technically or economically feasible for the applicant to use the prescribed quantification method or guideline.
5 A description of the alternative method to be used for each method or guideline in respect of which a permit is sought and information that demonstrates that the quantification method being proposed is at least as rigorous as the prescribed method or guideline and provides equivalent results to those that would have been obtained from the prescribed method or guideline.
6 The requested term of the permit, which must be the period for which the permit is necessary.
SCHEDULE 5(Section 52 and subsection 53(1)(b))Content of Verification Report
1 Information with respect to the person responsible for a covered facility:
(a) an indication as to whether they own or are otherwise responsible for the covered facility, including having the charge, management or control of the facility, or are the true decision maker with respect to the facility’s operations;
(b) their name (including any trade name or other name used by them) and civic address;
(c) the name, title, civic and postal addresses, telephone number and, if any, email address of their authorized official;
(d) the name, title, civic and postal addresses, telephone number and, if any, email address of a contact person, if different from the authorized official; and
(e) the federal Business Number assigned to them by the Canada Revenue Agency, if any.
2 Information with respect to the covered facility:
(a) its facility name and the civic address of its physical location, if any;
(b) its latitude and longitude coordinates in decimal degrees or degrees, minutes and seconds, except for a covered facility referred to in paragraph (b) of the definition of facility in subsection 1(1) of these Regulations;
(c) its six-digit North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) Canada code;
(c.1) the covered facility certificate number that was issued to it;
(d) if applicable, the National Pollutant Release Inventory (NPRI) identification number assigned to it for the purposes of the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999 and its Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program identification number; and
(e) in the case of an electricity generation facility or a covered facility referred to in paragraph 11(1)(c) that is composed, in part, of a unit or a group of units,
(i) the unique name for each unit,
(ii) the unit’s registration number under the Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity, if any, and
(iii) the unit’s registration number under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations, if any.
3 Information with respect to the verification:
(a) the name and civic address of the verification body, as well as the name, telephone number and email address of the lead verifier for the team that conducted the verification;
(b) the name and contact information of the accreditation organization by which the verification body is accredited and the date of the verification body’s accreditation;
(c) the names and functions of each member of the verification team;
(d) the version of the ISO Standard 14064-3 according to which the verification was conducted and a description of the objectives and scope of the verification and the verification criteria;
(e) a summary of the verification procedures conducted on the data and information supporting an annual report or a corrected report, including
(i) any assessments, data sampling, tests and reviews that were conducted during the verification,
(ii) any tests of the GHG information system and controls, and
(iii) the date of each visit conducted, for the purpose of section 51 of these Regulations;
(f) the total quantity of GHGs from a covered facility, other than a facility referred to in paragraph (g) or (h), during the compliance period and the production from each specified industrial activity during the compliance period that is used in the calculation of the emissions limit by the covered facility, as described in the annual report or corrected report, as the case may be, for the covered facility;
(f.1) if section 36.2 of these Regulations applies to a covered facility, the electricity generation attributed to the capacity added to the equipment and the electricity generation attributed to the capacity of the equipment before the additional capacity was added, as described in the annual report or corrected report, as the case may be;
(g) in the case of a verification of an electricity generation facility, the following information as described in its annual report or corrected report, as the case may be:
(i) the total GHGs from each unit within the electricity generation facility and the sum of the total GHGs from each unit within the facility during the compliance period, and
(ii) the production during the compliance period by each unit within the electricity generation facility for each of the industrial activities set out in paragraphs 38(a) to (c), column 1, of Schedule 1 and the sum of the production from all units within the electricity generation facility;
(h) in the case of a covered facility, where the specified industrial activities are both the production of coal by mining coal deposits and, if composed of a unit or a group of units that are registered under the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations, the generation of electricity, as described in its annual report or corrected report, as the case may be,
(i) the total quantity of GHGs from the covered facility during the compliance period, expressed in CO2e tonnes,
(ii) with respect to the production of coal by mining coal deposits, the production from each specified industrial activity during the compliance period that is used in the calculation of the emissions limit, and
(iii) with respect to the generation of electricity, the production during the compliance period by each unit within the electricity generation facility for each of the industrial activities set out in paragraphs 38(a) to (c), column 1, of Schedule 1 and the sum of the production from all units within the electricity generation facility;
(h.1) if section 41.2 of these Regulations applies to an electricity generation facility or a covered facility referred to in paragraph (h), the electricity generated that is attributed to the capacity added to each unit as described in its annual report or corrected report, as the case may be:
(i) for each unit whose electricity generation capacity from gaseous fuels was increased by 50 MW or more and has a thermal energy to electricity ratio of less than 0.9, separately, the gross amount of electricity generated during the compliance period by each unit that is attributed to the capacity added to the unit and the gross amount of electricity generated that is attributed to capacity of the unit before the additional capacity was added, and
(ii) the sum, from all of the units referred to in subparagraph (i), of gross amount of electricity generated that is attributed to the capacity added to the units and of the electricity generated attributed to the capacity of the units before the additional capacity was added, separately;
(i) in the case of a covered facility that calculated an output-based standard in accordance with section 37 of these Regulations, the calculated output-based standard and the information associated with each term in the equation;
(j) a record of errors or omissions capable of influencing the assessment of the quantity of GHGs that are emitted from a covered facility during the applicable compliance period against its applicable GHG emissions limit, identified during the verification, in the data, information or methods used in the preparation of the annual report or corrected report, as the case may be, that indicates,
(i) with respect to each error and omission, if it may be quantified,
(A) in relation to GHG emissions, the number of CO2e tonnes to which the error or omission corresponds, the related percentage calculated in accordance with subparagraph 49(2)(a)(i), (b)(i) or (c)(i) of these Regulations and a statement indicating whether the error or omission results in an understatement or overstatement, and
(B) in relation to the production of a given type of product, the quantification of that error or omission, expressed in the applicable unit of measurement, the related percentage calculated in accordance with paragraph 49(2)(d) of these Regulations and a statement indicating whether the error or omission results in an understatement or an overstatement, and
(ii) with respect to the aggregate of the errors or omissions in relation to GHG emissions, that may be quantified, the net result of the errors and omissions expressed in CO2e tonnes, the related percentage calculated in accordance with subparagraph 49(2)(a)(ii), (b)(ii) or (c)(ii) of these Regulations and a statement indicating whether the net result is an understatement or an overstatement;
(k) a record of any corrections made by the person responsible as a result of any errors or omissions capable of influencing the assessment of the quantity of GHGs that are emitted from a covered facility during the applicable compliance period against its applicable GHG emissions limit, identified during the verification;
(l) a declaration, signed and dated by the lead verifier, stating that the requirements of section 50 of these Regulations have been complied with and that any real or potential conflicts of interest have been effectively managed;
(m) a declaration, signed and dated by a reviewer who is not a member of the verification team, stating their approval of the verification report, including the name, civic address, telephone number and email address of that reviewer; and
(n) a verification statement by the verification body containing
(i) determinations as to whether a material discrepancy exists with respect to the total quantity of GHGs and the total production from each specified industrial activity used in the calculation of the emissions limit in the annual report or corrected report, as the case may be, and whether the annual report or corrected report was prepared in accordance with these Regulations, and
(ii) any qualifications or limitations the verification body has related to those determinations.
SCHEDULE
SCHEDULE [Amendments]
SCHEDULE 5(Section 5, subsection 6(1) and section 8.1)
Penalty Amounts
| Item | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | Column 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Violator | Violation Type | Baseline Penalty Amount ($) | History of Non-compliance Amount ($) | Economic Gains Amount ($) | |
| 1 | Individual | ||||
| 400 | 1,200 | 400 | ||
| 1,000 | 3,000 | 1,000 | ||
| 2 | Other person | ||||
| 2,000 | 6,000 | 2,000 | ||
| 5,000 | 15,000 | 5,000 |
- Date modified: