Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity (SOR/2018-261)
Full Document:
- HTMLFull Document: Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity (Accessibility Buttons available) |
- XMLFull Document: Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity [153 KB] |
- PDFFull Document: Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity [451 KB]
Regulations are current to 2024-11-26 and last amended on 2019-01-01. Previous Versions
Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity
SOR/2018-261
CANADIAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION ACT, 1999
Registration 2018-11-30
Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity
P.C. 2018-1482 2018-11-29
Whereas, pursuant to subsection 332(1)Footnote a of the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999Footnote b, the Minister of the Environment published in the Canada Gazette, Part I, on February 17, 2018, a copy of the proposed Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity, substantially in the annexed form, and persons were given an opportunity to file comments with respect to the proposed Regulations or to file a notice of objection requesting that a board of review be established and stating the reasons for the objection;
Whereas, pursuant to subsection 93(3) of that Act, the National Advisory Committee has been given an opportunity to provide its advice under section 6Footnote c of that Act;
And whereas, in accordance with subsection 93(4) of that Act, the Governor in Council is of the opinion that the proposed Regulations do not regulate an aspect of a substance that is regulated by or under any other Act of Parliament in a manner that provides, in the opinion of the Governor in Council, sufficient protection to the environment and human health;
Therefore, Her Excellency the Governor General in Council, on the recommendation of the Minister of the Environment and the Minister of Health, pursuant to subsections 93(1) and 330(3.2)Footnote d of the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999Footnote b, makes the annexed Regulations Limiting Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas-fired Generation of Electricity.
Return to footnote aS.C. 2004, c. 15, s. 31
Return to footnote bS.C. 1999, c. 33
Return to footnote cS.C. 2015, c. 3, par. 172(d)
Return to footnote dS.C. 2008, c. 31, s. 5
Overview
Marginal note:Purpose
1 These Regulations establish a regime for limiting carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions that result from the generation of electricity by means of thermal energy from the combustion of natural gas, whether in conjunction with other fuels, except coal, or not.
Interpretation
Marginal note:Definitions
2 (1) The following definitions apply in these Regulations.
- Act
Act means the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999. (Loi)
- API
API means the American Petroleum Institute. (API)
- ASTM
ASTM means ASTM International, formerly known as the American Society for Testing and Materials. (ASTM)
- auditor
auditor means a person who
(a) is independent of the responsible person that is to be audited; and
(b) has knowledge of and has experience with respect to
(i) the certification, operation and relative accuracy test audit of continuous emission monitoring systems, and
(ii) quality assurance and quality control procedures in relation to those systems. (vérificateur)
- authorized official
authorized official means
(a) in respect of a responsible person that is a corporation, an officer of the corporation who is authorized to act on its behalf;
(b) in respect of a responsible person that is an individual, that individual or an individual who is authorized to act on that individual’s behalf; and
(c) in respect of a responsible person that is another entity, a person authorized to act on that other entity’s behalf. (agent autorisé)
- biomass
biomass means a fuel that consists only of non-fossilized, biodegradable organic material that originates from plants or animals but does not originate from a geological formation, and includes gases and liquids that are recovered from the decomposition of organic waste. (biomasse)
- boiler unit
boiler unit means a unit that consists of at least one boiler but does not have a combustion engine. (groupe chaudière)
- capacity
capacity means
(a) in the case of a unit, the maximum continuous rating (the maximum net power that can be continuously sustained by the unit without the use of duct burners, at standard conditions), expressed in MW, as most recently reported to a provincial authority of competent jurisdiction or to the electric system operator in the province where the unit is located; and
(b) in the case of a combustion engine, the manufacturer provided capacity, expressed in MW. (capacité)
- combustion engine
combustion engine means an engine, other than an engine that is self-propelled or designed to be propelled while performing its function, that
(a) operates according to the Brayton thermodynamic cycle and combusts natural gas to produce a net amount of motive power; or
(b) combusts natural gas and uses reciprocating motion to convert thermal energy into mechanical work. (moteur à combustion)
- combustion engine unit
combustion engine unit means a unit that consists of at least one combustion engine and, if applicable, a heat recovery system, but does not have a boiler. (groupe moteur à combustion)
- continuous emission monitoring system
continuous emission monitoring system or CEMS means equipment for the sampling, conditioning and analyzing of emissions from a given source and the recording of data related to those emissions. (système de mesure et d’enregistrement en continu des émissions ou SMECE)
- facility
facility means all buildings, other structures and equipment, whether the equipment is stationary or not, that are located on a single site or adjacent sites and that are operated as a single integrated site. (installation)
- fossil fuel
fossil fuel means a fuel other than biomass. (combustible fossile)
- heat recovery system
heat recovery system means equipment, other than a boiler, that extracts heat from a combustion engine’s exhaust gases in order to generate steam or hot water. (système de récupération de la chaleur)
- heat to electricity ratio
heat to electricity ratio means, in respect of a unit, the total useful thermal energy production in a calendar year, expressed in GWh, divided by the total gross electricity generation in that calendar year, expressed in GWh. (rapport chaleur-électricité)
- natural gas
natural gas means a mixture of hydrocarbons — such as methane, ethane or propane — that is in a gaseous state at standard conditions and that is composed of at least 70% methane by volume or that has a higher heating value that is not less than 35 MJ/standard m3 and not more than 41 MJ/standard m3. It excludes landfill gas, digester gas, gas from wastewater treatment systems, refinery gas, sour gas, blast furnace gas, producer gas, coke oven gas, gas derived from petroleum coke or coal — including synthetic gas — or any gaseous fuel produced in a process that might result in highly variable sulphur content or heating value. (gaz naturel)
- operator
operator means a person who has the charge, management or control of a unit. (exploitant)
- performance test verifier
performance test verifier means a person who
(a) is independent of the responsible person for which the performance test is being conducted; and
(b) has knowledge of and has experience with respect to performance testing of boiler units. (vérificateur de l’essai de rendement)
- potential electrical output
potential electrical output means the quantity of electricity that would be generated by a unit in a calendar year if the unit were to operate at capacity at all times during that calendar year. (production potentielle d’électricité)
- Reference Method
Reference Method means the document entitled Reference Method for Source Testing: Quantification of Carbon Dioxide Releases by Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems from Thermal Power Generation, June 2012, published by the Department of the Environment. (Méthode de référence)
- responsible person
responsible person means an owner or operator of a unit. (personne responsable)
- standard conditions
standard conditions means a temperature of 15˚C and a pressure of 101.325 kPa. (conditions normales)
- standard m3
standard m3 means a volume expressed in cubic metres — at standard conditions. (m3 normalisé)
- unit
unit means an assembly comprised of a boiler or combustion engine and any other equipment that is physically connected to either, including duct burners and other combustion devices, heat recovery systems, steam turbines, generators and emission control devices and that operate together to generate electricity and, if applicable, produce useful thermal energy, from the combustion of natural gas. (groupe)
- useful life
useful life, in respect of a boiler unit referred to in subsection 3(4), has the same meaning as in subsection 2(1) of the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations. (vie utile)
- useful thermal energy
useful thermal energy means energy in the form of steam or hot water that is destined for a use — other than the generation of electricity — that would have required the consumption of energy in the form of fuel or electricity had that steam or hot water not been used. (énergie thermique utile)
Marginal note:Interpretation of documents incorporated by reference
(2) For the purposes of interpreting documents that are incorporated by reference into these Regulations, “should” must be read to mean “must” and any recommendation or suggestion must be read as an obligation.
Marginal note:Standards incorporated by reference
(3) Any standard of the ASTM, Gas Processors Association or the API that is incorporated by reference into these Regulations is incorporated as amended from time to time.
Application
Marginal note:New generation of electricity — boiler units
3 (1) These Regulations apply to any boiler unit that has a capacity of 25 MW or more, that begins generating electricity on or after January 1, 2019, beginning on January 1 of the calendar year during which it meets the following conditions:
(a) more than 30% of its heat input, on average, during the calendar year, comes from the combustion of natural gas;
(b) its heat to electricity ratio is not more than 0.9; and
(c) a quantity of the electricity that it generates is sold or distributed to the electric grid.
Marginal note:New generation of electricity — combustion engine units
(2) These Regulations apply to any combustion engine unit that has a capacity of 25 MW or more, that begins generating electricity on or after January 1, 2021, beginning on January 1 of the calendar year during which it meets the following conditions:
(a) more than 30% of its heat input, on average, during the calendar year, comes from the combustion of natural gas; and
(b) 33% or more of its potential electrical output is sold or distributed to the electric grid, without regard to the quantity of electricity sold or distributed to the electric grid coming from the unit if the unit is equipped with replacement combustion engines that are temporarily installed, for a period of not more than 90 days, as part of repairs or maintenance, during the replacement period.
Marginal note:Existing generation of electricity
(3) These Regulations also apply to any unit referred to in subsection (1) or (2) that generated electricity at a facility before January 1, 2019 in the case of a boiler unit and before January 1, 2021 in the case of a combustion engine unit and
(a) was moved to another facility on or after whichever of those dates is applicable; or
(b) is a combustion engine unit for which more than 50% of the total capacity of the combustion engines comes from combustion engines installed on or after January 1, 2021, unless they are engines that have a capacity of 150 MW or less and are installed to replace engines that have a capacity of 150 MW or less and that are installed before January 1, 2021.
Marginal note:Significantly modified — conversion to natural gas
(4) These Regulations also apply to any boiler unit referred to in subsection (1) that was registered under subsection 4(1) of the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations, and that generated electricity before January 1, 2019, beginning on January 1 of the calendar year following that in which the unit ceases to combust coal.
Marginal note:Hybrid configuration
(5) If a combustion engine unit and a boiler unit share the same steam turbine, the provisions of these Regulations apply as follows:
(a) with respect to a combustion engine unit, they apply to the assembly comprised of combustion engines and any other equipment connected to them including the steam turbine that it shares with the boiler unit; and
(b) with respect to a boiler unit, they apply to the assembly comprised of boilers and any other equipment connected to them including the steam turbine that it shares with the combustion engine unit.
Marginal note:Non-application
(6) These Regulations do not apply to units with respect to a calendar year in which they generate electricity and, if applicable, produce useful thermal energy from the combustion of coal as defined in subsection 2(1) of the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations.
Requirements
Emission Intensity Limits
Marginal note:General
4 (1) A responsible person for a unit must not emit from the unit an amount of CO2 from the combustion of fossil fuels in the unit, that is, during a calendar year, on average, greater than any of the following intensity limits, as applicable:
(a) 420 tonnes of CO2 emissions/GWh of energy produced
(i) in the case of boiler units, other than those referred to in subsection 3(4), and
(ii) in the case of combustion engine units that are equipped with at least one combustion engine that has a capacity of more than 150 MW; and
(b) 550 tonnes of CO2 emissions/GWh of energy produced in the case of combustion engine units that are equipped with combustion engines that have a capacity of 150 MW or less.
Marginal note:Significantly modified boiler units
(2) It is prohibited for a responsible person for a boiler unit referred to in subsection 3(4) to emit from the boiler unit an amount of CO2, from the combustion of fossil fuels in the unit, that is, during a calendar year, on average, greater than 420 tonnes of CO2 emissions/GWh of energy produced, as applicable, beginning in
(a) the year after the unit’s end of useful life, if the initial performance test conducted under subsection 5(1) indicates a CO2 emissions intensity greater than 600 t/GWh;
(b) the sixth year after the unit’s end of useful life, if the initial performance test conducted under subsection 5(1) indicates a CO2 emissions intensity greater than 550 t/GWh and less than or equal to 600 t/GWh;
(c) the ninth year after the unit’s end of useful life, if the initial performance test conducted under subsection 5(1) indicates a CO2 emissions intensity greater than 480 t/GWh and less than or equal to 550 t/GWh; or
(d) the eleventh year after the unit’s end of useful life, if the initial performance test conducted under subsection 5(1) results in a CO2 emissions intensity less than or equal to 480 t/GWh.
Marginal note:Quantification of energy and emissions
(3) For the purposes of subsections (1) and (2),
(a) the quantity of energy produced in the calendar year must be determined in accordance with section 11; and
(b) the quantity of CO2 emissions produced in the calendar year must be determined in accordance with sections 12 to 18, as applicable.
Marginal note:Special Rules
(4) For the purposes of subsection (3), if, in the calendar year, one of the combustion engines of the unit is repaired or maintained and one or more replacement combustion engines are temporarily installed, the quantity of energy and CO2 emissions produced during the replacement period, to a maximum of 90 days per calendar year, are excluded from the calculation referred to in that paragraph.
Marginal note:Exception — boiler unit
(5) Despite subsection (1), a boiler unit that, in a calendar year, does not meet one of the conditions set out in subsection 3(1), is not subject to the emission intensity limit for that calendar year.
Marginal note:Exception — combustion engine
(6) Despite subsection (1), a combustion engine unit that, in a calendar year, does not meet one of the conditions set out in subsection 3(2), is not subject to the emission intensity limit for that calendar year.
Performance Tests — Significantly Modified Boiler Units
Marginal note:Initial performance test
5 (1) An initial performance test must be conducted in the presence of the performance test verifier and in accordance with subsection (3) to determine the CO2 emission intensity for a boiler unit referred to in subsection 3(4) within 12 months following
(a) in the case of a unit that has ceased to combust coal before January 1, 2019, January 1, 2019; or
(b) in the case of a unit that ceases to combust coal on or after January 1, 2019, the day on which electricity generated from the boiler unit was first sold or distributed to the electric grid, in the calendar year in which the unit becomes subject to these Regulations.
Marginal note:Annual performance test
(2) Performance tests are to be subsequently conducted annually to determine the CO2 emission intensity for the boiler unit in question, in accordance with subsection (3), for as long as the responsible person for that boiler unit does not have to meet the emission limit referred to in subsection 4(2).
Marginal note:Conditions — test
(3) The initial and annual performance test must consist of a continuous test that lasts at least two hours and does not exceed 100% of the unit’s capacity.
Marginal note:Quantification
(4) For the purposes of subsections (1) and (2),
(a) the quantity of energy produced by the unit must be determined in accordance with section 11; and
(b) the quantity of CO2 emitted by the unit must be determined in accordance with sections 12, 13 and 15 to 18, as applicable: however, all emissions must be quantified including those from the combustion of biomass.
Marginal note:Adaptation
(5) For the performance test, the reference to “calendar year” in sections 11, 12, 15, 17 and 18 and in the Reference Method is replaced with a reference to “performance test period”.
Marginal note:Requirement
6 A responsible person for a unit referred to in subsection 3(4) must obtain an annual performance test result that shows less than a 2% increase in emission intensity from the previous performance test.
Emergency Circumstances
Marginal note:Application for exemption
7 (1) A responsible person for a unit may, under an emergency circumstance described in subsection (2), apply to the Minister for an exemption from the application of subsection 4(1) or (2) in respect of the unit if, as a result of the emergency, the operator of the electricity grid in the province in which the unit is located or an official of that province responsible for ensuring and supervising the electricity supply orders the responsible person to produce electricity to avoid a threat to the supply or to restore that supply.
Marginal note:Definition of emergency circumstance
(2) An emergency circumstance is a circumstance
(a) that arises due to an extraordinary, unforeseen and irresistible event; or
(b) under which one or more of the measures referred to in paragraph 1(a) of the Regulations Prescribing Circumstances for Granting Waivers Pursuant to Section 147 of the Act has been made or issued in the province where the unit is located.
Marginal note:Deadline for application
(3) The application for the exemption must be provided to the Minister within 15 days after the day on which the emergency circumstance arises. The application must include the information referred to in section 1 and paragraphs 2(a), (b) and (d) of Schedule 1 or the unit’s registration number, if any, the date on which the emergency circumstance arose and information, along with supporting documents, to demonstrate that the conditions set out in subsection (1) are met.
Marginal note:Minister’s decision
(4) If the Minister is satisfied that the conditions set out in subsection (1) are met, the Minister must, within 30 days after the day on which the application is received,
(a) grant the exemption; and
(b) if the unit has not been assigned a registration number, assign a registration number and inform the responsible person of that number.
Marginal note:Duration of exemption
(5) The exemption becomes effective on the day on which the emergency circumstance arises and ceases to have effect on the earliest of
(a) the ninetieth day after that day,
(b) the day specified by the Minister,
(c) the day on which the circumstance referred to in paragraph (2)(a) ceases to cause a disruption, or a significant risk of disruption, to the electricity supply in the province where the unit is located, and
(d) the day on which the measure, if any, referred to in paragraph (2)(b) ceases to have effect.
Marginal note:Application for extension of exemption
8 (1) If the conditions set out in subsection 7(1) will continue to exist after the day on which the exemption granted under paragraph 7(4)(a) is to cease to have effect, the responsible person may, before that day, apply to the Minister for an extension of the exemption.
Marginal note:Contents of application
(2) The application must include the unit’s registration number and information, along with supporting documents, to demonstrate that
(a) the conditions set out in subsection 7(1) will continue to exist after the day on which the exemption is to cease to have effect; and
(b) measures — other than the operation of the unit while the exemption has effect — have been or are being taken to end, decrease the risk of or mitigate the consequences of the disruption.
Marginal note:Minister’s decision
(3) If the Minister is satisfied that the elements referred to in paragraphs (2)(a) and (b) have been demonstrated, the Minister must grant the extension within 15 days after the day on which the application is received.
Marginal note:Duration of extension
(4) The extension ceases to have effect on the earliest of
(a) the ninetieth day after the day on which the application for the extension was made,
(b) the day specified by the Minister, and
(c) the day referred to in paragraph 7(5)(c).
Accuracy of Data
Marginal note:Measuring devices — installation, maintenance and calibration
9 (1) A responsible person for a unit must install, maintain and calibrate a measuring device — other than a continuous emission monitoring system and a measuring device that is subject to the Electricity and Gas Inspection Act — that is used for the purposes of these Regulations in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions or any applicable generally recognized national or international industry standard.
Marginal note:Frequency of calibration
(2) The responsible person must calibrate each of the measuring devices at the greater of the following frequencies:
(a) at least once in every calendar year but at least five months after a previous calibration, and
(b) the minimum frequency recommended by the manufacturer.
Marginal note:Accuracy of measurements
(3) The responsible person must use measuring devices that enable measurements to be made with a degree of accuracy of ± 5%.
Marginal note:Certification of CEMS
10 The responsible person must certify the CEMS in accordance with section 5 of the Reference Method, before it is used for the purposes of these Regulations.
Quantification Rules
Production of Energy
Marginal note:Quantity of energy
11 (1) The quantity of energy produced by a given unit is determined by the formula
G + (0.75 × Hpnet)
where
- G
- is
(a) the gross quantity of electricity generated by the unit in the calendar year expressed in GWh, as measured at the electrical terminals of the generators of the unit using meters that comply with the requirements of the Electricity and Gas Inspection Act and the Electricity and Gas Inspection Regulations, or
(b) in the case of a hybrid configuration – when the unit is either a combustion engine unit that shares a steam turbine with a boiler unit or a boiler unit that shares a steam turbine with a combustion engine unit – the quantity of electricity generated by the given unit in the calendar year expressed in GWh, determined by the formula in subsection (2); and
- Hpnet
- is the net quantity of useful thermal energy produced by the unit in a calendar year, expressed in GWh, determined by the formula in subsection (3).
Marginal note:Quantity of electricity — hybrid configuration
(2) The quantity of electricity generated by a given unit is determined by the formula
Gce + Gs – Gext
where
- Gce
- is the gross quantity of electricity that is generated by the generators of the combustion engines in a combustion engine unit that shares a steam turbine with a boiler unit, in the calendar year, expressed in GWh, as measured at the electrical terminals of the generators of the combustion engines using meters that comply with the requirements of the Electricity and Gas Inspection Act and the Electricity and Gas Inspection Regulations, if the given unit for which the electricity is being quantified is a combustion engine unit, or equal to zero, if the given unit for which the electricity is being quantified is a boiler unit;
- Gs
- is the gross quantity of electricity that is generated by the generators of the shared steam turbine in the calendar year, expressed in GWh, as measured at the electrical terminals of the generators of the shared steam turbine using meters that comply with the requirements of the Electricity and Gas Inspection Act and the Electricity and Gas Inspection Regulations; and
- Gext
- is the quantity of electricity that is generated by the unit other than the given unit for which the electricity is being quantified, in the calendar year, expressed in GWh and that is determined by the formula

where
- Gs
- is the gross quantity of electricity that is generated by the generators of the shared steam turbine in the calendar year, expressed in GWh, as measured at the electrical terminals of the generators of the shared steam turbine using meters that comply with the requirements of the Electricity and Gas Inspection Act and the Electricity and Gas Inspection Regulations,
- t
- is the tth hour, where “t” goes from the number 1 to x and where x is the total number of hours during which the generators of the shared steam turbine generated electricity in the calendar year,
- j
- is the jth external heat stream, originating from the other unit where “j” goes from the number 1 to m and where m is the total number of external heat streams that contributed to the electricity generated by the generators of the shared steam turbine of the unit,
- hext_j
- is the average specific enthalpy of the jth external heat stream, originating from the other unit that contributed to the electricity generated by the generators of the shared steam turbine, expressed in GJ/tonne, during period “t” and must be based on the measurement of the temperature and pressure of that heat stream and determined using a continuous measuring device,
- Mext_j
- is the mass flow of the jth external heat stream originating from the other unit that contributed to the electricity generated by the generators of the shared steam turbine, expressed in tonnes, during period “t”, determined using a continuous measuring device,
- k
- is the kth internal heat stream originating from the given unit, where “k” goes from the number 1 to l and where l is the total number of heat streams that originated from the combustion of fuel in the unit and that contributed to the electricity generated by the generators of the shared steam turbine,
- hint_k
- is the average specific enthalpy of the kth internal heat stream originating from the given unit and having contributed to the electricity generated by the generators of the shared steam turbine, expressed in GJ/tonne, during period “t” and must be based on the measurement of the temperature and pressure of that heat stream and determined using a continuous measuring device, and
- Mint_k
- is the mass flow of the kth internal heat stream originating from the given unit that contributed to the electricity generated by the generators of the shared steam turbine, expressed in tonnes, during period “t”, determined using a continuous measuring device.
Marginal note:Net quantity of useful thermal energy
(3) In the case of a unit that simultaneously generates electricity and produces useful thermal energy from the fuel combusted by a combustion engine or boiler, as the case may be, the net quantity of useful thermal energy produced by the unit in a calendar year, expressed in GWh, is determined by the formula

where
- t
- is the tth hour, where “t” goes from the number 1 to x and where x is the total number of hours during which the unit produced useful thermal energy in the calendar year;
- i
- is the ith heat stream exiting the unit, where “i” goes from the number 1 to n and where n is the total number of heat streams exiting the unit;
- hout_i
- is the average specific enthalpy of the ith heat stream exiting the unit, expressed in GJ/tonne, during period “t” and must be based on the measurement of the temperature and pressure of that heat stream and determined using a continuous measuring device;
- Mout_i
- is the mass flow of the ith heat stream exiting the unit, expressed in tonnes, during period “t”, determined using a continuous measuring device;
- j
- is the jth heat stream — other than condensate return — entering the unit, where “j” goes from the number 1 to m and where m is the total number of heat streams entering the unit;
- hin_j
- is the average specific enthalpy of the jth heat stream — other than condensate return — entering the unit, expressed in GJ/tonne, during period “t” and must be based on the measurement of the temperature and pressure of that heat stream and determined using a continuous measuring device; and
- Min_j
- is the mass flow of the jth heat stream — other than condensate return — entering the unit, expressed in tonnes, during period “t”, determined using a continuous measuring device.
CO2 Emissions
Quantification Methods
Marginal note:Choice of method
12 The quantity of CO2 emissions resulting from the combustion of fossil fuels in a unit in a calendar year must be determined
(a) in accordance with section 13 or 14, using a CEMS; or
(b) in accordance with sections 17 and 18, using a fuel-based method.
Continuous Emission Monitoring System
Marginal note:Unit not combusting biomass
13 Subject to section 15, the quantity of CO2 emissions resulting from combustion of fossil fuels in a unit that does not combust biomass that is measured using a CEMS must be calculated in accordance with sections 7.1 to 7.7 of the Reference Method.
Marginal note:Unit combusting biomass
14 (1) Subject to section 15, the quantity of CO2 emissions resulting from the combustion of fossil fuels in a unit combusting biomass in a calendar year that is measured using a CEMS must be determined in accordance with the following formula:
Eu × (Vff / VT) – Es
where
- Eu
- is the quantity of CO2 emissions, expressed in tonnes, from the unit, “u”, during the calendar year from the combustion of fuel, as measured by the CEMS, and calculated in accordance with sections 7.1 to 7.7 of the Reference Method;
- Vff
- is the volume of CO2 emissions released from combustion of fossil fuel in the unit during the calendar year, expressed in standard m3 and determined in accordance with the following formula:

where
- Qi
- is the quantity of fossil fuel type “i” combusted in the unit during the calendar year, determined
(a) for a gaseous fuel, in the same manner used in the determination of Vf in the formula set out in paragraph 18(1)(a) and expressed in standard m3,
(b) for a liquid fuel, in the same manner used in the determination of Vf in the formula set out in paragraph 18(1)(b) and expressed in kL, and
(c) for a solid fuel, in the same manner used in the determination of Mf in the formula set out in paragraph 18(1)(c) and expressed in tonnes,
- i
- is the ith fossil fuel type combusted in the unit during the calendar year, where “i” goes from the number 1 to n and where n is the number of fossil fuels so combusted,
- Fc,i
- is the fuel-specific carbon-based F-factor for each fossil fuel type “i” — being the factor set out in Appendix A of the Reference Method, or for fuels not listed, the one determined in accordance with that Appendix — corrected to be expressed in standard m3 of CO2/GJ, and
- HHVi
- is the higher heating value for each fossil fuel type “i” that is measured in accordance with subsection (2), or in the absence of a measured higher heating value, the default higher heating value, set out in column 2 of Schedule 2, for the fuel type, as set out in column 1;
- VT
- is the volume of CO2 emissions released from combustion of fuel — fossil fuel and biomass — in the unit during the calendar year determined in accordance with the following formula:

where
- t
- is the tth hour, where “t” goes from the number 1 to n and where n is the total number of hours during which the unit generated electricity in the calendar year,
- CO2w,t
- is the average concentration of CO2 in relation to all gases in the stack emitted from the combustion of fuel in the unit during each hour “t”, during which the unit generated electricity in the calendar year — or, if applicable, a calculation made in accordance with section 7.4 of the Reference Method of that average concentration of CO2 based on a measurement of the concentration of oxygen (O2) in those gases in the stack — expressed as a percentage on a wet basis, and
- Qw,t
- is the average volumetric flow during that hour, measured on a wet basis by the stack gas volumetric flow monitor, expressed in standard m3; and
- Es
- is the quantity of CO2 emissions, expressed in tonnes, that is released from the use of sorbent to control the emission of sulphur dioxide from the unit during the calendar year, determined in accordance with the following formula:
S × R × (44/MMs)
where
- S
- is the quantity of sorbent material, such as calcium carbonate (CaCO3), expressed in tonnes,
- R
- is the stoichiometric ratio, on a mole fraction basis, of CO2 released on usage of one mole of sorbent material, which is equal to 1 if the sorbent material is CaCO3, and
- MMs
- is the molecular mass of the sorbent material, which is equal to 100 if the sorbent material is CaCO3.
Marginal note:Higher heating value
(2) The higher heating value of a fuel is to be measured
(a) for a gaseous fuel,
(i) in accordance with whichever of the following standards that applies:
(A) ASTM D1826 - 94(2017), entitled Standard Test Method for Calorific (Heating) Value of Gases in Natural Gas Range by Continuous Recording Calorimeter,
(B) ASTM D3588 - 98(2017), entitled Standard Practice for Calculating Heat Value, Compressibility Factor, and Relative Density of Gaseous Fuels,
(C) ASTM D4891 - 13, entitled Standard Test Method for Heating Value of Gases in Natural Gas and Flare Gases Range by Stoichiometric Combustion,
(D) Gas Processors Association Standard 2172 - 14, entitled Calculation of Gross Heating Value, Relative Density, Compressibility and Theoretical Hydrocarbon Liquid Content for Natural Gas Mixtures for Custody Transfer, and
(E) Gas Processors Association standard 2261 - 13, entitled Analysis for Natural Gas and Similar Gaseous Mixtures by Gas Chromatography, or
(ii) by means of a direct measuring device that measures the higher heating value of the fuel, but if the measuring device provides only lower heating values, those lower heating values must be converted to higher heating values; and
(b) for a liquid fuel that is
(i) an oil or a liquid fuel derived from waste, in accordance with
(A) ASTM D240 - 17, entitled Standard Test Method for Heat of Combustion of Liquid Hydrocarbon Fuels by Bomb Calorimeter, or
(B) ASTM D4809 - 13, entitled Standard Test Method for Heat of Combustion of Liquid Hydrocarbon Fuels by Bomb Calorimeter (Precision Method), and
(ii) any other liquid fuel type, in accordance with an applicable ASTM standard for the measurement of the higher heating value of the fuel type or, if no such ASTM standard applies, in accordance with an applicable internationally recognized method.
Marginal note:Multiple CEMS per unit
15 (1) For the purposes of sections 13 and 14, the total quantity of CO2 emissions from a unit equipped with multiple CEMS is determined by adding together the quantity of emissions measured for each CEMS.
Marginal note:Units sharing common stack
(2) If a unit is located at a facility where there is one or more other units and a CEMS measures emissions from that unit and other units at a common stack rather than at the exhaust duct of that unit and of each of those other units that brings those emissions to the common stack, then the quantity of emissions attributable to that unit is determined based on the ratio of the heat input of that unit to the total of the heat input of that unit and of all of those other units sharing the common stack in accordance with the following formula:

where
- Qu,j
- is the quantity of fuel type “j” combusted in that unit “u” during the calendar year, determined
(a) for a gaseous fuel, in the same manner as the one used in the determination of Vf in the formula set out in paragraph 18(1)(a) and expressed in standard m3,
(b) for a liquid fuel, in the same manner as the one used in the determination of Vf in the formula set out in paragraph 18(1)(b) and expressed in kL, and
(c) for a solid fuel, in the same manner as the one used in the determination of Mf in the formula set out in paragraph 18(1)(c) and expressed in tonnes;
- HHVu,j
- is the higher heating value for each fossil fuel type “j” that is combusted in that unit “u” that is measured in accordance with subsection 14(2), or in the absence of a measured higher heating value, the default higher heating value, set out in column 2 of Schedule 2, for the fuel type, as set out in column 1;
- j
- is the jth fuel type combusted during the calendar year in a unit where “j” goes from the number 1 to y and where y is the number of those fuel types;
- Qi,j
- the quantity of fuel type “j” combusted in each unit “i” during the calendar year, determined for a gaseous fuel, a liquid fuel and a solid fuel, respectively, in the manner set out in the description of Quj;
- HHVi,j
- is the higher heating value for each fossil fuel type “j” that is combusted in that unit “i” that is measured in accordance with subsection 14(2), or in the absence of a measured higher heating value, the default higher heating value, set out in column 2 of Schedule 2, for the fuel type, as set out in column 1;
- i
- is the ith unit, where “i” goes from the number 1 to x, and where x is the number of units that share a common stack; and
- E
- is the quantity of CO2 emissions, expressed in tonnes, from the combustion of all fuels in all the units that share a common stack during the calendar year, measured by a CEMS at the common stack, and calculated in accordance with sections 7.1 to 7.7 of the Reference Method.
Marginal note:If using a CEMS
16 (1) A responsible person who uses a CEMS must ensure compliance with the Reference Method.
Marginal note:Auditor’s report
(2) For each calendar year during which the responsible person used a CEMS, they must obtain a report, signed by the auditor, that contains the information required by Schedule 3 and send it to the Minister with the report referred to in section 21.
Fuel-based Method
Marginal note:Quantification
17 The quantity of CO2 emissions resulting from the combustion of fossil fuels in a unit in a calendar year, that is not measured using a CEMS, is determined by the formula
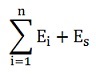
where
- i
- is the ith fossil fuel type that is combusted in the calendar year in a unit, where “i” goes from the number 1 to n and where n is the number of those fossil fuel types;
- Ei
- is the quantity of CO2 emissions that is attributable to the combustion of fossil fuels of type “i” in the unit in the calendar year, expressed in tonnes, as determined for that fuel type in accordance with section 18; and
- Es
- is the quantity of CO2 emissions that is released from the sorbent used to control the emission of sulphur dioxide from the unit in the calendar year, expressed in tonnes, as determined by the formula
S × R × (44/MMs)
where
- S
- is the quantity of sorbent material, such as calcium carbonate (CaCO3) , expressed in tonnes,
- R
- is the stoichiometric ratio, on a mole fraction basis, of CO2 released on usage of 1 mole of sorbent material, which is equal to 1 if the sorbent material is CaCO3, and
- MMs
- is the molecular mass of the sorbent material, which is equal to 100 if the sorbent material is CaCO3.
Marginal note:Measured carbon content
18 (1) The quantity of CO2 emissions, that is attributable to the combustion of a fossil fuel in a unit in a calendar year is determined by one of the following formulas, whichever applies:
(a) for a gaseous fuel,
Vf × CCA × (MMA/MVcf) × 3.664 × 0.001
where
- Vf
- is the volume of the fuel combusted in the calendar year, determined using flow meters, expressed in standard m3,
- CCA
- is the weighted average of the carbon content of the fuel, determined in accordance with subsection (2), expressed in kg of carbon per kg of the fuel,
- MMA
- is the average molecular mass of the fuel, determined based on fuel samples taken in accordance with section 19, expressed in kg per kg-mole of the fuel, and
- MVcf
- is the molar volume conversion factor of 23.645 standard m3 per kg-mole of the fuel at standard conditions;
(b) for a liquid fuel,
Vf × CCA × 3.664
where
- Vf
- is the volume of the fuel combusted in the calendar year, determined using flow meters, expressed in kL , and
- CCA
- is the weighted average of the carbon content of the fuel, determined in accordance with subsection (2), at the same temperature as that used in the determination of Vf, expressed in tonnes of carbon per kL of the fuel; and
(c) for a solid fuel,
Mf × CCA × 3.664
where
- Mf
- is the mass of the fuel combusted in the calendar year, determined, as the case may be, on a wet or dry basis using a measuring device, expressed in tonnes, and
- CCA
- is the weighted average of the carbon content of the fuel, determined in accordance with subsection (2), on the same wet or dry basis as that used in the determination of Mf, expressed in kg of carbon per kg of the fuel.
Marginal note:Weighted average
(2) The weighted average “CCA” referred to in paragraphs (1)(a) to (c) is determined by the formula
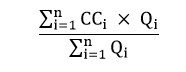
where
- CCi
- is the carbon content of each sample or composite sample, as the case may be, of the fuel for the ith sampling period, expressed for gaseous fuels, liquid fuels and solid fuels, respectively, in the same unit of measure as that set out in CCA, as provided by the supplier of the fuel to the responsible person or, if not so provided, as determined by the responsible person in the following manner:
(a) for a gaseous fuel,
(i) in accordance with whichever of the following standards for the measurement of the carbon content of the fuel that applies:
(A) ASTM D1945-14, entitled Standard Test Method for Analysis of Natural Gas by Gas Chromatography,
(B) ASTM UOP539-12, entitled Refinery Gas Analysis by Gas Chromatography,
(C) ASTM D7833-14, entitled Standard Test Method for Determination of Hydrocarbons and Non-Hydrocarbon Gases in Gaseous Mixtures by Gas Chromatography, and
(D) API Technical Report 2572, 1st edition, published in May 2013 and entitled Carbon Content, Sampling, and Calculation, or
(ii) by means of a direct measuring device that measures the carbon content of the fuel,
(b) for a liquid fuel, in accordance with whichever of the following standards or methods for the measurement of the carbon content of the fuel that applies:
(i) API Technical Report 2572, 1st edition, published in May 2013 and entitled Carbon Content, Sampling, and Calculation,
(ii) ASTM D5291-16, entitled Standard Test Methods for Instrumental Determination of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Nitrogen in Petroleum Products and Lubricants,
(iii) the ASTM standard that applies to the type of fuel, or
(iv) if no ASTM standard applies, an applicable internationally recognized method, and
(c) for a solid fuel, on the same wet or dry basis as that used in the determination of CCA, in accordance with,
(i) for a solid fuel derived from waste, ASTM E777-08, entitled Standard Test Method for Carbon and Hydrogen in the Analysis Sample of Refuse-Derived Fuel, and
(ii) for any other solid fuel, the following standard or method for the measurement of the carbon content of the fuel:
(A) the ASTM standard that applies to the type of fuel, and
(B) if no ASTM standard applies, an applicable internationally recognized method;
- i
- is the ith sampling period that is referred to in section 19, where “i” goes from the number 1 to n and where n is the number of those sampling periods; and
- Qi
- is the volume or mass, as the case may be, of the fuel combusted during the ith sampling period, expressed
(a) in standard m3, for a gaseous fuel,
(b) in kL, for a liquid fuel, and
(c) in tonnes, for a solid fuel, on the same wet or dry basis as that used in the determination of CCA.
Sampling and Missing Data
Marginal note:Sampling
19 (1) Subject to subsection (2), the determination of the value of the elements related to carbon content referred to in section 18 must be based on fuel samples taken in accordance with this section.
Marginal note:Carbon content provided by the supplier
(2) If the supplier of the fuel has provided the carbon content of the fuel, the responsible person can obtain from that supplier the carbon content of the fuel for the specified sampling period and at the specified minimum sampling frequency rather than taking samples in accordance with subsection (3).
Marginal note:Frequency
(3) Each fuel sample must be taken at a time and location in the fuel handling system of the facility that provides the following representative samples of the fuel combusted at the applicable minimum frequency:
(a) for natural gas, during each sampling period consisting of each year that the unit generates electricity or produces useful thermal energy, two samples taken that year, with each of those samples being taken at least four months after any previous sample has been taken, in accordance with whichever of the following standard that applies:
(i) ASTM D4057-12, entitled Standard Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products,
(ii) ASTM D4177-16e1, entitled Standard Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products,
(iii) ASTM D5287-08(2015), entitled Standard Practice for Automatic Sampling of Gaseous Fuels, and
(iv) ASTM F307-13, entitled Standard Practice for Sampling Pressurized Gas for Gas Analysis;
(b) for refinery gas, during each sampling period consisting of each day that the unit generates electricity or produces useful thermal energy, one sample per day that is taken at least six hours after any previous sample has been taken, in accordance with any applicable standard referred to in paragraph (a);
(c) for a type of liquid fuel or of a gaseous fuel other than refinery gas and natural gas, during each sampling period consisting of each month that the unit generates electricity or produces useful thermal energy, one sample per month that is taken at least two weeks after any previous sample has been taken, in accordance with any of the standards referred to in paragraph (a); and
(d) for a solid fuel, one composite sample per month that consists of sub-samples, each having the same mass, that are taken from the fuel that is fed for combustion during each week that begins in that month and during which the unit generates electricity or produces useful thermal energy, and after all fuel treatment operations have been carried out but before any mixing of the fuel from which the sub-sample is taken with other fuels, and at least 72 hours after any previous sub-sample has been taken.
Marginal note:Additional samples
(4) For greater certainty, the responsible person who, for the purposes of these Regulations, takes more samples than the minimum required under subsection (3) must make the determination referred to in subsection (1) based on each sample taken — and in the case of composite samples, each sub-sample taken — including those additional samples.
Marginal note:Significantly modified boiler units
(5) In the case of a boiler unit referred to in subsection 3(4), one fuel sample is required for the initial performance test and each subsequent performance test and it must be taken in accordance with one of the applicable standards set out in subparagraphs (3)(a)(i) to (iv).
Marginal note:Missing data
20 (1) Except in the case of an initial performance test or any subsequent performance test referred to in section 5, if, for any reason beyond the responsible person’s control, the emission intensity referred to in subsection 4(1) or 4(2) cannot be determined in accordance with a formula set out in any of sections 11, 17 and 18 because data required to determine the value of an element of that formula is missing for a given period in a calendar year, replacement data for that given period must be used to determine that value.
Marginal note:Replacement data — CEMS
(2) If a CEMS is used to determine the value of an element of a formula set out in section 17 but data is missing for a given period, the replacement data must be obtained in accordance with Section 3.5.2 of the Reference Method.
Marginal note:Replacement data — fuel-based methods
(3) If a fuel-based method is used to determine the value of any element — related to the carbon content or molecular mass of a fuel — of a formula set out in section 17 or 18 but data is missing for a given period, the replacement data is to be the average of the available data for that element, using the fuel-based method in question, during the equivalent period prior to and, if the data is available, subsequent to that given period. However, if no data is available for that element for the equivalent period prior to that given period, the replacement data to be used is the value determined for that element, using the fuel-based method in question, during the equivalent period subsequent to the given period.
Marginal note:Replacement data — multiple periods
(4) Replacement data may be used in relation to a maximum of 28 days in a calendar year.
Reporting, Sending, Recording and Retaining Information
Marginal note:Annual reports
21 (1) Subject to subsection (2), a responsible person for a unit must send one of the following reports, to the Minister on or before the June 1 that follows the calendar year that is the subject of the report:
(a) a report containing the information set out in Schedule 1 in respect of each calendar year in which the unit meets the conditions set out in subsection 3(1) or (2), as the case may be;
(b) a short report containing the information referred to in sections 1 and 2, except paragraph 2(h), of Schedule 1 in respect of each calendar year in which the unit no longer meets one of the conditions referred to in subsection 3(1) or (2), as the case may be.
Marginal note:Significantly modified boiler units
(2) A responsible person for a boiler unit referred to in subsection 3(4) must send the reports referred to in subsection (1), beginning in the year in which it must meet the emission limit referred to in subsection 4(2).
Marginal note:Permanent cessation of electricity generation
(3) If a unit permanently ceases to generate electricity in a calendar year, a responsible person for the unit must so notify the Minister in writing not later than 60 days after the day on which the unit ceases generating electricity. A report is not necessary in respect of the calendar years following the calendar year in which the unit ceases generating electricity.
Marginal note:Registration number
(4) On receipt of a first report in respect of a unit referred to in paragraph (1)(a), the Minister must assign a registration number to the unit and inform the responsible person of that number.
Marginal note:Change of information
(5) If there is a change to the information referred to in section 1 of Schedule 1 that was provided in the most recent report, the responsible person must notify the Minister of the change in writing not later than 30 days after the day on which the change is made.
Marginal note:Performance test reporting
22 (1) A responsible person for a boiler unit referred to in subsection 3(4) must send, to the Minister, a report containing the information referred to in Schedule 4 in relation to the performance test identified in section 5 no later than 60 days after the performance test was conducted.
Marginal note:Performance test verifier’s report — initial test
(2) In the case of a boiler unit referred to in subsection 3(4), the responsible person must obtain a report, signed by the performance test verifier, on the initial performance test, that contains the information referred to in Schedule 5 and send it to the Minister with their report referred to in subsection (1).
Marginal note:Electronic report, notice and application
23 (1) A report or notice that is required, or an application that is made, under these Regulations must be sent electronically in the form specified by the Minister and must bear the electronic signature of an authorized official of the responsible person.
Marginal note:Paper report or notice
(2) If the Minister has not specified an electronic form or if the person is unable to send the report, notice or application electronically in accordance with subsection (1) because of circumstances beyond the person’s control, the report, notice or application must be sent on paper, in the form specified by the Minister, if applicable, and be signed by an authorized official of the responsible person.
Marginal note:Maintain copy
24 (1) A responsible person for a unit must make a record containing the following documents and information:
(a) any notice referred to in subsection 21(5) that was sent to the Minister along with supporting documents;
(b) any application referred to in subsection 7(3) or 8(2), whichever applies, along with supporting documents;
(c) every measurement and calculation used to determine the value of an element of a formula used for the purposes of section 4 and, if applicable, section 5, along with an indication of the standards that were used to determine the value of the elements used in those formula and any necessary supporting documents;
(d) an indication of the standards or methods referred to in the description of CCi in subsection 18(2) that were used to determine the value of CCA in paragraph 18(1)(a), (b) or (c), as the case may be, or, for a sample of gaseous fuel, a statement that indicates that a direct measuring device was used to determine that value;
(e) information demonstrating that any meter referred to in section 11 complies with the requirements of the Electricity and Gas Inspection Act and the Electricity and Gas Inspection Regulations, including a certificate referred to in section 14 of that Act;
(f) information demonstrating that the installation, maintenance and calibration of the measuring devices referred to in subsection 9(1) were done in accordance with that subsection and subsection 9(2) and that the measuring devices used comply with subsection 9(3);
(g) supporting documents that confirm the CEMS certification under section 10;
(h) any document, record or information referred to in section 8 of the Reference Method, for each calendar year during which a responsible person used a CEMS;
(i) the results of the analysis of every sample taken in accordance with section 19, as well as the date that each sample was taken and an indication of the standards that were used to take representative samples of the fuel;
(j) information demonstrating the unit capacity set out in the annual report;
(k) in the case of a unit that has a combustion engine that is temporarily installed for a period of 90 days or less as part of repair or maintenance,
(i) evidence that the combustion engine underwent repairs or maintenance and that a replacement combustion engine was temporarily connected to the unit for the duration of the repairs or maintenance,
(ii) the number of days that a replacement combustion engine was connected to the unit, and
(iii) the number of days that the repairs or maintenance lasted;
(l) information demonstrating each combustion engine capacity set out in the annual report, the date on which each combustion engine was installed and, in the case of a combustion engine with a capacity of 150 MW or less, a statement that, if applicable, the combustion engine was installed to replace an engine, with a capacity of 150 MW or less, as part of repair or maintenance; and
(m) any report referred to in section 22, along with supporting documents.
Marginal note:30 days
(2) The record referred to in subsection (1) must be made as soon as feasible but not later than 30 days after the day on which the information and documents to be included in it become available.
Marginal note:Retention of records and reports
25 A responsible person who is required under these Regulations to make a record or send a report or notice must keep the record or a copy of the report or notice, along with the supporting documents, at their principal place of business in Canada for at least seven years after they make the record or send the report or notice.
Coming into Force
Marginal note:Registration
26 (1) Subject to subsection (2), these Regulations come into force on January 1, 2019.
Marginal note:Deferred application
(2) These Regulations become applicable to combustion engine units on January 1, 2021.
SCHEDULE 1(Subsection 7(3), paragraphs 21(1)(a) and (b) and subsection 21(5))Annual Report — Information Required
1 The following information respecting the responsible person:
(a) an indication of whether they are the owner or operator of the unit and their name and civic address;
(b) the name, title, civic and postal addresses, telephone number and, if any, email address and fax number of their authorized official; and
(c) the name, title, civic and postal addresses, telephone number and, if any, email address and fax number of a contact person, if different from the authorized official.
2 The following information respecting the unit:
(a) for each responsible person for the unit, other than the responsible person mentioned in paragraph 1(a), if any,
(i) their name, title and civic address, and
(ii) an indication of whether they are the owner or operator;
(b) the unit’s name and civic address, if any;
(c) the unit’s registration number, if any;
(d) the name of the facility where the unit is located;
(e) the facility’s National Pollutant Release Inventory identification number assigned by the Minister for the purposes of section 48 of the Act, if any;
(f) the unit’s registration number, if any, assigned by the Minister under subsection 4(2) of the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations;
(g) whether the unit is a boiler unit or a combustion engine unit;
(h) a process flow diagram that shows
(i) the unit’s major equipment that operates together to generate electricity and, if applicable, produce thermal energy, including boilers, combustion engines, duct burners and other combustion devices, heat recovery systems, steam turbines, generators and emission control devices,
(ii) the unit boundaries used to identify the unit,
(iii) the electric flows crossing the unit boundaries, and
(iv) the heat streams crossing the unit boundaries and an indication of their average temperature, pressure and hourly mass flow rate;
(i) the unit’s capacity;
(j) for each of the unit’s combustion engines, the engine capacity and the date on which each combustion engine was installed, and in the case of combustion engine with a capacity of 150 MW or less, a statement that, if applicable, the combustion engine was installed to replace an engine, with a capacity of 150 MW or less, as part of repair or maintenance;
(k) the unit’s potential electrical output for the calendar year, expressed in GWh;
(l) as the case may be,
(i) in the case of a combustion engine unit, the percentage of the unit’s potential electrical output that is sold or distributed to the electric grid for the calendar year, and
(ii) in the case of a boiler unit, the quantity of electricity that is sold or distributed to the electric grid for the calendar year;
(m) the percentage of the unit’s heat input that comes from natural gas, on average for the calendar year; and
(n) in the case of a boiler unit, the value of the unit’s heat to electricity ratio.
3 The following information respecting the emission intensity referred to in subsection 4(1) or (2) of these Regulations resulting from the combustion of fossil fuel in the unit during the calendar year:
(a) the emission intensity for the unit — that is, the ratio of the quantity of CO2 emissions referred to in paragraph (c) to the quantity of energy referred to in subparagraph (b)(i) — expressed in tonnes per GWh;
(b) in respect of the quantity of energy produced by the unit,
(i) that quantity determined in accordance with section 11 of these Regulations, expressed in GWh,
(ii) the value determined for G and Hpnet in the formula set out in subsection 11(1) of these Regulations, expressed in GWh, and
(iii) the value determined for Gce, Gs and Gext in the formula set out in subsection 11(2) of these Regulations, expressed in GWh;
(c) in respect of the quantity of CO2 emissions from the combustion of fuels in the unit,
(i) if paragraph 12(a) of these Regulations applies, the result of the calculation made in accordance with section 13 or 14 and, if applicable, section 15 of these Regulations, expressed in tonnes, and
(ii) if paragraph 12(b) of these Regulations applies, the result of the calculation made in accordance with sections 17 and 18 of these Regulations, expressed in tonnes; and
(d) for each type of fuel combusted,
(i) the type and, if that type is biomass, an explanation of why that type is biomass as defined in subsection 2(1) of these Regulations, and
(ii) the quantity of fuel combusted.
4 The following information:
(a) in the case of a unit that is granted an exemption under paragraph 7(4)(a) of these Regulations, the duration of the emergency circumstance, such as the date on which the circumstance arose and the date on which it ceased; and
(b) in the case of a unit referred to in subsection 4(4) of these Regulations that is temporarily connected to one or more replacement combustion engines,
(i) the duration of the repairs or maintenance, such as the day in the calendar year on which the repairs or maintenance began and the day in the calendar year on which they ended, and
(ii) the reason why the replacement combustion engine was used.
5 A copy of the auditor’s report referred to in subsection 16(2) of these Regulations.
6 The following information respecting the replacement data referred to in section 20 of these Regulations that were used for a given period during the calendar year, if applicable:
(a) the reason why data required to determine the value of an element of a formula referred to in section 11, 17 or 18 of these Regulations was not obtained and an explanation why that reason was beyond the responsible person’s control;
(b) the element of the formula for which data was not obtained and the date of the day on which the data were not obtained and, if that data were not obtained for a period of several days, the dates of the days on which the period begins and ends; and
(c) the value determined for the element referred to in paragraph (b) using replacement data, along with details of that determination, including
(i) the data used to make that determination for each period of one or more days,
(ii) the method used to obtain that data, and
(iii) in the case of a determination of the value of an element referred to in subsection 20(3) of these Regulations, a justification for the given period being used as the basis of that determination.
SCHEDULE 2(Subsections 14(1) and 15(2))
List of Fuels
| Column 1 | Column 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Item | Fuel type | Default higher heating value (GJ/kL)Footnote for List of Fuels2 |
| 1 | Distillate fuel oil No.1 | 38.78 |
| 2 | Distillate fuel oil No. 2 | 38.50 |
| 3 | Distillate fuel oil No. 4 | 40.73 |
| 4 | Kerosene | 37.68 |
| 5 | Liquefied petroleum gases (LPG) | 25.66 |
| 6 | Propane (pure, not mixtures of LPGs)Footnote for List of Fuels1 | 25.31 |
| 7 | Propylene | 25.39 |
| 8 | Ethane | 17.22 |
| 9 | Ethylene | 27.90 |
| 10 | Isobutane | 27.06 |
| 11 | Isobutylene | 28.73 |
| 12 | Butane | 28.44 |
| 13 | Butylene | 28.73 |
| 14 | Natural gasoline | 30.69 |
| 15 | Motor gasoline | 34.87 |
| 16 | Aviation gasoline | 33.52 |
| 17 | Kerosene-type aviation | 37.66 |
| 18 | Pipeline quality natural gas | 0.03793Footnote for List of Fuels2 |
Return to footnote 1The default higher heating value and the default CO2 emission factor for propane are only for pure gas propane. The product commercially sold as propane is to be considered LPG for the purpose of these Regulations.
Return to footnote 2The default higher heating value for pipeline quality natural gas is expressed in GJ/standard m3
SCHEDULE 3(Subsection 16(2))CEMS Auditor’s Report — Information Required
1 The name, civic address and telephone number of the responsible person.
2 The name, civic address, telephone number and qualifications of the auditor and, if any, the auditor’s email address and fax number.
3 The procedures followed by the auditor to assess whether
(a) the responsible person’s use of the CEMS complied with the Quality Assurance/Quality Control manual referred to in section 6.1 of the Reference Method; and
(b) the responsible person complied with the Reference Method and the CEMS met the specifications set out in the Reference Method, in particular, in its sections 3 and 4.
4 A statement of the auditor’s opinion as to whether
(a) the responsible person’s use of the CEMS complied with the Quality Assurance/Quality Control manual referred to in Section 6.1 of the Reference Method; and
(b) the responsible person complied with the Reference Method and the CEMS met the specifications set out in the Reference Method, in particular, in its sections 3 and 4.
5 A statement of the auditor’s opinion as to whether the responsible person has ensured that the Quality Assurance/Quality Control manual has been updated in accordance with sections 6.1 and 6.5.2 of the Reference Method.
SCHEDULE 4(Subsection 22(1))Performance Test Report — Information Required
1 The following information respecting the responsible person:
(a) an indication of whether they are the owner or operator of the unit and their name and civic address;
(b) the name, title, civic and postal addresses, telephone number and, if any, email address and fax number of their authorized official; and
(c) the name, title, civic and postal addresses, telephone number and, if any, email address and fax number of a contact person, if different from the authorized official.
2 The following information respecting the unit:
(a) for each responsible person for the unit, other than the responsible person mentioned in paragraph 1(a), if any,
(i) their name, title and civic address, and
(ii) an indication of whether they are the owner or operator;
(b) the unit’s name and civic address, if any;
(c) the unit’s registration number, if any;
(d) the name of the facility where the unit is located;
(e) the facility’s National Pollutant Release Inventory identification number assigned by the Minister for the purposes of section 48 of the Act, if any;
(f) the unit’s registration number assigned by the Minister under subsection 4(2) of the Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations; and
(g) the unit’s capacity.
3 The following information respecting the emission intensity referred to in subsection 4(2) of these Regulations resulting from the combustion of fuel in the unit during the performance test period:
(a) the emission intensity for the unit — that is, the ratio of the quantity of CO2 emissions referred to in paragraph (c) to the quantity of energy referred to in paragraph (b) — expressed in tonnes per GWh;
(b) in respect of the quantity of electricity generated by the unit, the value determined for G;
(c) in respect of the quantity of CO2 emissions from the combustion of fuel in the unit,
(i) if paragraph 12(a) of these Regulations applies, the result of the calculation made in accordance with section 13 or 14 and, if applicable, section 15 of these Regulations, expressed in tonnes, or
(ii) if paragraph 12(b) of these Regulations applies, the result of the calculation made in accordance with sections 17 and 18 of these Regulations, expressed in tonnes; and
(d) in respect of each type of fuel combusted, the quantity combusted.
4 The date that the test was performed.
SCHEDULE 5(Subsection 22(2))Initial Performance Test Verifier’s Report — Information Required
1 The name, civic address and telephone number of the responsible person.
2 The name, civic address, telephone number and qualifications of the performance test verifier and, if any, the performance test verifier’s email address and fax number.
3 The procedures followed by the performance test verifier to assess whether the performance test result was obtained in accordance with section 5 of these Regulations.
4 A statement of the performance test verifier’s opinion as to whether the performance test result was obtained in accordance with section 5 of these Regulations.
- Date modified: